
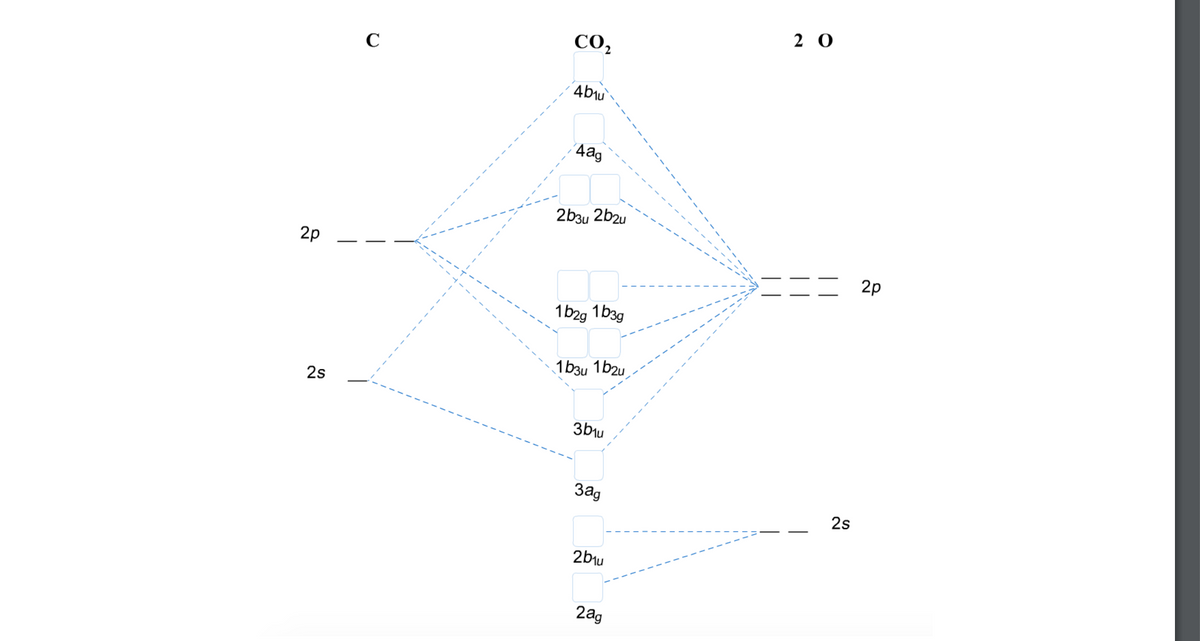
A MO scheme for CO2 is shown below. Fill in the electrons for both the atoms and the molecule. Notice that since there are 2 oxygens, there are six p orbitals and two s orbitals associated with the right hand column of the MO scheme. Determine which orbitals are bonding vs. nonbonding, vs. antibonding and calculate the bond order. Notice that the names of the MO’s are no longer s and p - they have other names. (Hint: bonding vs. antibonding vs. nonbonding can be figured out based on the energy of the MOs and the positioning of the dashed lines.) Compare the bond order to the valence bond picture of CO2, [O=C=O]. How are they related?
To identify the bonding, antibonding and non-bonding orbitals of the carbon dioxide given that the molecular orbital diagram of carbon dioxide will be as follows:
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 2 images

- XeF + ions can react with Xe gas and other molecules SbF5 to produce + Xe2 ion.a. Write the reaction equation for this reaction!b. Describe the hybridization process for compound SbF5!c. Draw the MO (molecular orbital) schematic for Xe2+. State the bond order magnitude and magnetic properties of the particle!Atomic Number Sb = 51, F = 9arrow_forwardConstruct the MO diagram of hydrazine (H2NNH2). Compare to its Lewis structure and describe bonding .arrow_forward22). Draw a Lewis structure for cyanamide, NH₂CN, where all atoms have formal charge of zero. Then use the Lewis Structure to sketch a bonding diagram for NH₂CN. Include all overlapping orbitals, and orbitals containing lone pair electrons. Use hybrid orbitals for the carbon and the nitrogen atoms. Make sure to label all orbitals appropriately as (sp, sp2, sp³, 2p, 1s...). Identify all bonding interactions as σ oг л.arrow_forward
- Draw an MO diagram to explain the existence of the trihydrogen cation (H3+). Hint: it forms a cyclic structure. Use individual 1s orbitals from H atoms to form your molecular orbitals (don’t worry about forming LGOs; determine the symmetries of the MOs using the projection operator method and sketch approximate wavefunctions for each). How many electrons are present in this molecule? What is the bond order? What type of bonding is this?arrow_forwardwhat is the molecular orbital diagram of AlP? scale it to show splitting and all co tributions to MO from the AO. Draw MO modes for each MO formed. can this exist in the real world?arrow_forwardDraw the molecular orbital diagram for HCI. Clearly label the axes, MO's, atomic orbitals. Show the distibution of the electrons in the MO's. Roughly sketch the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO). Answer the next two questions based on your HCI MO diagram. Based on your MO diagram, what would be the bond order of HCI+2 jon? In the molecular orbital diagram of HCI, there are two non-bonding molecular orbitals with a total of 4 electrons occupying them. O True O Falsearrow_forward
- Use the template below to construct a MO diagram for the CN* molecule and use it to answer the following questions. In the completed diagram for CN*, the number of electrons in bonding orbitals is: in antibonding orbitals is: What is the bond order? If a fraction is needed, use a decimal number. CN* is Molecular orbitals Atomic orbitals (Atom A) Atomic orbitals (Atom B) 2p Encrgyarrow_forwardStudy the following sketch of a molecular orbital (MO) in a homonuclear diatomic molecule. This MO was formed by combining one 3p atomic orbital from each atom. O The dark dots in this sketch are the nuclei. Now use the sketch to complete the table below. Write the symbol for this MO. Is this a bonding or antibonding MO? What is the energy of this MO, compared to the energy of a 3p orbital on one of the separate. atoms? 0 O bonding O antibonding ο οποίο O higher O lower O the same not enough information to decide a 2 Do X B 5 Śarrow_forward6. For heteronuclear diatomic molecules, the energy-level diagrams of the molecular orbitals need to be modified via calculation. For both NO and CN', the order of molecular orbitals are similar to that of O,. Write electron configurations of NO and CN including core electrons, starting with o1,'01,*². Which bond is stronger? (hint: bond order)arrow_forward
- O CHEMICAL BONDING Recognizing typical LCAO molecular orbitals Heather V Stua, che following sketch of a molecular orbital (MO) in a homonuclear diatomic molecule. This MO was formed by combining one 3p atomic orbital from each atom. The dark dots in this sketch are the nuclei. do Now use the sketch to complete the table below. Write the symbol for this MO. O bonding O antibonding O higher Is this a bonding or antibonding MO? On O lower What is the energy of this MO, compared to the energy of a 3p orbital on one of the separate atoms? O the same O not enough information to decide Explanation Check O 2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy| Accessibilityarrow_forward2) a) Consider the following molecule . Given what you have learned about hybridization theory, draw an image or images explaining the bonding situation in this molecule. I want you to draw out all of the orbitals, hybrid orbitals and how they overlap to form the bonds in the molecule. Indicate the % s or p character in the given atomic and hybrid orbitals. Which C-C bond or bonds are the longest? In a paragraph or so explain the image or images you just drew. b) Lastly, consider the molecule below. Indicate the Molecular formula, the molar mass, label the hybridization of each atom except for hydrogen, indicate any chiral centers with a *, which bond or bonds are the shortest, identify by name of each functional group with an arrow pointing to the group.arrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution ...arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





