
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
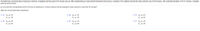
Transcribed Image Text:A hospital was concerned about reducing its wait time. A targeted wait time goal of 25 minutes was set. After implementing an improvement framework and process, a sample of 351 patients showed the mean wait time was 23.05 minutes, with a standard deviation of 16.27 minutes. Complete
parts (a) and (b) below.
a. If you test the null hypothesis at the 0.05 level of significance, is there evidence that the population mean wait time is less than 25 minutes?
State the null and alternative hypotheses.
Ο . H μ2 25
H1:µ<25
Ο Β. Ho μ< 25
H: µ> 25
O c. H : μ2 25
H1: µ#25
Ο D . H : μ# 25
H: H2 25
Ο Ε. H μ < 25
H1: µ2 25
Ο F. Ho: μ> 25
H,: µ<25
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A metropolitan transportation authority has set a bus mechanical reliability goal of 3,900 bus miles. Bus mechanical reliability is measured specifically as the number of bus miles between mechanical road calls. Suppose a sample of 100 buses resulted in a sample mean of 3,925 bus miles and a sample standard deviation of 225 bus miles. Complete parts (a) and (b) below. a. Is there evidence that the population mean bus miles is more than 3,900 bus miles? (Use a 0.05 level of significance.) Identify the critical value(s). Determine the test statistic. State the conclusion. Determine the p-value and interpret its meaningarrow_forwardAn article in the San Jose Mercury News stated that students in the California state university system take 6 years, on average, to finish their undergraduate degrees. A freshman student believes that the mean time is less and conducts a survey of 66 students. The student obtains a sample mean of 5.9 with a sample standard deviation of 0.7. Is there sufficient evidence to support the student's claim at an a = 0.1 significance level? Preliminary: a. Is it safe to assume that n < 5% of all college students in the local area? Yes No b. Is n ≥ 30? Yes No Test the claim: a. Determine the null and alternative hypotheses. Enter correct symbol and value. Ho: μ Η μ? ? a⋅ b. Determine the test statistic. Round to four decimal places. t c. Find the p-value. Round to 4 decimals. p-value = d. Make a decision. Reject the null hypothesis. Fail to reject the null hypothesis. e. Write the conclusion. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that that the mean time to complete an…arrow_forwardPandemic-fueled challenges forced consumers to wait significantly longer in drive-thru lanes. QSR magazine studied drive-thru times for 10 fast-food restaurants the lengths of time customers would spend in the drive-thru lane – and found that KFC in 2020, had the shortest mean time with a mean time spent in the drive-through lane of 283.3 seconds. Assuming drive-through times are Normally distributed with a standard deviation of 33 seconds, answer the following. a. What percentage of drive-through times at KFC will last more than 300 seconds? b. The longest 10% of drive-through times are longer than how many seconds? round top the nearest second. c. If we select a customer in the drive-through lane at KFC at random, what is the probability that their drive-through time is between 275 and 290 seconds? d. Dring Lunchtime, it is estimated that 230 customers go through the drive-thru, how many customers have to wait for less than 305 seconds.arrow_forward
- Dr. Graham is interested in determining if middle-aged adults use text messaging more or less frequently than the general population. Dr. Graham collects information on text messaging from a random sample of 50 adults ages 25 to 44. Dr. Graham finds that these individuals send or receive an average of 68 text messages per day. Using the population mean (and standard deviation) of 41.5 texts per day (34 texts per day), determine whether adults in this age group use text messaging more than the general public.arrow_forwardAn electronics production sequence includes a process where a film of metal is deposited on a board. The film must be more than 1.000 mm thick. If the film is too thin the process fails. The engineer ran a test where the null hypothesis was that the mean thickness was at most 1.000 mm. A sample of 100 boards had a mean thickness of 1.007 mm and a standard deviation of 0.050 mm.At what level of significance would the null hypothesis be rejected? Express your answer at a decimal (not a percent) rounded to three places.arrow_forwardA college entrance exam company determined that a score of 21 on the mathematics portion of the exam suggests that a student is ready for college-level mathematics. To achieve this goal, the company recommends that students take a core curriculum of math courses in high school. Suppose a random sample of 250 students who completed this core set of courses results in a mean math score of 21.2 on the college entrance exam with a standard deviation of 3.3. Do these results suggest that students who complete the core curriculum are ready for college-level mathematics? That is, are they scoring above 21 on the math portion of the exam? Complete parts a) through d) below. iueiuiy uie LUSI SiauSuc. to = 0.96 (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Identify the P-value, P-value = (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
- Watching TV: In 2012, the General Social Survey asked a sample of 1318 people how much time they spent watching TV each day. The mean number of hours was 2.95 with a standard deviation of 2.63. A sociologist claims that people watch a mean of 3 hours of TV per day. Do the data provide sufficient evidence to conclude that the mean hours of TV watched per day differs from the claim? Use the a= 0.01 level of significance and the critical value method. Part: 0 / 5 Part 1 of 5 State the appropriate null and alternate hypotheses. H: H₁ : This hypothesis test is a (Choose one) test. 0<0 ☐☐ X □<口 μ 0=0 Śarrow_forwardA hospital was concerned about reducing its wait time. A targeted wait time goal of 25 minutes was set. After implementing an improvement framework and process, a sample of 325 patients showed the mean wait time was 23.05 minutes, with a standard deviation of 16.14 minutes. Complete parts (a) and (b) below. a. If you test the null hypothesis at the 0.10 level of significance, is there evidence that the population mean wait time is less than 25 minutes? State the null and alternative hypotheses. Ο Β. Η0: μ 25 H1: µ 25 H1: µ< 25 Ο D . H : μ# 25 H,: µ2 25 Ο Ε. Ho: μ < 25 H,: µ2 25 O F. Ho: µ2 25 H,: µ# 25 Find the test statistic for this hypothesis test. tSTAT = (Type an integer or a decimal. Round to two decimal places as needed.) Find the p-value. The p-value is (Type an integer or a decimal. Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardA metropolitan transportation authority has set a bus mechanical reliability goal of 3,900 bus miles. Bus mechanical reliability is measured specifically as the number of bus miles between mechanical road calls. Suppose a sample of 100 buses resulted in a sample mean of 3,950 bus miles and a sample standard deviation of 225 bus miles. a. Is there evidence that the population mean bus miles is more than 3,900 bus miles? (Use a 0.10 level of significance.) State the null and alternative hypotheses. H0: μ ___ _____H1: μ ____ _____ (Type integers or decimals.) Find the test statistic for this hypothesis test. tSTAT=______ (Round to two decimal places as needed.) The critical value(s) for the test statistic is(are) _____ (Round to two decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) Is there sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis using α=0.10? A. Reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence at…arrow_forward
- A hospital was concerned about reducing its wait time. A targeted wait time goal of 25 minutes was set. After implementing an improvement framework and process, a sample of 364 patients showed the mean wait time was 23.04 minutes, with a standard deviation of 16.14 minutes. Complete parts (a) and (b) below. Question content area bottom Part 1 a. If you test the null hypothesis at the 0.10 level of significance, is there evidence that the population mean wait time is less than 25 minutes? State the null and alternative hypotheses. A. H0: μ<25 H1: μ>25 B. H0: μ≥25 H1: μ<25 C. H0: μ<25 H1: μ≥25 D. H0: μ>25 H1: μ<25 E. H0: μ≠25 H1: μ≥25 F. H0: μ≥25 H1: μ≠25 Part 2 Find the test statistic for this hypothesis test. tSTAT=enter your response here (Type an integer or a decimal. Round to two decimal places as needed.) Part 3 Find the p-value. The p-value is enter your…arrow_forwardIn a study of computer use, 1000 randomly selected Canadian Internet users were asked how much time they spend using the Internet in a typical week. The mean of the sample observations was 12.8 hours. (a) The sample standard deviation was not reported, but suppose that it was 6 hours. Carry out a hypothesis test with a significance level of 0.05 to decide if there is convincing evidence that the mean time spent using the Internet by Canadians is greater than 12.6 hours. (Use a statistical computer package to calculate the P-value. Round your test statistic to two decimal places and your P-value to four decimal places.) t=P-value= State the conclusion in the problem context. Reject H0. We have convincing evidence that the mean weekly time spent using the Internet by Canadians is greater than 12.6 hours.Do not reject H0. We have convincing evidence that the mean weekly time spent using the Internet by Canadians is greater than 12.6 hours. Reject H0. We do not have convincing…arrow_forwardAn article in the San Jose Mercury News stated that students in the California state university system take 6 years, on average, to finish their undergraduate degrees. A freshman student believes that the mean time is less and conducts a survey of 53 students. The student obtains a sample mean of 4.1 with a sample standard deviation of 1.9. Is there sufficient evidence to support the student's claim at an �=0.1 significance level? Test the claim: Determine the null and alternative hypotheses. Enter correct symbol and value.�0: �=Incorrect��: � Correct< Incorrect Determine the test statistic. Round to four decimal places.�=Incorrect Find the �-value. Round to 4 decimals.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman