
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
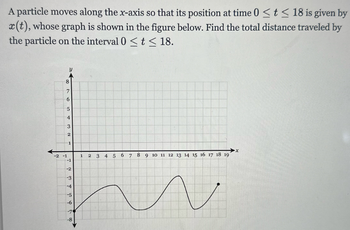
Transcribed Image Text:A particle moves along the x-axis so that its position at time 0 ≤ t ≤ 18 is given by
x(t), whose graph is shown in the figure below. Find the total distance traveled by
the particle on the interval 0 ≤ t ≤ 18.
8
7
6
5
-2 -1
4
32
1
-1
-2
-3
-4
-5
-6
-7
-8
1 23
4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
x
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An object moves in a plane from position r1=(-1,-2) m to the position r2=(-2,7 m and then to r3=(3,8)m. The time of the motion is t=30s. Find (a) total displacement; (b) distance between the initial and final positions; (c)distance travelled (d)average velocity and average speedarrow_forwardAn object's (one dimensional) motion is represented by the following graph of position 5) versus time. x (meters) (5,3) (0,2). (2,1) + t (s) (7, -1) (f) Find the velocity of the object at t = 3 s. (g) Find the velocity of the object at t = 6 s. (h) Find the position of the object at t = 3 s. (i) What is the average velocity from t = 0 to t = 7 s.? G) What is the average speed from t = 0 to t = 7 s.? (k) What is the average speed from t = 1 s to t = 5 s.?arrow_forwardA graph of position versus time for a certain particle moving along the x-axis is shown in the figure below. Find the average velocity in the following time intervals. x (m) 10 8 1000049 2 M 1 2 3 4 5 6 7/8 (d) 4.00 s to 7.00 s m/s (e) 0 to 8.00 s m/sarrow_forward
- External stimuli are communicated to the brain by means of electrical signals propagating along nerve cells at a speed of approximately 25 m/s. Similarly, electrical messages are sent at the same speed from the brain along nerve cells to the muscles. Reflex actions are controlled by a relatively simple nerve circuit from a muscle to the spine and back to the muscle. Estimate the reflex time for a stimulus at the knee. (Assume that the signal resulting from the stimulus must travel a distance Δs = 1 m.)arrow_forward(1) 1.24 1.0+ 0.84 0.6+ 0.4+ 0.2+ 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 (A) B A particle moves along the x-axis so that its acceleration a (t) is given by the graph above for all values of t where 0 ≤ t ≤ 1. At time t = 0, the velocity of the particle is. Which of the following statements must be true? D BAM! (E The particle passes through x = 0 for some t between t = 0 and t = 1. The velocity of the particle is 0 for some t between t = 0 and t = 1. The velocity of the particle is negative for all values of t between t = 0 and t = 1. The velocity of the particle is positive for all values of t between t = 0 and t = 1. *** The velocity of the particle is less than for all values of tbetween t = 0 and t = 1. Rarrow_forwardThe position versus time for a certain particle moving along the x axis is shown in the figure below. Find the average velocity in the following time intervals. х (m) 10 8 4 t (s) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 -2 -4 -6 (a) 0 to 2 S m/s (b) 0 to 3 s m/s (c) 3 to 6 s m/sarrow_forward
- 15 25 30 35 50 60 (sec) v(1) (f/sec) -20 -30 -20 -14 -10 10 a(t) 2 2. 4 (1/sec") A car travels on a straight track. During the time interval 0sts 60 seconds, the car's velocity v, measured in feet per second, and acceleration a, measured in feet per second per second, are continuous functions. The table above shows selected values of these functions. а, For 0arrow_forwardA particle moves along the x-axis so that its position at time 0arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON