
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
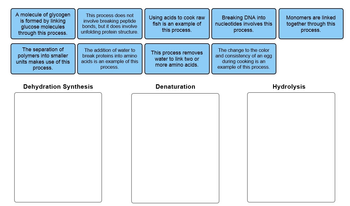
Transcribed Image Text:A molecule of glycogen
is formed by linking
glucose molecules
through this process.
The separation of
polymers into smaller
units makes use of this
process.
This process does not
involve breaking peptide
bonds, but it does involve
unfolding protein structure.
The addition of water to
break proteins into amino
acids is an example of this
process.
Dehydration Synthesis
Using acids to cook raw
fish is an example of
this process.
This process removes
water to link two or
more amino acids.
Denaturation
Breaking DNA into
nucleotides involves this
process.
The change to the color
and consistency of an egg
during cooking is an
example of this process.
Monomers are linked
together through this
process.
Hydrolysis
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Ribosomes are the cellular structures responsible for synthesizing proteins. They accomplish this goal by facilitating the formation of between individual amino acids. Group of answer choices Hydrolysis Bonds Condensation Reactions Peptide bonds Protein Bondsarrow_forwardReductase is the Fe protein composed of two: polypeptide chains linked by three disulfide bonds. polypeptide chains linked by a 4Fe–4S cluster. α subunits and two β subunits. polypeptide chains linked by a 2Fe–2S cluster.arrow_forwardusing cysteine, serine, and aspartic acid create a tripeptide by performing 2 dehydration synthesis reactionsarrow_forward
- The disulfide bond between two cysteine residues— is a weak ion-induced dipole attraction. is an ionic bond that is stable at physiological pH. is a covalent bond formed by oxidation. is a hydrogen bond between the two sulfhydryl groups. is a special form of peptide bond.arrow_forwardWhich of the following are NOT a level of biological structure? macromolecular level cellular/ organelle levels tissue/ organ level organismal level all of the above none of the above Which of the following are steps in the biosynthesis of proteins can be regulated? macromolecular level cellular/ organelle levels tissue/ organ level organismal level all of the above none of the above.arrow_forwardWhen pharmacology researchers design drugs that must enter into cells in order to be effective, they often add functional groups to the drug to make it more likely to pass through the plasma membrane. The addition of which of the following functional groups would be most likely to increase the permeability of a drug across a membrane? Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. a Amino. Carboxyl. Hydroxyl. d Methyl. e Phosphate.arrow_forward
- Which of the following regarding disulfide bonds is/are true? Disulfide bonds are the most common intrachain covalent linkage in proteins Disulfide bond formation is critical for correct protein folding into the native conformation Disulfide bonds impart a large degree of stability to the secondary structure of proteins The intracellular environment is too oxidizing to allow disulfide bond formation A and Darrow_forwardDuring hydrogenation, cis double bonds are converted to trans double bonds. In the lab, we compare three fats, each of which has fatty acid chains that are exactly the same length (number of carbons) and observe the following: Fat 1 contains only saturated fatty acids 16 carbons long, and has a melting point of 65 degrees C. Fat 2 contains only cis unsaturated fatty acids 16 carbons long, and has a melting point of 35 degrees C. Fat 3 contains only trans fatty acids 16 carbons long, and has a melting point of 65 degrees C. Both Fat 2 and Fat 3 contain fatty acids with a single double bond; fat 1 has no double bonds. Why do Fat 3 and Fat 1 have more similar melting points than Fat 3 and Fat 2? Group of answer choices The number of hydrogen atoms in the fatty acids of fats 1 & 3 is higher, and having more hydrogen atoms raises the melting point of the fat. The fatty acids in fats 1 & 3 have a linear shape, so they pack tightly together and have lots of hydrophobic…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education