
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
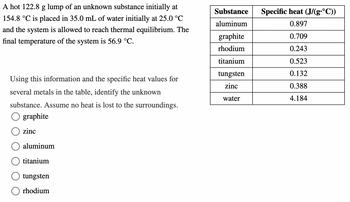
Transcribed Image Text:**Experiment Description:**
A hot 122.8 g lump of an unknown substance initially at 154.8 °C is placed in 35.0 mL of water initially at 25.0 °C, and the system is allowed to reach thermal equilibrium. The final temperature of the system is 56.9 °C.
**Objective:**
Using this information and the specific heat values for several metals in the table, identify the unknown substance. Assume no heat is lost to the surroundings.
**Options:**
- ○ graphite
- ○ zinc
- ○ aluminum
- ○ titanium
- ○ tungsten
- ○ rhodium
**Table of Specific Heat Values:**
| Substance | Specific heat (J/(g·°C)) |
|------------|--------------------------|
| aluminum | 0.897 |
| graphite | 0.709 |
| rhodium | 0.243 |
| titanium | 0.523 |
| tungsten | 0.132 |
| zinc | 0.388 |
| water | 4.184 |
**Instructions:**
Analyze the problem using the principle of heat transfer (Q = mcΔT) to determine the identity of the unknown substance based on the provided specific heat values.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1

Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The table lists the specific heat capacities of select substances. Substance Specific heat capacity (J/g °C) lead 0.128 silver 0.235 0.385 0.449 0.903 4.184 copper iron aluminum water An unknown substance has a mass of 18.9 g. The temperature of the substance increases by 16.5 °C when 73.3 J of heat is added to the substance. What is the most likely identity of the substance? water Olead O copper iron. silver aluminumarrow_forwardThe table lists the specific heat capacities of select substances. Substance Specific heat capacity (J/g °C) lead 0.128 silver 0.235 соpper 0.385 iron 0.449 aluminum 0.903 water 4.184 An unknown substance has a mass of 10.5 g. The temperature of the substance increases by 13.3 °C when 53.8 J of heat is added to the substance. What is the most likely identity of the substance? iron lead aluminum copper water silver O O Carrow_forwardIf the same amount of heat is added to 5.00 g samples of each of the metals below, which metal will experience the largest temperature change? Metal Specific Heat Capacity (J/g-K) A 0.753 B 0.129 C 0.385 D 0.449 E 0.897arrow_forward
- A particular sample of cold graphite at 10.20 °C was added to 988.5 g of water at 25.31 °C in a constant pressure calorimeter. If the final temperature of the graphite and water was 25.17 °C, what was the mass of the graphite sample? Assume no heat was lost to the surroundings. The specific heat for water is 4.184 J/g•°C and the specific heat for this graphite is 0.7069 J/g•°C.arrow_forward17. An ice cube is placed in a sealed insulated container of hot water at 80°C. After five minutes, the ice cube disappears. Ice Cube Heat ener Hot Water 5 min. Water Which best describes the change that took place inside the container? The total heat energy in the container was reduced by the ice cube. The hot water lost the same amount of heat energy as the ice cube gained. in the hot water was reduced by kinetic energy in the ice cube. O Heat energy in the ice cube was dissipated into the hot water.arrow_forward8. Heat is applied to 50g of water (specific heat of 4.18J/°C) at 25°C. The temperature of the water increases to 98°C. What was the total amount of heat energy that was applied?arrow_forward
- Calculate the specific heat capacity of an unknown metal if 30 grams of the unknown metal at 24.5°C is placed in a container containing 68.0 grams of water at 85°C. Then the water cools down and the metal warms up until thermal equilibrium is achieved at 79.1°C. Assume all the heat lost by the water is gained by the metal and the container is insulated. The specific heat capacity of water is 4.18 J g-1°C-1 1.02 5.32 2.81 0.45arrow_forwardWhen a 0.740-g sample of trinitrotoluene (TNT), C,H,N,O, is burned in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature increases from 23.4 °C to 26.9 °C. The heat capacity of the calorimeter and its content is 3.35 kJ/°C. How much heat was produced by the combustion of the TNT sample? O 34.2 kJ O 11.7 kJ O 101.5 kJarrow_forwardThe specific heat of substance C is 0.93 J/(g K) and that of substance D is 1.8 J/(g K). You are given an unknown that could be pure substance C, pure substance D, or a homogeneous mixture of C and D. In the lab you determine that it requires 23.3 J of heat energy to raise the temperature of a 25.0 g sample of the unknown by 1.0 K. What conclusions can you make about the identity of your unknown, from this data?arrow_forward
- 3. A piece of metal weighing 59.047 g was heated to 100.0 °C and then put it into 100.0 mL of water (initially at 23.7 °C). The metal and water were allowed to come to an equilibrium temperature, determined to be 27.8 °C. Assuming no heat lost to the environment, calculate the specific heat of the metal.arrow_forwardA 135.0-g piece of iron is heated to 225 ℃ in an oven. It is then dropped into a calorimeter containing 250.0-mL of glycerol (d = 1.261 g/mL) at 23.5 ℃. The temperature of glycerol rises to a maximum value of 44.7 ℃. Determine the specific heat of glycerol.arrow_forwardA metal object with mass of 21.4 g is heated to 97.0 °C and then transferred to an insulated container containing 81.7 g of water at 20.5°C. The water temperature rises and the temperature of the metal object falls until they both reach the same final temperature of 23.1 °C. What is the specific heat of this metal object? Assume that all the heat lost by the metal object is absorbed by the water. cal specific heat:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY