
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
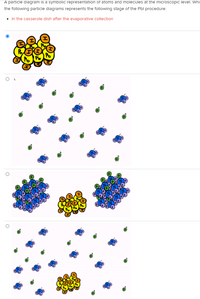
Transcribed Image Text:A particle diagram is a symbolic representation of atoms and molecules at the microscopic level. Whi
the following particle diagrams represents the following stage of the Pbl procedure:
• In the casserole dish after the evaporative collection
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- To find the molarity of sulfuric acid, H,SO, it is titrated with 0.9 M KOH. It requires 22.5 mL of KOH to neutralize a 85.6 mL sample of sulfuric acid. Calculate the concentration (mol/L) of the sulfuric acid. H,SO,+2KOH→K,SO,+2H,O « Previous Next No new data to save. Last checked at 1:35pm Submit DOLL EVD RW MUTNarrow_forwardPls help ASAP. Pls circle the final answer.arrow_forward22:48 Tue May 4 Done < AA A session.masteringchemistry.comarrow_forward
- (1) (2) ] A certain species of trout requires dissolved oxygen of 7.5 mg/L. Would it be wise to release the trout in a mountain stream at an altitude with a Po2 = 0.17 atm. (KH (02) = 1.3x10-³ mol/Latm). Calculate the mole fraction for the following: 14.5 g of HNO3 in 150 g of H₂O. (b) moles of Solute kg Solvent X (a) H=1.01 N = 14.00- 50 mm= 63.01 g/mol 03=16.0x3 Imol 14.6g HNO3 63.01g 149 150 g 1000g = 0.15 kg 6.00 M HCI. (notice, concentration is an extensive property. You can assume any volume!) 0.23 mol HNO3 0.16 kg H2O 1.53 = 0.23 mol HNO3arrow_forwardYou are asked to prepare a 1.000 L solution of 4.5 M you commit a user error while preparing this solution. Assumed volume Volumetric error Preparation details Added water 2.0 cm above the line, which corresponds to 8.2 mL (0.0082 L) additional solution volume C6H12O6 (glucose; molar mass = 180.16 g/mol) in a lab by dissolving 811.0 g of glucose in water. Consider the following two scenarios in whic Prepared in a beaker Prepared in a volumetric flask 1.000 L You add the glucose to a volumetric flask and then add water until it dissolves. The water bottle you are using has a worn tip, and you inadvertently add too much water such that the meniscus is above the line. The diameter of the neck of the volumetric flask is 2.29 cm. 811.0 g glucose Concentration: You decide to evaluate and compare the errors you made while preparing the solutions using the different methods. Calculate the actual concentrations of the intended 4.5 M glucose solutions prepared by each method based on their…arrow_forwardClaim: My answer to the question is.... Evidence: The evidence from the document that supports my answer is... Reasoning: The reasonI chose this evidence is...arrow_forward
- On an emergency cart, you have sodium bicarbonate solution (NaHCO3), 44.6 mEq/50 ml. A physician orders an aerosol of 5 cc and 3.25% strength. How many milliliters of the bicarbonate solution do you need? 1 mEq=1/1000 GEW; GEW= gram formula wt/valence Atomic weights: Na, 23; H, 1; C, 12; 0, 16arrow_forwardPaus gnment/takeCovalentActivity.do?locator=assignment-take 国Rei O Jesuit Extreme Oath. O App Academy Open B Free College - Top.. O Robinhood - Print Coinbase - Buy & S. A https://www.e-read.. [References] entration Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. What is the solubility of carbon dioxide (in units of grams per liter) in water at 25 °C, when the CO, gas over the solution has a partial pressure of 0.337 atm? ky for CO, at 25 °C is 3.36x102 mnol/L'atm. g/L Submit Answer Retry Entire Group 9 more group attempts remaining KPravious Email Instructor Save and Exit 9:10 AM 72°F Cloudy 9/10/2021 * 10 brt sc delete 6 8. backspace enter L.arrow_forward7.0 mL of 3.0 M NaOH are diluted with water to a volume of 400 mL. (a) Determine the molarity of the resulting solution. How many moles of NaOH there are in 7.0 mL of 3.0 M NaOH? Hint: Use Eq. 1 and make sure the volume is in liters: MA = mol A / soln (L) OR mol A = MA x V ___________ moles (b) The total number of moles of NaOH is not changed on dilution. The molarity after dilution can therefore be found by MA = mol A / soln (L) OR mol A = MA x V using the final volume of the solution. Calculate that molarity.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY