
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337093347
Author: Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
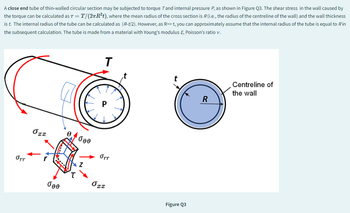
Transcribed Image Text:A close end tube of thin-walled circular section may be subjected to torque Tand internal pressure P, as shown in Figure Q3. The shear stress in the wall caused by
the torque can be calculated as T = T/(2πR²t), where the mean radius of the cross section is R (i.e., the radius of the centreline of the wall) and the wall thickness
is t. The internal radius of the tube can be calculated as (R-t/2). However, as R>>t, you can approximately assume that the internal radius of the tube is equal to R in
the subsequent calculation. The tube is made from a material with Young's modulus E, Poisson's ratio v.
Orr
T
Centreline of
the wall
R
P
022
dee
бут
Z
бее
T
Ozz
Figure Q3
![[(a) If the change of the diameter cannot exceed 0.1 m under elastic deformation, calculate the minimum allowable wall thickness of the cylindrical pressure vessel.
(P= 23.6 MPa, T=0 KN.m, R = 2 m, Young's modulus E = 246 GPa, and Poisson's ratio v = 0.21)]
Step-4
The minimum allowable wall thickness of the cylindrical pressure vessel can be calculated as
(Units: mm and rounded to three decimal places)
Select one
O 1.8.481
O 2.4.240
○ 3.6.869
○ 4. 16.961
5. 13.738
O 6.3.434](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/cdbeedd9-7160-4e48-8601-b290608df50c/b0307a92-8f36-490e-99b1-95db80c105ed/7uqzjw_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:[(a) If the change of the diameter cannot exceed 0.1 m under elastic deformation, calculate the minimum allowable wall thickness of the cylindrical pressure vessel.
(P= 23.6 MPa, T=0 KN.m, R = 2 m, Young's modulus E = 246 GPa, and Poisson's ratio v = 0.21)]
Step-4
The minimum allowable wall thickness of the cylindrical pressure vessel can be calculated as
(Units: mm and rounded to three decimal places)
Select one
O 1.8.481
O 2.4.240
○ 3.6.869
○ 4. 16.961
5. 13.738
O 6.3.434
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- (a) Solve part (a) of the preceding problem if the pressure is 8.5 psi, the diameter is 10 in., the wall thickness is 0,05 in., the modulus of elasticity is 200 psi, and Poisson's ratio is 0.48. (b) If the strain must be limited to 1.01, find the maximum acceptable inflation pressurearrow_forwardA wine of length L = 4 ft and diameter d = 0.125 in. is stretched by tensile forces P = 600 lb. The wire is made of a copper alloy having a stress-strain relationship that may be described mathematically by =18,0001+30000.03(=ksi) in which is nondimensional and has units of kips per square inch (ksi). (a) Construct a stress-strain diagram for the material. (bj Determine the elongation, of the wire due to the Forces P. (c) IF the forces are removed, what is the permanent set of the bar? (d) If the forces are applied again, what is the proportional limit?arrow_forwardSolve the preceding problem if the diameter is 480 mm, the pressure is 20 MPa, the yield stress in tension is 975 MPa, the yield stress in shear is 460 MPa, the factor of safety is 2,75, the modulus of elasticity is 210 GPa, Poissorfs ratio is 0.28, and the normal strain must not exceed 1190 x 10" . For part (b), assume that the tank thickness is 8 mm and the measured normal strain is 990 x 10~ .arrow_forward
- A hollow, circular, cast-iron pipe (Ec =12,000 ksi) supports a brass rod (Ec= 14,000 ksi} and weight W — 2 kips, as shown. The outside diameter of the pipe is dc= 6 in. (a) If the allowable compressive stress in the pipe is S00O psi and the allowable shortening of the pipe is 0.02 in., what is the minimum required wall thickness trmm? (Include the weights of the rod and steel cap in your calculations.) (b) What is the elongation of the brass rod Srdue to both load Wand its own weight? (c) What is the minimum required clearance h?arrow_forwardSolve the preceding problem for the following data: diameter LO m, thickness 48 mm, pressure 22 MPa, modulus 210 GPa. and Poisson's ratio 0.29arrow_forwardA standard brick (dimensions 8 in. × 4 in. × 2.5 in ) is compressed lengthwise by a force P. as shown in the figure, If the ultimate shear stress for brick is 1200 psi and the ultimate compressive stress is 3600 psi. what force Pmax is required to break the brick?arrow_forward
- A circular cylindrical steel tank (see figure) contains a volatile fuel under pressure, A strain gage at point A records the longitudinal strain in the tank and transmits this information to a control room. The ultimate shear stress in the wall of the tank is 98 MPa, and a factor of safety of 2,8 is required. (a) At what value of the strain should the operators take action to reduce the pressure in the tank? (Data for the steel are modulus of elasticity E = 210 GPa and Poisson's ratio v = 0.30.) (b) What is the associated strain in the radial directionarrow_forwardFor a 60° angle lamina of graphite/epoxy with 70% fibre volume fraction under stresses in global axes as σx = 6 MPa, σy = 2 MPa, and τxy = –4 MPa, and using the properties of the given unidirectional lamina from the book, find the followings; a. Local stresses and strains b. Principal normal stresses and principal normal strains c. Maximum shear stress and maximum shear strainarrow_forwardanswer as soon as possiblearrow_forward
- What’s the answer for this please ?arrow_forward2. A thin steel tire is shrunk on to a locomotive wheel of 1.2 m diameter. Find the internal diameter of the tire if after shrinking on, the hoop stress in the tire is 100 MPa. Assume E=200kN/mm2. Also find the least temperature to which the tire must be heated above that of the wheel before it could be slipped on. The coefficient of linear expansion for the tire is 6.5×10–6 per °C.arrow_forwardA rubber ball is inflated to a pressure of 60KPa. At that pressure, the diameter of the ball is 230mm and the wall thickness is 1.2mm. The rubber has a modulus of elasticity of E = 3.5MPa and Poisson’s ratio of 0.45. (a)Compute the maximum tensile stress. (b)If the allowable tensile stress of the rubber ball wall is 2.5MPa, compute the internal pressure the rubber ball could be inflated.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning