
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
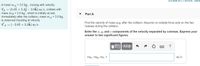
Find the velocity of mass mBmB after the collision. Assume no outside force acts on the two masses during the collision.
Transcribed Image Text:Constants | Perlodic Table
A mass ma = 3.0 kg , moving with velocity
VA = (5.0î + 5.4j – 2.0k) m/s, collides with
mass mB = 3.4 kg , which is initially at rest.
Immediately after the collision, mass ma = 3.0 kg
is observed traveling at velocity
VA = (-2.0i + 3.2k) m/s.
Part A
Find the velocity of mass mB after the collision. Assume no outside force acts on the two
masses during the collision.
Enter the x, y, and z components of the velocity separated by commas. Express your
answer to two significant figures.
V AZO
VBr, VBy, VBz =
m/s
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The contraction of the four-momentum with itself is " the energy of the particle at rest." Why is this statement true?arrow_forwardA 3kg mass with an initial velocity of (6)m/ collides with and sticks to a Skg mass with an initial velocity of(-2)m/s. The final velocity (in /s) of the composite mass is Select one: 4.5î –0.53 a. b. 2.25i –1.253 Sî – 0.33} C. 2î –1.5ĵ d.arrow_forwardTwo manned satellites approaching one another at a relative speed of 0.450 m/s intend to dock. The first has a mass of 3.00 ✕ 103 kg, and the second a mass of 7.50 ✕ 103 kg. Assume that the positive direction is directed from the second satellite towards the first satellite. (a) Calculate the final velocity after docking, in the frame of reference in which the first satellite was originally at rest. m/s(b) What is the loss of kinetic energy in this inelastic collision? J(c) Repeat both parts, in the frame of reference in which the second satellite was originally at rest. final velocity (m/s) loss of kinetic energy (J)arrow_forward
- Two manned satellites approaching one another at a relative speed of 0.100 m/s intend to dock. The first has a mass of 5.00 ✕ 103 kg, and the second a mass of 7.50 ✕ 103 kg. Assume that the positive direction is directed from the second satellite towards the first satellite. (a) Calculate the final velocity after docking, in the frame of reference in which the first satellite was originally at rest.m/s(b) What is the loss of kinetic energy in this inelastic collision?J(c) Repeat both parts, in the frame of reference in which the second satellite was originally at rest.final velocitym/sloss of kinetic energyJarrow_forwardAn unstable particle is at rest and suddenly breaks up into two fragments. No external forces act on the particle or its fragments. One of the fragments has a velocity of +0.837c and a mass of 1.77 × 10-27 kg, and the other has a mass of 5.29 × 10-27 kg. What is the velocity of the more massive fragment (as a multiple of c)? (Hint: This problem is similar to Example 6 in Chapter 7.) Unstable particle at rest Number i V2 m2 Units m1 V1 Recoiling fragmentsarrow_forwardTwo manned satellites approaching one another, at a relative speed of 0.200 m/s, intending to dock. The first has a mass of 5.00 ✕ 103 kg, and the second a mass of 7.50 ✕ 103 kg. a. Calculate the final velocity (after docking) in m/s by using the frame of reference in which the first satellite was originally at rest. (Assume the second satellite moves in the positive direction. Include the sign of the value in your answer.) m/s b. What is the loss of kinetic energy (in J) in this inelastic collision? J c. Repeat both parts by using the frame of reference in which the second satellite was originally at rest. final velocity (m/s) m/sloss of kinetic energy (J) J Explain why the change in velocity is different in the two frames, whereas the change in kinetic energy is the same in both.arrow_forward
- In 1977 the planet Alderaan, with a mass of 3 x 1024 kg, exploded. Assuming it was initially at rest and experienced no external interactions, 3. A) If the planet blew apart into two pieces with 40% of its mass flying away in one piece at 4,000 km/s, what speed did the rest of the planet have relative to its original frame? B) If the planet blew apart into three pieces, with 30% of its mass flying away at 3,000 km/s, and 20% of its mass flying away at 5,000 km/s at an angle of 120° relative to the velocity direction of the first fragment, what velocity did the rest of the planet have? Report the direction by specifying its angle relative to the velocity direction of the first fragment.arrow_forwardAn unstable particle is at rest and suddenly breaks up into two fragments. No external forces act on the particle or its fragments. One of the fragments has a velocity of +0.811c and a mass of 1.57 × 10-27 kg, and the other has a mass of 5.98 × 10-27 kg. What is the velocity of the more massive fragment (as a multiple of c)? (Hint: This problem is similar to Example 6 in Chapter 7.) Unstable particle at rest V2 m2 m1 V1 Recoiling fragmentsarrow_forwardThe carbon isotope 14C is used for carbon dating of objects. A 14C nucleus can change into a different kind of element, a neighbor on the periodic table with lower mass, by emitting a beta particle – an electron or positron – plus a neutrino or an anti-neutrino. Consider the scenario where 14C ( mass of 2.34 x 10 -26) decays by emitting an electron and anti neutrino. The electron has a mass of 9.11x 10-31 kg and a speed of 5.5 x107 m/s. While the anti neutrino has a momentum of 8.5x10-24 kg-m/s. If the electron and anti neutrino are emitted at right angles from each other, calculate the recoil speed of the nucleus.arrow_forward
- A 212^Bi (bismuth) nucleus undergoes alpha decay, resulting in a 208^Tl (thallium) nucleus and a 4He (helium) nucleus as per the following reaction: 212^Bi →208^Tl + 4^He The masses of each nucleus is listed in the table below. Given that the bismuth atom was at rest before the reaction, if the resulting thallium nucleus is traveling 3.3 × 105 m/s, how fast is the helium nucleus traveling?arrow_forwardAn electron-positron collider creates muons through the reaction et +e →µ* +µ. In the center-of-momentum frame, what is the minimum speed of the electron for this reaction to occur, in terms of the masses me and mu of the electron and muon? Oc(1-) 2m 7ne - my O This process can occur at any speed.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON