
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
A heat engine constructed with one mole of an ideal monatomic gas operates on a reversible cycle a→b→c→d→a. The system goes from a→b in a isochoric process from Pa (pressure ) to Pb=4Pa. The system then expands in an isothermal process b→cf from Va to 2Va. A second isochoric process c→d takes the system to pressure back to Pa after which an isobaric process d→a return the system to its original state.
what is the energy efficiency?
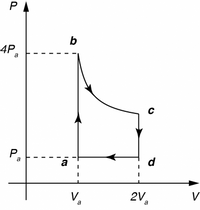
Transcribed Image Text:PA
b
4P,
a
Pa
d
a
V,
2Va
V
a
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Ethylene at 30 bar and 100°C passes through a throttling valve and heat exchanger, emerging at 20 bar and 150°C. Assuming that ethylene obeys the Peng-Robinson equation of state, compute the flow of heat (J/mol) into the heat exchanger per mole of ethylene.arrow_forwardSteam at 0.9 MPa and dryness fraction 0.86 expands in a cylinder behind a piston isothermally and reversibly to a pressure of 0.05 MPa and temperature of 250°C. Calculate: 3.1. Change of internal energy. 3.2. Change of enthalpy per kg of steam. 3.3. Change of entropy. 3.4. The heat supplied during the process is found to be 560 kJ/kg, calculate the work done per kilogram of steam.arrow_forwardA heat exchanger is used to transfer heat from a steam stream to a chlorine gas stream. 100 kg of steam at 1 bar and 200 °C enters the heat exchanger and leaves the exchanger as saturated steam at 1 bar. Chlorine gas enters the exchanger at 1 bar and 48.0 °C and leaves the exchanger at 141.0 °C. Assume the heat exchanger is adiabatic. What is the specific enthalpy of the inlet steam stream? (Use liquid water at 0.01 °C as a reference state.) Ĥ și= kJ/kg What is the specific enthalpy of the outlet steam stream? (Use the same reference state.) 50= kJ/kg What is the specific enthalpy of the inlet chlorine gas stream? (Use chlorine gas at 1 bar and 48.0 °C as a reference state.) Ĥci= kJ/mol What is the specific enthalpy of the outlet chlorine gas stream? (Use chlorine gas at 1 bar and 48.0 °C as a reference state.) ÊĤ co= kJ/mol How many moles of chlorine gas enter the heat exchanger? nc = mol What is the ratio of the volume of inlet steam to the volume of inlet chlorine gas? Use the ideal…arrow_forward
- A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between two or more fluids. Consider the steady flow of a substance through a heat exchanger at atmospheric pressure and determine the exit temperature of the substance for the following processes. The constant-pressure heat capacities are well described by the following equation: Cp R = A + BT+ CT², T[=]K (1.1) 1.967, = where A = 1.924, B = 14.394 × 10-³ K-¹, and C = -4.392×10-6 K-2 for ethylene, and A B = 31.630 × 10-³ K-1, and C = -9.873x10-6 K-2 for 1-butene. (a) Ethylene at 200°C is fed at 10 mol/s into a heat exchanger that adds heat at a rate of 400 kW. Hint: To obtain a numerical solution, you may need to use a "solver" or an iterative method. (b) 1-butene at 260°C is fed at 15 mol/s into a heat exchanger that adds heat at a rate of 2000 kW. Now suppose you take the streams exiting from (a) and (b) and allow them to exchange heat between each other. Both streams exit at the same final temperature. (c) What is the exit…arrow_forward2. Nitrogen turbine. Nitrogen expands from 30 bar, 600°C to 12 bar in a turbine operating at steady-state. Assume nitrogen to be an ideal gas (C = 29 J/mol-K). a. Calculate the amount of work and the final temperature if expansion is reversible. b. Repeat the calculation if the efficiency of the turbine is 82% and report the lost work.arrow_forwardSteam at 10bar absolute with 190°C of superheat is fed to a turbine at a rate _ m 2000kg/h. The turbine operation is adiabatic, and the effluent is saturated steam at 1bar. Calculate the work output of the turbine in kilowatts, neglecting changes in kinetic and potential energy. Inlet Steam: Table B.7 indicates that steam at 10bar is saturated at 180°C(verify), so that the inlet steam temperature is 180°C +190°C =370°C. Interpolating in the same table, Hin(10 bar, 370°C) =3201kJ/kg Here are my questions: Where do you locate 180 degrees C and also locate 3201 KJ/kg at 10 bar, 370 degrees C? Use Table B.7arrow_forward
- A piston–cylinder device contains 0.05 kg of steam at 1 MPa and 300°C. Steam now expands to a final state of 200 kPa and 150°C, doing work. Heat losses from the system to the surroundings are estimated to be 2 kJ during this process. Assuming the surroundings to be at T0 = 25°C and P0 = 100 kPa, determine the exergy change of the steam.arrow_forwardMethane in a piston-cylinder assembly undergoes an adiabatic compression from an initial state (0.5 bar, 0.05 m³/mol) to a final state (10 bar, 3×10-³ m³/mol). Use the van der Waals equation of state to calculate the amount of work done on the system, in J/mol. Note that if ideal gas, the heat capacity of methane is given by Cp = 1.702 +9.081 × 10-³ T-2.164 x 10-6 T², where T is in K. Rarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The