
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A pair of rods and disc form a triangle with a spring (a spring connects A to C). The spring has a spring constant of 20 N/m and an unstretched length of 1.5m. each rod has a length of 3m and a mass of 10kg. The disk has a mass of 5kg, a radius of .5 and rolls without slipping. The system starts with an angle between the spring and rods of 60 degrees, determine the angular velocity of the rods after it has dropped to a 30 degree angle.
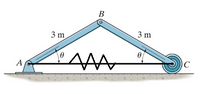
Transcribed Image Text:B
3 m
3 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 9 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A drum can rotate about a fixed-point O. The A block is attached to a cord wrapping around the drum. The mass of the drum is md = 100kg and the radius is r = 0.5 m. The radius of gyration of the drum about point O is ko=0.3 m. The mass of the block is mb= 20kg. The block is released from rest. The acceleration due to gravity is g=9.81 m/s2. (3) Calculate the angular acceleration of the drum α= ________ (rad/s2) (two decimal places)arrow_forwardTwo gears (A and B) are in mesh (they are interlocked) and both spin around their centers of gravity. Gear A has a radius of .8 ft and is experinceing a 10 ft-lb CW moment Gear B has a radius of 1.2 ft If gear A is initially moving at 60 rpm CW, determine how long it will take for gear B to be rotating at 300 rpm CCWarrow_forwardT2 = ? T1 = ? M2 = 2 kg M1 = 5 kg M2 = 20 kg 1. Find the acceleration 2. Tension on the stringsarrow_forward
- A stepped cylinder has the dimensions R₁ = 0.30 m, R₂ = 0.65 m, and the radius of gyration, k, is 0.35 m. The mass of the stepped cylinder is 100 kg. Weights A and B are connected to the cylinder. If weight B has a mass of 80 kg, and weight A has a mass of 50 kg, how far does A move in 5 seconds? In which direction does it move? (Draw all FBDs)arrow_forwardDraw a free body diagram and solve the problem.arrow_forwardA flywheel weighing 4480 lbs has a radius of gyration of 3 ft. If there is a driving torque of 600 lb-ft, and a resisting torque of 250 lb-ft, find the time required to increase its speed from 20 to 80 rpm. The correct answer is 22.5 seconds.arrow_forward
- Please I want a detailed explanation of the energy method rule placed in the first line and how these numbers appeared to us. I want a detailed explanation please urgent .arrow_forwardIn the image on the right, there is a red gear G1 on the left with a radius of r1 = 2.81cm. Gear G1 is locked to the green gear G2 with a radius of r2 = 0.734cm. Gear G2 then shares the same axle as the blue circular saw G3, which has a radius of r3 known to make a full rotation every T = 0.836s. Using at least 6 significant digits in your calculations, compute the following: V3! 12.8cm. Gear G1 is W1 a) The angular speed wi of gear G1. Remember that angular speed is measured in radians per T3 r2 unit time. G2 b) The rim speed vi of gear G1. Since gears G1 and G2 are locked together, the rim speed of G2 is also v1. G1 G3 c) The angular speed w2 of gear G2. Since gear G2 and saw G3 share the same axle, the angular speed of G3 is also w2. d) The rim speed v3 of saw G3.arrow_forwardPlease answer the question in 5mins I will rate your answer. Cam mechanisms are used in many machines. For example, cams open and close the valves in your car engine to admit gasoline vapor to each cylinder and to allow the escape of exhaust. The principle is illustrated in the figure below, showing a follower rod (also called a pushrod) of mass m resting on a wedge of mass M. The sliding wedge duplicates the function of a rotating eccentric disk on a camshaft in your car. Assume that there is no friction between the wedge and the base, between the pushrod and the wedge, or between the rod and the guide through which it slides. When the wedge is pushed to the left by the force F, the rod moves upward and does something such as opening a valve. By varying the shape of the wedge, the motion of the follower rod could be made quite complex, but assume that the wedge makes a constant angle of ? = 19.0°. Suppose you want the wedge and the rod to start from rest and move with constant…arrow_forward
- The slender 8-kg bar AB is horizontal and at rest. The spring has an unstretched length sọ of 1 m and a spring constant of 15 N/m. the length of the bar AB is l1.Sm Find the angular velocity when e - 45° when the bar has rotate clockwise - 45° after being released. Give your answer with 2 decimals and include the signarrow_forwardSuppose a 30 lb truck wheel 18 in. in diameter has a radius of gyration of 4 in. and the 6120 lb truck’s weight is distributed equally to each of the four wheels.a. If the truck can supply 150 lb x ft of torque to each wheel, how fast would the wheel want to accelerate if it didn’t slip? b. What would the coefficient of friction have to be in order to keep the wheel from slippingarrow_forward100 lbs, 2 inches and v is 2 ft/s. Everything else is in the picture!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY