
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question

Transcribed Image Text:**Problem Description:**
A man holds a 164-N ball in his hand, with the forearm horizontal. He can support the ball in this position because of the flexor muscle force \( \vec{M} \), which is applied perpendicular to the forearm. The forearm weighs 23.7 N and has a center of gravity as indicated.
**Tasks:**
- (a) Find the magnitude of \( \vec{M} \).
- (b) Find the magnitude and
- (c) direction (as a positive angle counterclockwise from horizontal) of the force applied by the upper arm bone to the forearm at the elbow joint.
**Diagram Explanation:**
- A skeletal forearm is shown horizontally with a hand holding a ball.
- The forces acting are indicated with arrows:
- **Flexor Muscle Force \( \vec{M} \):** Shown as a blue arrow perpendicular to the forearm, pointing upwards.
- Important measurements:
- The distance from the elbow joint to the point of application of \( \vec{M} \) is 0.0510 m.
- The distance from the elbow joint to the forearm's center of gravity is 0.0890 m.
- The distance from the elbow joint to the point where the ball is held is 0.330 m.
This setup highlights the mechanics of balancing torques around the elbow joint to maintain the horizontal position.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1: Draw the free-body diagram of the forearm.
No force is acting along the horizontal. Thus, the force by the upper arm bone to the forearm will be along the vertical direction. Thus, consider that the force is acting in an upward direction.
Draw the free-body diagram of the forearm.
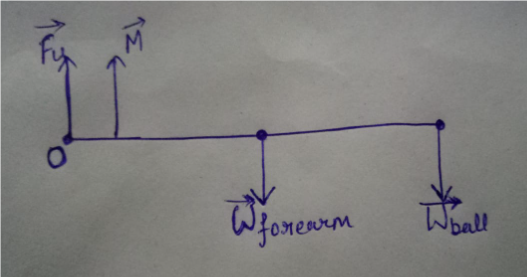
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- One end of a uniform ℓ = 4.50-m-long rod of weight w is supported by a cable at an angle of θ = 37° with the rod. The other end rests against a wall, where it is held by friction (see figure). The coefficient of static friction between the wall and the rod is μs = 0.480. Determine the minimum distance x from point A at which an additional weight w (the same as the weight of the rod) can be hung without causing the rod to slip at point A. marrow_forwardIn order to get his car out of the mud, a man ties one end of a rope to the front bumper and the other end to a tree 7.4 m away, as shown below. He then pulls on the center of the rope with a force of 490 N, which causes its center to be displaced 0.98 m, as shown. What is the force (in N) of the rope on the car? (Enter the magnitude.) 490 N 0.98 m 7.4 marrow_forwardcan you please solve (c) ?arrow_forward
- Mark is trying to rescue Mary from a castle by climbing a uniform ladder that is 5 m long and weighs 180 N. Mark, who weighs 800 N, stops a third of the way up the ladder . The base of the ladder rets on a horizontal ground and leans in equilibrium against a vertical frictionless wall. The ladder makes an angle of 53.1 degrees with the horizontal, and forming a 3-4-5 right triangle. Find the force exerted by the ground at the base of the ladder.arrow_forwardChapter 12, Problem 034 In the figure, a thin horizontal bar AB of negligible weight and length L = 3.1 m is hinged to a vertical wall at A and supported at B by a thin wire BC that makes an angle e = 42° with the horizontal. A block of weight W = 250 N can be moved anywhere along the bar; its position is defined by the distance x = 1.75 m from the wall to its center of mass. Find (a) the tension in the wire, and the (b) horizontal and (c) vertical components of the force on the bar from the hinge at A. Com A B (a) Number Units (b) Number Units (c) Number Units Click if you would like to Show Work for this question: Open Show Workarrow_forwardA man holds a 183-N ball in his hand, with the forearm horizontal (see the figure). He can support the ball in this position because of the flexor muscle force M→, which is applied perpendicular to the forearm. The forearm weighs 24.5 N and has a center of gravity as indicated. Find (a) the magnitude of M→ and the (b) magnitude and (c) direction (as a positive angle counterclockwise from horizontal) of the force applied by the upper arm bone to the forearm at the elbow joint.arrow_forward
- Chapter 12, Problem 037 GO In the figure, a uniform plank, with a length L of 6.83 m and a weight of 386 N, rests on the ground and against a frictionless roller at the top of a wall of height h = 2.78 m. The plank remains in equilibrium for any value of e = 70.0° or more, but slips if e < 70.0°. Find the coefficient of static friction between the plank and the ground. Roller Number Units the tolerance is +/-2% Click if you would like to Show Work for this question: Open Show Workarrow_forwardA diver of weight 580 N stands at the end of a diving board of length L= 4.3 m and negligible mass (see the figure below). The board is fixed to two pedestals separated by distance d = 1.3 m. Take the upward direction to be positive. Of the forces acting on the board, what are (a) the force from the left pedestal and (b) the force from the right pedestal? (a) Number (b) Number 368.9 948.9 Units Units TOENE N Narrow_forwardA 740 N bear is standing on a metal plank supported by the cable shown in the figure. At the end of the plank hangs a basket weighing 80 N. Assume the plank is uniform, weighs 200 N, is 5.50 m long, and 0 = 60.0°. Goodies (a) When the bear is at x = 1.10 m, find the tension in the cable supporting the plank and the components of the force exerted by the wall on the left end of the plank. (Enter the magnitudes of your answers in N.) T = F = F = N N N (b) If the cable can withstand a maximum tension of 875 N, what is the maximum distance (in m) the bear can walk before the cable breaks? (Measure this distance from the wall.) marrow_forward
- One end of a uniform 4.40-m-long rod of weight F is supported by a cable at an angle of 0 = 37° with the rod. The other end rests against the wall, where it is held by friction as shown in the figure below. The coefficient of static friction between the wall and the rod is μ = 0.465. Determine the minimum distance x from point A at which an additional object, also with the same weight F, can be hung without causing the rod to slip at point A. A 0 B X You will need to work with the equations F net = 0 and 7 = 0 and manipulate the equations symbolically to solve for the distance. m netarrow_forwardA man holds a 186-N ball in his hand, with the forearm horizontal (see the figure). He can support the ball in this position because of the flexor muscle force M, which is applied perpendicular to the forearm. The forearm weighs 21.6 N and has a center of gravity as indicated. Find (a) the magnitude of M and the (b) magnitude and (c) direction (as a positive angle counterclockwise from horizontal) of the force applied by the upper arm bone to the forearm at the elbow joint. (a) Number (b) Number i (c) Number i Upper arm bone- Elbow joint 0.0510 m+ Units Units Units Flexor muscle M -0.0890 m -0.330 m-arrow_forwardA lunch tray is being held in one hand, as the drawing illustrates. The mass of the tray itself is 0.300 kg, and its center of gravity is located at its geometrical center. On the tray is a 1.00 kg plate of food and a 0.330 kg cup of coffee. Obtain the force T exerted by the thumb and the force F exerted by the four fingers. Both forces act perpendicular to the tray, which is being held parallel to the ground.T = N (downward)F = N (upward)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON