
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
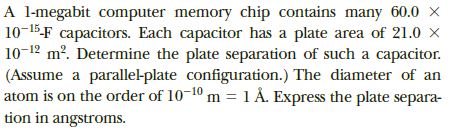
Transcribed Image Text:A l-megabit computer memory chip contains many 60.0 X
10-15-F capacitors. Each capacitor has a plate area of 21.0 X
10-12 m. Determine the plate separation of such a capacitor.
(Assume a parallel-plate configuration.) The diameter of an
atom is on the order of 10-10 m 1 Å. Express the plate separa-
tion in angstroms.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A capacitor with capacitance 5.75 μF is connected to a(n) 5.75-V battery. (a) Find the charge on the capacitor in coulombs. 3.30-5 С (b) What voltage battery would be required to store 8.00 x 10-5 C on the capacitor? 6.95 X Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. Varrow_forward13 Dry air is a pretty decent insulator; it has a very high resistivity of 3 × 105 2 · m. Consider a capacitor that has square plates 15 cm on a side, separated by 0.8 mm of dry air. The capacitor is charged such that it has a potential of 320 V between the plates.arrow_forward13 Dry air is a pretty decent insulator; it has a very high resistivity of 3 × 10º Q · m. Consider a capacitor that has square plates 15 cm on a side, separated by 0.8 mm of dry air. The capacitor is charged such that it has a potential of 320 V between the plates.arrow_forward
- Three capacitors of capacitance C1 1.35 иF, С2 %3 3.95 иF, and Сз 4.20 µF are connected in series. A potential difference of AVb 94.0 V is maintained by a battery. Find the equivalent capacitance of the series of capacitors and the charge on each capacitor. Сед Did you accidentally divide or take the inverse in your calculation? µF µC Determine the effect on the equivalent capacitance of reducing the second capacitance to 0.1 times its previous value. Ceq = HFarrow_forwardProblem 7: Capacitor C, is initially charged to V, and capacitor C, is initially charged to V. The capacitors are then connected to each other, positive terminal to positive terminal and negative terminal to negative terminal. If C = 16 µF with initial voltage of 25 V, and capacitor C2 = 13 µF is charged to 7 V. What is the final voltage, in volts, across C;? V =arrow_forwardWhat is the voltage across the plates of the capacitor if the capacitance is 10 uF and the Charge stored is 30 uC?arrow_forward
- Suppose a capacitor consists of two coaxial thin cylindrical conductors. The inner cylinder of radius ra has a charge of +Q, while the outer cylinder of radius ry has charge -Q. The electric field E at a radial distance r from the central axis is given by the function: E = aer/a0 + B/r + bo where alpha (a), beta (8), an and bo are constants. Find an expression for its capacitance. First, let us derive the potential difference Vah between the two conductors. The potential difference is related to the electric field by: Vah = Edr= - Fdr Calculating the antiderivative or indefinite integral, Vab = (-aager/a0 +8 + bo By definition, the capacitance Cis related to the charge and potential difference by: C = Evaluating with the upper and lower limits of integration for Vab, then simplifying: C= Q/( (e"b/a0 .eralao) + B In( )+ bo ( ))arrow_forwardAn uncharged capacitor is connected to the terminals of a 4.0 V battery, and 12 μC flows to the positive plate. The 4.0 V battery is then disconnected and replaced with a 6.0 V battery, with the positive and negative terminals connected in the same manner as before. How much additional charge flows to the positive plate? I tried 05 but that wasnt the answerarrow_forwardQuestion 3 and 4arrow_forward
- Consider a cylindrical capacitor with two layers of dielectric materials. The inner conductor radius is a and the outer conductor radius is c. The inner dielectric material fills the thickness (b-a) and its permittivity is & and the outer dielectric material fills the thickness (c-b) and its permittivity is ε, as shown in the figure. Find the capacitance of the capacitor if its length is 1. Consider a spherical capacitor with two layers of dielectric materials. The inner conductor radius is a and the outer conductor radius is c. The inner dielectric material fills the thickness (b-a) and its permittivity is & and the outer dielectric material fills the thickness (c-b) and its permittivity is ६, Find the capacitance of the capacitor.arrow_forwardItem 15 Now we will consider some slightly different related scenarios to Example 21-18. Part A Example 21-18 depicts the following scenario. A circuit consists of a resistor R₁ = 126-, a resistor R₂ = 275-, a capacitor C = 182-μF, a switch, and an € = 3.00-V battery all connected in series. Initially the capacitor is uncharged and the switch is open. At time t=0 the switch is closed. increase decrease stay the same 3.00 V Suppose the resistance of the 126-2 resistor is reduced by a factor of 2. Assume everything else in the problem remains the same. Does the final value of the charge on the capacitor increase, decrease, or stay the same? Submit Request Answer ww 126 Ω 182 μF HH 275 Ω < 15 of 15 Reviewarrow_forwardA parallel plate capacitor is composed of two rectangular plates with length 5mm and width 3 mm. The thickness of the insulating material is 0.5 mm. Find the permittivity of the insulating material if the capacitance is 2 μF.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON