
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
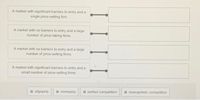
Transcribed Image Text:A market with significant barriers to entry and a
single price-setting firm.
A market with no barriers to entry and a large
number of price-taking firms.
A market with no barriers to entry and a large
number of price-setting firms.
A market with significant barriers to entry and a
small number of price-setting firms.
:: oligopoly
:: monopoly
: perfect competition
:: monopolistic competition
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the only internet service provider in a small town, which you can assume operates as a natural monopoly. The following graph shows the demand curve for internet services per month, as well as the provider's marginal revenue (MR) curve, marginal cost (MC) curve, and average total cost (ATC) curve. PRICE (Dollars per subscription) 100 20 88288 2 10 ATC MC MR D 0 + + 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 QUANTITY (Thousands of subscriptions) (?.arrow_forwardEach of the statements below describes a characteristic of the following market structures: perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and monopoly. Identify which market structure displays each of the characteristics. (There may be more than one.) a) Each firm produces at Minimum efficient scale (MES) in long-run equilibrium. b) Firms earn profit in long-run equilibrium. c) Each firm produces output where MC=MR. d) Each firm produces output where P=MC. e) There is free entry to the industryarrow_forwardThe automobile, household appliance, and automobile tire industries are all illustrations of Multiple Choice O pure monopoly. homogeneous oligopoly. differentiated oligopoly. monopolistic competition.arrow_forward
- How short-run profit or losses induce entry or exit Fantastique Bikes is a company that manufactures bikes in a monopolistically competitive market. The following graph shows Fantastique's demand curve, marginal revenue curve (MR), marginal cost curve (MC), and average total cost curve (ATC). 2. How short-run profit or losses induce entry or exit Fantastique Bikes is a company that manufactures bikes in a monopolistically competitive market. The following graph shows Fantastique's demand curve, marginal revenue curve (MR), marginal cost curve (MC), and average total cost curve (ATC). Place the black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the short-run profit-maximizing price and quantity for this monopolistically competitive company. Then, use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to shade the area representing the company's profit or loss 500 400 350 300 ATC 250 * 200 150 100 MO MR 450 50 30 PRICE (Dollars per l 0 Demand A 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 QUANTITY…arrow_forwardFew firms in the United States are monopolies because A) few firms experience economies of scale. B) of antitrust laws. C) when a firm earns profits, other firms will enter its market. D) most products that firms produce have substitutes.arrow_forwardHow many of the below statements are incorrect? -> Under discriminating monopoly, different prices may be charged to different buyers for the same product. -> Each oligopolist firm is of the opinion that its competitors will match its increase in price above the prevailing level. -> Monopolistic competition is a theoretical concept.arrow_forward
- Define the following terms in your own words Law of Supply Law of Demand Law of Supply and Demand Monopoly, Monopsony Oligopoly, Oligopsonyarrow_forward2. Study Questions and Problems #2 A is the one and only producer in a market, while a market. Due in large part to these characteristics, a is one of many producers in a faces a horizontal demand curve, and a faces a downward-sloping demand curve. Grade It Now Save & Continuearrow_forward1) A monopoly faces a demand curve P(Q) = 120 – 2Q, and has a marginal cost of 60. a. What is profit-maximizing level of output? What is the profit-maximizing price? How much profit the firm will make? b. Assume that a second firm enters the market. The new firm has an identical cost function. If the two firms enter in a Cournot competition, what will be the price in equilibrium? How much will each firm produce in equilibrium? How much profit will each firm make? c. If, instead, the two firms compete in a Stackelberg game (assume the incumbent firm is the leader), what will be the price in equilibrium? How much each firm will produce in equilibrium? How much profit will each firm make? d. Now assume the follower has to pay a fixed cost, f =100 if q>0. Does it change the follower's decision? Assume again they are playing a Stackelberg game.? e. The leader knows that the follower has to pay the fixed cost and decides produce one third more than the quantity found in part c). Does it…arrow_forward
- QUESTION 4 Suppose a stream is discovered whose water has remarkable healing powers. You decide to bottle the liquid and sell it. The market demand curve is linear and is given as follows: P = 53 - Q. The marginal cost to produce this new drink is $5. What price would this new drink sell for if the market was a Stackelberg duopoly? A. $17 В. $21 C. $29 D. $16.50arrow_forwardPrice II. Q2 is the profit maximizing point. III. Q3 is the perfectly competitive output level. Multiple Choice I only Ill only Q₁ Q2 Q3 II and III only This graph shows the cost and revenue curves faced by a monopoly. Which of the following statements is true? I. Q1 is the efficient point. I and II only 4 MC MR ATC Quantityarrow_forwardAn industry comprising 40 firms, none of which has more than 3 percent of the total market for a differentiated product, is an example of Multiple Choice monopolistic competition. oligopoly. pure monopoly. pure competition.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education