
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
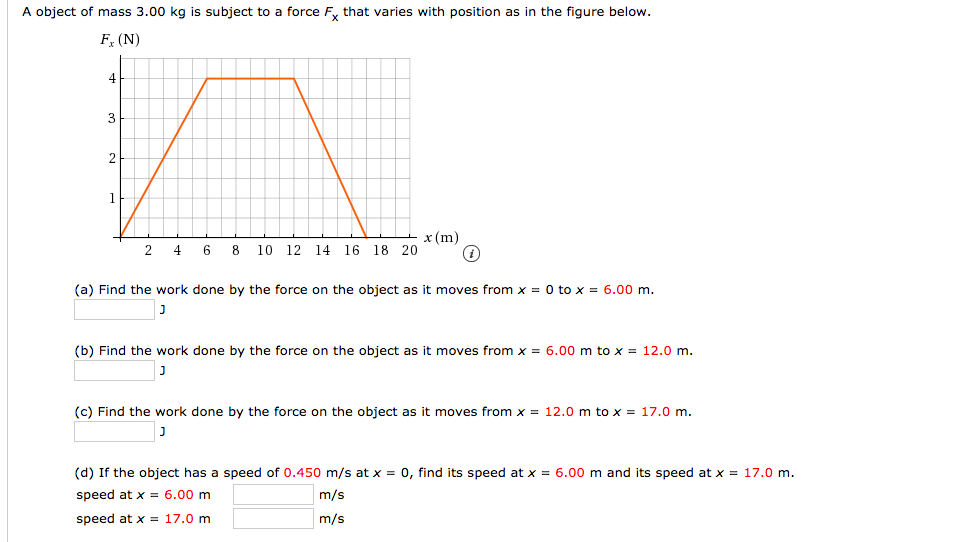
Transcribed Image Text:A object of mass 3.00 kg is subject to a force F, that varies with position as in the figure below.
F, (N)
4
x (m)
10 12
18 20
2 4 6 8
14
16
(a) Find the work done by the force on the object as it moves from x = 0 to x = 6.00 m.
(b) Find the work done by the force on the object as it moves from x = 6.00 m to x = 12.0 m.
(c) Find the work done by the force on the object as it moves from x = 12.0 m to x = 17.0 m.
(d) If the object has a speed of 0.450 m/s at x = 0, find its speed at x = 6.00 m and its speed at x = 17.0 m.
speed at x = 6.00 m
m/s
m/s
speed at x = 17.0 m
2.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A object of mass 3.00 kg is subject to a force Fx that varies with position as in the figure below. (a) Find the work done by the force on the object as it moves from x = 0 to x = 4.00 m. (b) Find the work done by the force on the object as it moves from x = 4.00 m to x = 11.0 m. (c) Find the work done by the force on the object as it moves from x = 11.0 mto x = 17.0 m. (d) If the object has a speed of 0.600 m/s at x = 0,find its speed at x = 4.00 m and its speed at x = 17.0 m. speed at x = 4.00 m m/s speed at x = 17.0 m m/sarrow_forwardAn object of mass 3.00 kg is subject to a force E, that varies with the position as in the figure below. (a) Find the work done by the force on the object as it moves from x = 0 to x = 5.00 m. (b) Find the work done by the force on the object as it moves from x = 5.00 m to x = 12.0 m. (c) Find the work done by the force on the object as it moves from x = 12.0 m to x = 17.0 m. (d) If the object has a speed of 0.400 m/s at x 0, find its speed at x = 5.00 m and its speed at x = 17.0 m. F, (N) 4 3 2 x (m) 4 8 10 12 14 16 18 20arrow_forwardA particle is subject to a force Fx that varies with position as shown. Find the work done by the force on the particle as it moves (a) from x = 0 to x = 5.00 m, (b) from x = 5.00 m to x = 10.0 m, and (c) from x = 10.0 m to x = 15.0 m. (d) What is the total work done by the force over the distance x = 0 to x = 15.0 m?arrow_forward
- An object has several forces acting on it. One of these forces is F=αxyî, a force in the x-direction whose magnitude depends on the position of the object, with α=2.50N/m2. Calculate the work done on the object by this force for the following displacements of the object: (a) the object starts at the point (x=0, y=3.00 m) and moves parallel to the x-axis to the point (x=2.00m, y=3.00m). (b) the object starts at the point (x=2.00m, y=0) and moves in the y-direction to the point (x=2.00m, y=3.00m). (c) the object starts at the origin and moves on the line y=1.5x to the point (x=2.00m, y=3.00m).arrow_forwardA object of mass 3.00 kg is subject to a force F, that varies with position as in the figure below. Fx (N) 3 2 1 X (m) 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 (a) Find the work done by the force on the object as it moves from x = 0 to x = 5.00 m. J (b) Find the work done by the force on the object as it moves from x = 5.00 m to x = 10.0 m. J (c) Find the work done by the force on the object as it moves from x = 10.0 m to x = 17.0 m. J (d) If the object has a speed of 0.600 m/s at x = 0, find its speed at x = 5.00 m and its speed at x = 17.0 m. speed at x = 5.00 m m/s speed at x = 17.0 m m/sarrow_forwarda block of mass m=5 kg is pulled at a constant speed along a rough horizontal surface by a rope at 30 degree. the tension in the rope is T and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface is 0.25. (a) find the tension in the rope. (b) if the block travels a distance of 4.5 m along the surface, what is the work done by the tension force from the rope? (c) find the work done by friction on the rock.arrow_forward
- A particle is subject to a force F, that varies with position as shown in the following figure. F, (N) 3 1 х (m) 4 6 10 12 14 16 (a) Find the work done by the force on the particle as it moves from x = 0 to x = :3.00 m. (b) Find the work done by the force on the particle as it moves from x = 5.00 m to x = 9.00 m. J (c) Find the work done by the force on the particle as it moves from x = 11.0 m to x = 15.0 m. (d) What is the total work done by the force over the distance x = 0 to X = 15.0 m?arrow_forwardThe force acting on a particle varies as in the figure below. (The x axis is marked in increments of 2.50 m.) F (N) x (m) Find the work done by the force as the particle moves across the following distances. (a) from x = 0 m to x = 20.0 m (b) from x = 20.0 m to x = 30.0 m (c) from x = 0 m to x = 30.0 marrow_forwardConsider an object of mass m = 4 kg on a frictionless table. The object experiences a repulsive force F = a/x2 + b/x, where F is in newtons and x is the position of the object relative to the origin. Write an expression for the work done by the repulsive force on the object as it moves from an initial position of x1 to a final position of x2. If the object starts at a position of x1 = 8.5 m apart, how much work, in joules, is required by an external force to bring it to a position of x2 = 2.5 m apart when a = 19 and b = 11? If the object starts at rest at a position x3 = 1.3 m and is released, at what speed v, in meters per second, will the object be moving when it is at position x4 = 12.5 m?arrow_forward
- A spring with a spring constant of 18.0 N/cm has a cage attached to its free end. (a) How much work does the spring force do on the cage when the spring is stretched from its relaxed length by 7.60 mm? (b) How much additional work is done by the spring force when the spring is stretched by an additional 7.60 mm?arrow_forwardThe force F(x) varies with position, as shown below. Find the work done by this force on a particle as it moves from x = 1.0 m to x = 5.0 m. F(x) (N) 4 6.0 4.0 2.0 0 -2.0 -4.0 2.0 4.0 6.0 8.0 x(m)arrow_forwardA block of mass m = 3.00 kg is pushed a distance d = 6.30 m along a frictionless horizontal table by a constant applied force of magnitude F = 16.0 N directed at an angle 0 = 21.0° below the horizontal as shown in the figure below. m (a) Determine the work done on the block by the applied force. (b) Determine the work done on the block by the normal force exerted by the table. (c) Determine the work done on the block by the force of gravity. (d) Determine the work done by the net force on the block. Jarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON