
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
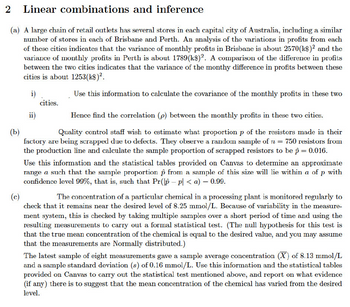
Transcribed Image Text:2 Linear
combinations and inference
(a) A large chain of retail outlets has several stores in each capital city of Australia, including a similar
number of stores in each of Brisbane and Perth. An analysis of the variations in profits from each
of these cities indicates that the variance of monthly profits in Brisbane is about 2570(k$)² and the
variance of monthly profits in Perth is about 1789 (k$)2. A comparison of the difference in profits
between the two cities indicates that the variance of the monthy difference in profits between these
cities is about 1253(k$)².
i)
Use this information to calculate the covariance of the monthly profits in these two
ii)
cities.
Hence find the correlation (p) between the monthly profits in these two cities.
(b)
Quality control staff wish to estimate what proportion p of the resistors made in their
factory are being scrapped due to defects. They observe a random sample of n = 750 resistors from
the production line and calculate the sample proportion of scrapped resistors to be p = 0.016.
Use this information and the statistical tables provided on Canvas to determine an approximate
range a such that the sample proportion from a sample of this size will lie within a of p with
confidence level 99%, that is, such that Pr(p - p| <a) = 0.99.
(c)
The concentration of a particular chemical in a processing plant is monitored regularly to
check that it remains near the desired level of 8.25 mmol/L. Because of variability in the measure-
ment system, this is checked by taking multiple samples over a short period of time and using the
resulting measurements to carry out a formal statistical test. (The null hypothesis for this test is
that the true mean concentration of the chemical is equal to the desired value, and you may assume
that the measurements are Normally distributed.)
The latest sample of eight measurements gave a sample average concentration (X) of 8.13 mmol/L
and a sample standard deviation (s) of 0.16 mmol/L. Use this information and the statistical tables
provided on Canvas to carry out the statistical test mentioned above, and report on what evidence
(if any) there is to suggest that the mean concentration of the chemical has varied from the desired
level.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Noise pollution is measured in decibels. In California any motorcycle made after 1980 may not be any louder than 80 decibels. Harley Davidson claims their mean decibel rating on bikes is 70 with a variance of 10. The variance of the noise is questioned. Just because Harley has a mean that is less than 80, they could still be producing louder than acceptable bikes. The federal EPA conducts a sample of 30 bikes and determines the variance to be 20 decibels. Is there enough evidence to question Harley’s claim of 10 decibels?arrow_forwardSuppose the variance of X is 14. What is the variance of .47X?arrow_forwardActuaries use various parameters when evaluating the cost of a life insurance policy. The variance of the life spans of a population is one of the parameters used for the evaluation. Each year, the actuaries at a particular insurance company randomly sample 30 people who died during the year (with the samples chosen independently from year to year) to see whether the variance of life spans has changed. The life span data from this year and from last year are summarized below. Current Last Year Year x1 = 75.8 | x,= 76.2 si= 47.61 s3= = 92.16 (The first row gives the sample means and the second row gives the sample variances.) Assume that life spans are approximately normally distributed for each of the populations of people who died this year and people who died last year. Can we conclude, at the 0.05 significance level, that the variance of the life span for the current year, of, differs from the variance of the life span for last year, o,? Perform a two-tailed test. Then complete the…arrow_forward
- Actuaries use various parameters when evaluating the cost of a life insurance policy. The variance of the life spans of a population is one of the parameters used for the evaluation. Each year, the actuaries at a particular insurance company randomly sample 30 people who died during the year (with the samples chosen independently from year to year) to see whether the variance of life spans has changed. The life span data from this year and from last year are summarized below. Current Last Year Year *1 = 75.8 x2 = 76.2 s3 = 47.61 s3= 92.16 (The first row gives the sample means and the second row gives the sample variances.) Assume that life spans are approximately normally distributed for each of the populations of people who died this year and people who died last year. Can we conclude, at the 0.05 significance level, that the variance of the life span for the current year, of, differs from the variance of the life span for last year, o,? Perform a two-tailed test. Then complete the…arrow_forwardPart 1. .If b = 0.523, then for every 1 unit increase in the independent variable, there is a 0.523 unit increase in the dependent variable. True or false? 2. .If b = .704, then 70.4% of the variance in the dependent variable can be explained by the variance in the independent variable. In contrast, 29.6% of the variance in the dependent variable can be explained by outside factors. True or false? 3. .If r = 0.444, then for every 1 unit increase in the independent variable, there is a 0.444 unit increase in the dependent variable. True or false?arrow_forwardOnce the correlation coefficient is known, how can we find the amount of the shared variance?arrow_forward
- It is possible to have a variance of 625,000625,000 for some data set. true or falsearrow_forward/Skip/1 A beverage company has two bottling plants in different parts of the world. To insure uniformity in their product, the variances of the weights of the bottles at the two plants should be equal. But Stephanie, the company's vice president of quality assurance, suspects that the variance at bottling plant A is more than the variance at bottling plant B. To test her suspicions, Stephanie samples 37 bottles from bottling plant A and 33 bottles from bottling plant B, with the following results (in ounces): Bottling Plant A: 12.4, 12.4, 13.4, 14.3, 12.7, 12.7, 13.7, 12.4, 12.8, 12.4, 12.9, 12.7, 12.8, 13.3, 13.8, 12.7, 12.4, 11.9, 12.9, 13, 13.1, 12.4, 12.7, 12.6, 12.5, 13.3, 12.2, 13.3, 12.8, 12.7, 13.2, 13.1, 11.7, 13, 12.3, 13.1, 12.4 Bottling Plant B: 12.9, 12, 13.4, 12.4, 12.4, 12.9, 12.7, 12.1, 11.4, 13.1, 14.1, 12.5, 12.7, 11.5, 12.3, 12.7, 13.7, 12.6, 13.9, 12.7, 12, 12.5, 11.7, 13.6, 11.4, 13.6, 14, 12, 11.5, 12, 11.7, 13, 11.8 Perform a hypothesis test using a 3% level of…arrow_forwardConsider data on every game played by the Brooklyn Nets in 2014 (82 games) that includes the variables margin; - the Net's margin of victory (number of points the Nets scored minus the number of points their opponent scored) for game i, and • home; - a dummy variable equal to 1 when the Nets are the home team (game i was played in their home arena) and equal to 0 when they are the away team (game i was played in the opponent's arena). I use the least-squares method to estimate the following regression model margin = a + ßhome; + ei Below is the Stata output corresponding to the estimated regression line: regress margin home if team==== "Brooklyn Nets" Source Model Residual Total margin home _cons SS 1459.95122 15252.0488 16712 df 1 80 Coef. Std. Err. MS 81 206.320988 8.439024 3.049595 -5.219512 2.156389 1459.95122 190.65061 t Number of obs F (1, 80) Prob > F R-squared. Adj R-squared = Root MSE P>|t| 2.77 0.007 -2.42 0.018 82 7.66 0.0070 0.0874 0.0760 13.808 [95% Conf. Interval]…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman