Question
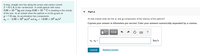
Transcribed Image Text:A long, straight wire lies along the r-axis and carries current
I = 60.0 A in the +x-direction. A small particle with mass
3.00 x 10-6 kg and charge 8.00 × 10-3 C is traveling in the vicinity
of the wire. At an instant when the particle is on the y-axis at
y = 7.00 cm, its acceleration has components
a, = -5.00 x 10³ m/s? and a, = 19.00 x 103 m/s².
Part A
At that instant what are the - and y-components of the velocity of the particle?
Express your answer in kilometers per second. Enter your answers numerically separated by a comma.
Vz, Vy =
km/s
Submit
Request Answer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Two long, parallel wires are hung by cords of length 6.0cm. Each wire has a mass per unit length of 25g/m, and they carry the same current in opposite directions. What is the current if the cords hang at 9.0° with respect to the vertical?arrow_forwardA proton is accelerated from rest through 2.0 kV. It then enters a uniform magnetic field of 0.30 T that is oriented perpendicular to its direction of motion. What is the radius of the path the proton follows in the magnetic field? O 11 cm O 11 mm O 22 cm O 1.1 m O 22 mmarrow_forwardA coil with the radius of 20 cm has 10 turns and carries a current of 4 A. A charged particle whose charge equals 60 µ C moves at 1500 m/s through the center of the coil at an angle of 300 to the axis. Compute the magnitude of the force exerted on the particle.arrow_forward
- A helium nucleus (2 protons, 2 neutrons) is traveling at a velocity of 5.27 x 10^6 m/s a distance of 4.88 cm away from a wire carrying a current of 3.01 A. The helium nucleus is traveling in a direction parallel to the current in the wire. How much acceleration does the helium nucleus experience due to the magnetic force from the current in the wire?arrow_forwardA wire is held horizontally in a vacuum chamber, and carries a current of 1.40 µA. A proton is traveling in a direction parallel to the wire (opposite the current) with a constant speed of 2.60 ✕ 104 m/s at a distance d above the wire. Ignoring the magnetic field due to the Earth, determine the value of d (in cm). What If? At what distance, d (in m) would an electron moving with the same speed as the proton moves parallel to the wire? What direction would the electron have to move? In the same direction as the proton. In the opposite direction as the proton. There is too little information to determine the direction.arrow_forwardProblem 13: Suppose the starter cable of a car is carrying 130 A of current. Assume this cable is long and straight. How many meters from the cable must you be to experience a field less than the Earth's (5.00 × 10-5 T)? r =arrow_forward
- The figure below shows, in cross section, four wires that are parallel, straight and very long. The currents in the wires are as follows: i1 = 148 A, i2 = 246 A, i3 = 297 A, and i4 = 78.0 A. The distance shown is 0.0360 m. What is the magnitude of the force per unit length on wire 2?arrow_forwardA particle with a charge of −1.24×10−8C is moving with instantaneous velocity v⃗ v→ = (4.19×104m/s)i^ + (−−3.85×104m/s)j^ . a)What is the force exerted on this particle by a magnetic field B⃗ B→ = (2.80 T )i^ ? Enter the x, y, and z components of the force separated by commas. b)What is the force exerted on this particle by a magnetic field B⃗ B→ = (2.80 T )k^ ? Enter the x, y, and z components of the force separated by commas.arrow_forwardA charge q = 4 µC moves with velocity v = 30 i km/s in a magnetic field B = (0.2 j + 0.5 k) T. Find the magnetic force on the charge. (24 j + 60 k) mN (−24 j + 60 k) mN 65 i mN (−60 j + 24 k) mN (60 j − 24 k) mNarrow_forward
- The magnetic dipole moment of Earth has magnitude 8.00 x 1022 J/T. Assume that this is produced by charges flowing in Earth's molten outer core. If the current is measured to be 2.08 x 109 A, what is the radius of the charges' circular path?arrow_forwardA helium nucleus (2 protons, 2 neutrons) is traveling at a velocity of 5.06 x 10^6 m/s a distance of 4.93 cm away from a wire carrying a current of 2.81 A. The helium nucleus is traveling in a direction parallel to the current in the wire. How much acceleration does the helium nucleus experience due to the magnetic force from the current in the wire? 1.66E+09 m/s^2 3.86E+09 m/s^2 4.97E+09 m/s^2 2.76E+09 m/s^2arrow_forwardA helium nucleus (2 protons, 2 neutrons) is traveling at a velocity of 9.07 x 10^6 m/s a distance of 1.21 cm away from a wire carrying a current of 2.64 A. The helium nucleus is traveling in a direction parallel to the current in the wire. How much acceleration does the helium nucleus experience due to the magnetic force from the current in the wire? 3.23E+10 m/s^2 1.90E+10 m/s^2 1.14E+10 m/s^2 2.66E+10 m/s^2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios