
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
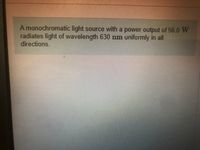
Transcribed Image Text:A monochromatic light source with a power output of 56.0 W
radiates light of wavelength 630 nm uniformly in all
directions.
Transcribed Image Text:6.0 W
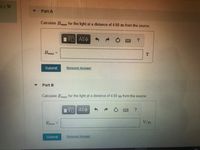
Part A
Calculate Bmaz for the light at a distance of 4.60 m from the source.
Bmaz =
Submit
Request Answer
Part B
Calculate E,,maz for the light at a distance of 4.60 m from the source.
Emaz =
V/m
Submit
Request Answer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Unpolarized light with intensity 350 W/m² passes first through a polarizing filter with its axis vertical, then through a second polarizing filter. It emerges from the second filter with intensity 131 W/m². What is the angle from vertical of the axis of the second polarizing filter?arrow_forwardThe GPS (Global Positioning System) satellites are approximately 5.18 m across and transmit two low-power signals, one of which is at 1575.42 MHz (in the UHF band). In a series of laboratory tests on the satellite, you put two 1575.42 MHz UHF transmitters at opposite ends of the satellite. These broadcast in phase uniformly in all directions. You measure the intensity at points on a circle that is several hundred meters in radius and centered on the satellite. You measure angles on this circle relative to a point that lies along the centerline of the satellite (that is, the perpendicular bisector of a line which extends from one transmitter to the other). At this point on the circle, the measured intensity is 2.00 W/m². At how many other angles in the range 0° < 0 < 90° is the intensity also 2.00 W/m²? Express your answer as an integer. N = Submit Part B 0 = Submit 2 Find the four smallest (positive) angles in the range 0° < 0 < 90° for which the intensity is 2.00 W/m². Express your…arrow_forwardA microscope contains two polarizers, one below the stage to polarize the light and another polarizer (the analyzer) between the objective lens and the eyepiece. (a) White light with an intensity of 50 W/m2 is passed through the two polarizers in the microscope. If the analyzer is at an angle of 60° to the first polarizer. What is the intensity of light reaching the eyepiece? (b) The microscope is used to inspect a block of Si (n = 3.5) which is coated with a thin layer (t = 200 nm) of SiO (n = 1.45). What is the longest wavelength of light reflected strongly and thus not transmitted through the sample?arrow_forward
- Consider an unpolarized light with intensity I sub 0=16W / m^2 incident on a pair of polarizers. The first polarizer has its transmission axis aligned at 40 degrees from the vertical, while the second polarizer has its transmission axis aligned at 70 degrees from the vertical. What is the intensity of the light when it emerges from the second polarizer?arrow_forwardConsider two identical antennas separated by 9.00 m that radiate in phase at 120 MHz. A receiver placed 150 m from both antennas measures an intensity I0. The receiver is moved so that it is 1.8 m closer to one antenna than to the other. a) What is the phase difference ϕ between the two radio waves produced by this path difference? b) In terms of I0, what is the intensity measured by the receiver at its new position?arrow_forwardRed light has an magnetic field component amplitude Bm = 8 μT, and wavelength λ= 440 nm - calculate the angular wave numberarrow_forward
- A beam of initially unpolarized light of intensity 227 W/m^2 passes through a series of polarizing filters, each one's axis aligned at a 11.1-degree angle with respect to the previous filter s axis. The beam of light emerging from the final filter in the series has an intensity of 64.4 W/m^2. How many polarizing filters did the beam pass through? 24 16 8 32arrow_forwardTwo identical sources A and B emit in-phase plane radio waves with frequency 5.21E4 Hz and intensity 2.45E2 W/m2. A detector placed at location P closer to source B than source A detects a constructive interference. What is the minimum value of the path difference |AP–BP| (in m)?arrow_forwardProblem 8: Unpolarized light of intensity I0 = 850 W/m2 is incident upon two polarizers. After passing through both polarizers the intensity is I2 = 220 W/m2. Part (a) What is the intensity of the light after it passes through the first polarizer in W/m2? Part (b) Write an equation for the angle between the polarizers in terms of the initial (I0) and final (I2) intensities. Part (c) Find the angle between the polarizers in degrees.arrow_forward
- 25. An intense light source radiates uniformly in all directions. At a distance of 5.0 m from the source, the radiation pressure on a perfectly absorbing surface is 9.0 x 10-6 Pa. What is the total average power output of the source?arrow_forwardA beam of initially unpolarized light of intensity 249 W/m^2 passes through a series of polarizing filters, each one s axis aligned at a 25.7-degree angle with respect to the previous filter s axis. The beam of light emerging from the final filter in the series has an intensity of 5.5 W/m^2. How many polarizing filters did the beam pass through? 24 16 8 32arrow_forwardUnpolarized light passes through two ideal polarizers. The axis of the first is vertical, and the axis of the second is at 70° to the vertical. What fraction of the incident light is transmitted through both polarizers? 0.342 0.171 0.0585 0.117arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON