
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A hovercraft weighs M = 1500 kg and hovels without changing altitude. The exit flow exhausts to atmospheric pressure at sea-level. The flow is steady, incompressible and uniform properties can be assumed on all control surfaces. Assume air density = 122 kg/m^3.
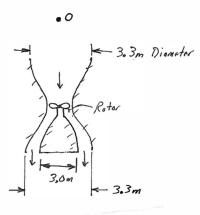
Transcribed Image Text:### Diagram Explanation: Funnel Structure with Rotor
The diagram shows a funnel-shaped structure with a rotor placed at the narrowest point. Below is the detailed breakdown of the diagram:
1. **Funnel Structure:**
- The diagram illustrates a symmetrical funnel-shaped structure.
- The widest part of the funnel has a diameter of 3.3 meters on both the top and the bottom.
- The narrowest part of the funnel, where the rotor is located, has a diameter slightly less than 3.3 meters but this specific measurement is not provided in the diagram.
2. **Rotor:**
- Inside the funnel, there is a rotor positioned at the narrowest point.
- The rotor is depicted inside a conical section which has a height of 3.0 meters.
This diagram might be illustrating a mechanical or fluid dynamics concept where the rotor's position within the funnel is crucial, likely for regulating flow or for a mechanical advantage based on the funnel's shape. The detailed measurements indicate that precision is important in whatever application this structure and rotor assembly are used for.

Transcribed Image Text:### Hovercraft Power Requirements
#### a) Develop an equation for the required power input to the rotor of the hovercraft. Assume negligible internal change, potential energy change, flow work (e.g., pressure effects), and heat transfer.
---
#### b) Calculate a numerical value for the required power input.
---
### Explanations:
1. **Equations for Power Input**:
- When developing an equation for the power input, consider the principles of conservation of energy and the specific parameters and assumptions provided.
- Negligible internal changes, potential energy changes, flow work, and heat transfer simplify the problem to focus primarily on the kinetic aspects and operational needs of the rotor.
2. **Numerical Calculation**:
- Once the equation is established, substitute the relevant numerical values to estimate the actual power input required for the hovercraft's operations.
This setup guides students through theoretical formulation and practical calculation, integrating principles of mechanical engineering and physics focused on hovercraft design.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Pravinbhaiarrow_forwardAn ideal rocket has characteristic velocity c* = 1800 m/s, nozzle throat diameter of 25 cm, thrust coefficient CF = 1.47, and mass flow rate of 48 kg/s. Find: (1) the Chamber Pressure P1 Po, (2) the Thrust F, and (3) the Specific Impulse Iş. Show all calculations.arrow_forwardAn ideal water jet with volume flow rate of 0.05 m^ 3 / s strikes a flat plate placed normal to its path and exerts a force 1000 N Considering the density of water as 1000 kg / (m ^ 3) , find the diameter (in mm) of the water jet.arrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY