
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
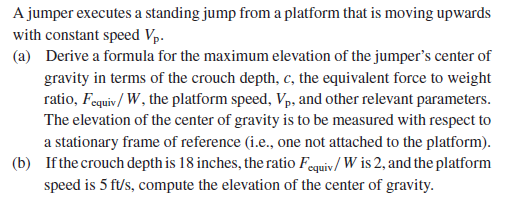
Transcribed Image Text:A jumper executes a standing jump from a platform that is moving upwards
with constant speed Vp.
(a) Derive a formula for the maximum elevation of the jumper's center of
gravity in terms of the crouch depth, c, the equivalent force to weight
ratio, Fequiv/ W, the platform speed, Vp, and other relevant parameters.
The elevation of the center of gravity is to be measured with respect to
a stationary frame of reference (i.e., one not attached to the platform).
(b) If the crouch depth is 18 inches, the ratio Fequiv/ W is 2, and the platform
speed is 5 ft/s, compute the elevation of the center of gravity.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- If the magnitude of the net force acting on the particle is F, how long does it take the particle to acquire its final velocity, 2v in the positive y direction? Express your answer in terms of m, F, and v. If you use a numerical coefficient, use three significant figures.arrow_forwardA toy rocket engine is securely fastened to a large puck that can glide with negligible friction over a horizontal surface, taken as the xy plane. The 4.20-kg puck has a velocity of 2.00î m/s at one instant. Eight seconds later, its velocity is (6.00î + 4.0ĵ) m/s. (a) Assuming the rocket engine exerts a constant horizontal force, find the components of the force. (b) Find its magnitude.arrow_forward30. 31. 32. For the graphs of g versus m shown below. (A) 91- (B) m (D) "K m (D) (C) "KK m Which graph shown below, (A) (B) Which graph best represents the acceleration due to gravity g as a function of mass m, near the surface of the earth? V m K V (E) P Ka V V (C) m 2 best represents the magnitude of the centripetal force F as a function of the speed v for an object moving in a fixed circular path? This means that the object has a (a) constant displacement. (b) steadily increasing acceleration. (c) steadily decreasing acceleration. (d) constant velocity. (e) steadily increasing velocity. The position-time graph of an object moving due north is a straight line with a positive slope.arrow_forward
- Discuss the motion of the bead according to the equation of motionq¨2 − ω2sin2α q = −g cos αas completely as you can. Find explicit solutions. What will happen if the beadis slightly displaced from the point where it has no acceleration.arrow_forwardA student of weight 651 N rides a steadily rotating Ferris wheel (the student sits upright). At the highest point, the magnitude of the normal force FN on the student from the seat is 589 N. (a) What is the magnitude of FN at the lowest point? If the wheel's speed is doubled, what is the magnitude FN at the (b) highest and (c) lowest point? (a) Number Units (b) Number Units (c) Number Unitsarrow_forwardA body of mass m is projected with speed u in a medium that exerts a resistance force of magnitude (i) mk| v |, or (ii) m K| v |2, where k and K are positive constants and v is the velocity of the body. Gravity can be ignored. Determine the subsequent motion in each case. Verify that the motion is bounded in case (i), but not in case (ii).arrow_forward
- Needs Complete typed solution with 100/% accuracy.arrow_forwardA bag is gently pushed off the top of a wall at A and swings in a vertical plane at the end of a rope of length I. Determine the angle 0 for which the rope will break, knowing that it can withstand a maximum tension equal to twice the weight of the bag.arrow_forwardA cart with mass 15.7 kg is intitally at rest. You get it moving by pushing on the cart at an angle of 0 = 37° as shown above. The magnitude of your force as a function of time is given by: Fyc(t) = Foe-bt, where b = 0.55 s-1 and Fo = 138.1 N. You can assume that the wheels roll perfectly on the ground. What is the speed of the cart when t = 3.3 s? Don't Know Where to Start? ... A Hint About N2L A Hint About the Proces ...... ........................ Vf = 10.25m/sarrow_forward
- A 2.2-lb slider is propelled upward at A along the fixed curved bar which lies in a vertical plane. If the slider is observed to have a speed of 7.8 ft/sec as it passes position B, determine (a) the magnitude N of the force exerted by the fixed rod on the slider and (b) the rate v at which the speed of the slider is changing (positive if speeding up, negative if slowing down). Assume that friction is negligible. B 30 2.6' Answers: N = i Ib シ= i ft/sec2arrow_forwardA particle of mass 25 kg moves in a straight line such that the force (in Newtons) acting on it at time ₺ (in seconds) is given by 225 to +175 + + 200. If at time t = 0 its velocity, v (in ms-¹), is given by v(0) = 14, and its position (in m) is given by (0) = 10, what is the position of the particle at time t? l The position is m.arrow_forwardA mysterious force acts on all particles along a particular line and always points towards a particular point P on the line. The magnitude of the force on a particle increases as the cube of the distance from that point, that is, F∝ r3, if the distance from the P to the position of the particle is r. It has been determined that the constant of proportionality is 0.23 N/m3, i.e. the magnitude of the force on a particle can be written as 0.23r3, when the particle is at a distance r from the force center. Find the magnitude of the potential energy, in joules, of a particle subjected to this force when the particle is at a distance 0.21 m from point P assuming the potential energy to be zero when the particle is at P. PE= ?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON