
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
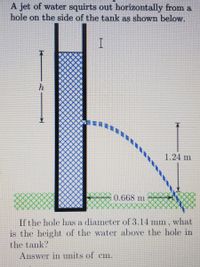
Transcribed Image Text:A jet of water squirts out horizontally from a
hole on the side of the tank as shown below.
h
1.24 m
0.668 m
If the hole has a diameter of 3.14 mm, what
is the height of the water above the hole in
the tank?
Answer in units of
Cm.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- SP5. A pipe with a circular cross section has a diameter of 9 cm. It narrows at one point to a diameter of 5.2 cm. The pipe is carrying a steady stream of water that completely fills the pipe and is moving with a speed of 1.6 m/s in the wider portion. a. What are the cross-sectional areas of the wide and nar- row portions of the pipe? (A = ar", and the radius is half the diameter.) b. What is the speed of the water in the narrow portion of the pipe? c. Is the pressure in the narrow portion of the pipe greater than, less than, or equal to the pressure in the wider portion? Explain.arrow_forwardA rectangular bucket, open at the top, is 29.6 cm high and 14.7 cm long, and 11.4 cm wide. A circular hole with a cross-sectional area of 1.91 cm? is cut in the center of the bottom of the bucket. Water flows into the bucket from an external tube above it at the rate of 2.27x10-4 m3/s. What is the maximum height (in meters) reached by the water? Final answer in two decimal places.arrow_forwardA drinking straw is placed in a glass of water. A student places their finger over the top opening of the straw and lifts the straw vertically a distance d with the water in the straw staying in the straw. Refer to the figure. Point B is at the surface of the water in the straw and point A is at the surface of the water in the glass. a)The straw is cylindrical with a radius of 2.5 mm. What is the weight of the water in the straw, in newtons?arrow_forward
- *49. A hollow cubical box is 0.30 m on an edge. This box is fl oating in alake with one-third of its height beneath the surface. The walls of the boxhave a negligible thickness. Water from a hose is poured into the open topof the box. What is the depth of the water in the box just at the instant thatwater from the lake begins to pour into the box from the lake?arrow_forwardA liquid-filled tube called a manometer can be used to measure the pressure inside a container by comparing it to the atmospheric pressure and measuring the height of the liquid. Such a device (filled with water) is shown in the figure, measuring the pressure inside a balloon filled with an unknown gas. The water level on the side of the manometer which is open to the air is 22.3 cm higher than on the side connected to the balloon. a) Find the gauge pressure in the balloon, in units of Pa. Recall the density of water is 1000 kg/m3. b) Find the absolute pressure in the balloon, in units of Pa.arrow_forward3. What fraction of a piece of iron will be submerged when it floats in mercury? 4. A nozzle with a diameter of 0.500 cm is attached to a garden hose with a radius of 0.900 cm where water flows at 1.96 m/s. Calculate the pressure in the hose, given that the absolute pressure in the nozzle is 1.01x10°N/m² and assuming level, frictionless flow.arrow_forward
- An open, clean glass tube (0 = 0°) is inserted vertically into a pan of water (see the Video). What tube diameter, d, is needed if the water level in the tube is to rise 0.25 tube diameter's (due to surface tension)? d = i ftarrow_forwardWater flowing out of a horizontal pipe emerges through a nozzle. The radius of the pipe is 1.6 cm, and the radius of the nozzle is 0.67 cm. The speed of the water in the pipe is 0.58 m/s. Treat the water as an ideal fluid, and determine the absolute pressure of the water in the pipe. P₁ = Jakaarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON