
University Physics Volume 2
18th Edition
ISBN: 9781938168161
Author: OpenStax
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A long,
Distances provided in image.
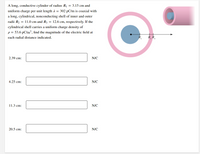
Transcribed Image Text:A long, conductive cylinder of radius R1 = 3.15 cm and
uniform charge per unit length A = 302 pC/m is coaxial with
a long, cylindrical, nonconducting shell of inner and outer
radii R2 = 11.0 cm and R3 = 12.6 cm, respectively. If the
cylindrical shell carries a uniform charge density of
p = 53.6 pC/m3, find the magnitude of the electric field at
each radial distance indicated.
R, Ř,
2.39 cm:
N/C
4.25 cm:
N/C
11.3 cm:
N/C
20.5 cm:
N/C
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- If a solid conducting sphere of radius 50.0 cm carries a total charge of 150 nC uniformly distributed throughout its volume. Find the (a) charge density of the sphere and (b) the magnitude of the electric field at r = 10 cm.arrow_forwardA long, conductive cylinder of radius R1=2.80 cm and uniform charge per unit length 1-453 pC/m is coaxial with a long, cylindrical, nonconducting shell of inner and outer radii R2=9.80 cm and R3=11.2 cm, respectively. If the cylindrical shell carries a uniform charge density of p=79.8 pC/m3, find the magnitude of the electric field at each radial distance indicated. 1.15 cm: 8.96 cm: 10.6 cm: 14.3 cm:arrow_forwards of the 15.13 The Coaxial Cable. A long coaxial cable con- sists of an inner cylindrical conductor with radius a and an outer coaxial cylinder with inner radius b and outer eld also radius c. The outer cylinder is mounted on insulating supports and has no net charge. The inner cylinder has a uniform positive charge per unit length A. Calculate the electric field a) at any point between the cylinders, a distance r from the axis; b) at any point outside the outer cylinder. c) Graph the magnitude of the electric field as a function of the distance r from the axis of the cable, from r=0 to r = 2c. d) Find the charge per unit length on the inner surface and on the outer surface of -ntained by the can you %3D the outer cylinder.arrow_forward
- A long solid copper cylinder has a radius of R=3.0cmR=3.0cm and a uniform (linear) surface charge density of 5.75μC/mμC/m. What is the magnitude of the electric field, in newtons per coulomb, at a distance of 1.5 cm from the symmetry axis of the cylinder?arrow_forwardA solid insulating sphere of radius a=5.0 cm carries a net positive charge of Q=6.0 µC uniformly distributed throughout its volume. Concentric with this sphere is a conducting spherical shell with inner radius b=10 cm and outer radius c=15 cm and having net charge Q2= -8 µC, as shown. The electric field at a point r=12 cm from the center is: Insulator Conductor O 1.3×106 N/C O 3.8×106 N/C 5.0x106 N/C zeroarrow_forwardA long, nonconducting, solid cylinder of radius 4.1 cm has a nonuniform volume charge density p that is a function of radial distance r from the cylinder axis: p= Ar². For A = 3.4 µC/m³, what is the magnitude of the electric field at (a) r = 2.3 cm and (b) r = 8.9 cm. (a) Number i 1.1685819 (b) Number 9.063739132 Units Units N/C or V/m N/C or V/marrow_forward
- A charge of uniform linear density 2.20 nC/m is distributed along a long, thin, nonconducting rod. The rod is coaxial with a long conducting cylindrical shell (inner radius = 5.40 cm, outer radius 10.0 cm). The net charge on the shell is zero. (a) What is the magnitude of the electric field at distance r = 15.4 cm from the axis of the shell? What is the surface charge density on the (b) inner and (c) outer surface of the shell? Stell-arrow_forwardA thin rod carries linear charge density according to the distribution X(z) = Aox/L, where Xo = 29.7 nC/cm and L is the length of the rod. The rod extends from x = 0 cm tc I=28 cm. What is the magnitude of the electric field at a location = 6.0 cm? (please provide your answer in kN/C to 1 decimal place) Type your answer.....arrow_forwardA long, conductive cylinder of radius R₁ = 3.20 cm and uniform charge per unit length = 151 pC/m is coaxial with a long, cylindrical, nonconducting shell of inner and outer radii R₂ = 11.2 cm and R3 = 12.8 cm, respectively. If the cylindrical shell carries a uniform charge density of p 115 pC/m³, find the magnitude of the electric field E(r) at each radial distance indicated. E (1.95 cm) = E (12.0 cm) 0 Incorrect N/C N/C C E (9.76 cm) = E (18.9 cm) = R₁ R₂R, 84.6 Incorrect Incorrect N/C N/Carrow_forward
- A charge of uniform linear density 1.90 nC/m is distributed along a long, thin, nonconducting rod. The rod is coaxial with a long conducting cylindrical shell with an inner radius of 6.34 cm and an outer radius of 10.4 cm. If the net charge on the shell is zero, what is the surface charge density on the outer surface of the shell?arrow_forwardA long, conductive cylinder of radius R₁ = 3.20 cm and uniform charge per unit length λ = 151 pC/m is coaxial with a long, cylindrical, nonconducting shell of inner and outer radii R₂ = 11.2 cm and R3 = 12.8 cm, respectively. If the cylindrical shell carries a uniform charge density of p = 115 pC/m³, find the magnitude of the electric field E(r) at each radial distance indicated. E (1.95 cm) = E (12.0 cm) = 0 N/C N/C E (9.76 cm) = E (18.9 cm) = x10 R₁ TOOLS R, R₁ (6) N/C N/Carrow_forwardFigure (a) shows a narrow charged solid cylinder that is coaxial with a larger charged cylindrical shell. Both are nonconducting and thin and have uniform surface charge densities on their outer surfaces. Figure (b) gives the radial component E of the electric field versus radial distance r from the common axis. The vertical axis scale is set by E, = 3.0 x 10° N/C. What is the linear charge density of the shell? 12.6 -Es r (cm) (a) (b) Number i -5.8 Units nC/marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
