
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
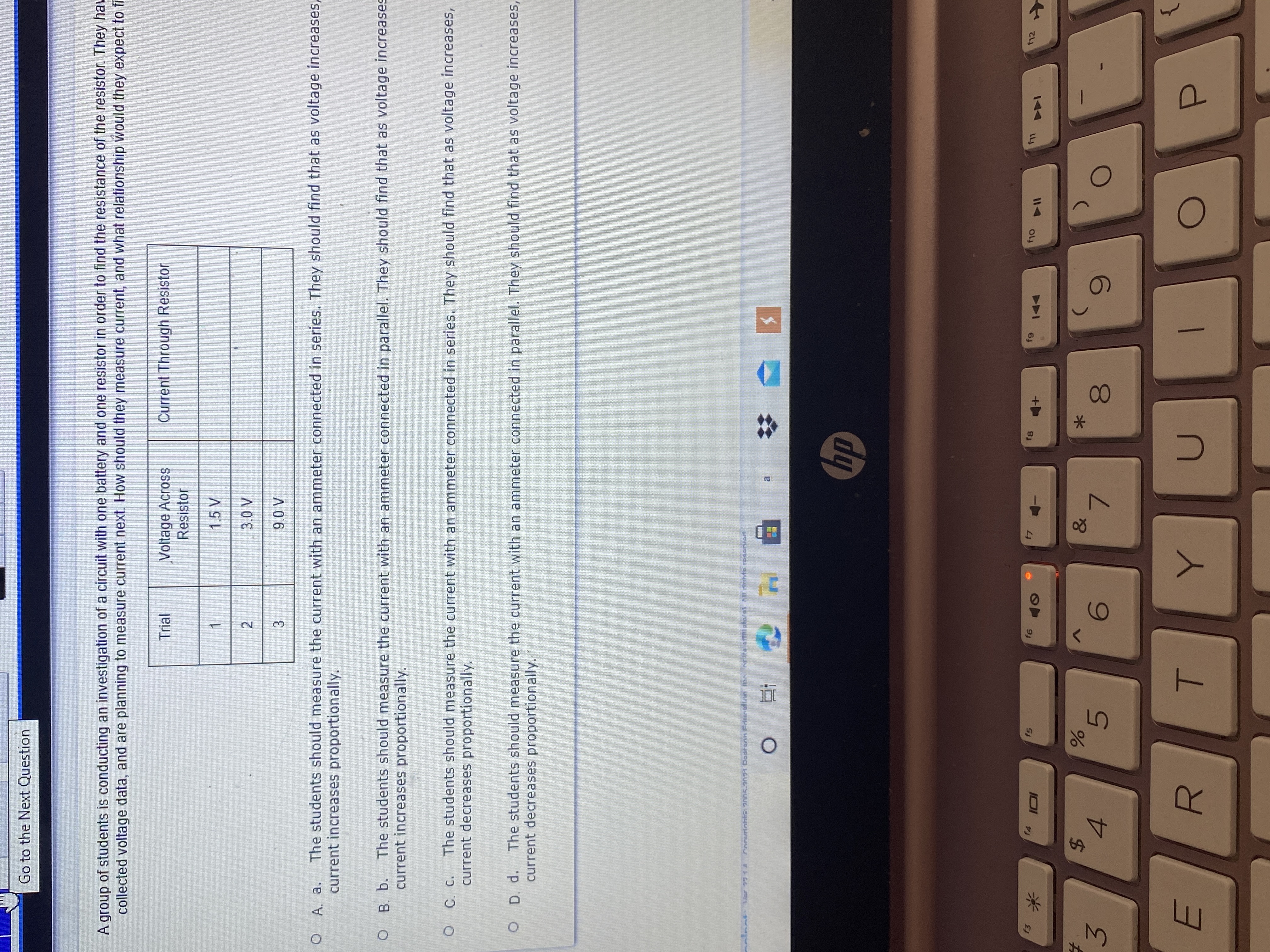
A group of students is
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A defibrillator is designed to pass a large current through a patient’s torso in order to stop dangerous heart rhythms. Its key part is a capacitor that is charged to a high voltage. The patient’s torso plays the role of a resistor in an RC circuit. When a switch is closed, the capacitor discharges through the patient’s torso. A jolt from a defibrillator is intended to be intense and rapid; the maximum current is very large, so the capacitor discharges quickly. This rapid pulse depolarizes the heart, stopping all electrical activity. This allows the heart’s internal nerve circuitry to reestablish a healthy rhythm.A typical defibrillator has a 32 μF capacitor charged to 5000 V. The electrodes connected to the patient are coated with a conducting gel that reduces the resistance of the skin to where the effective resistance of the patient’s torso is 100 Ω. Which pair of graphs shown best represents the capacitor voltage and the current through the torso as a function of time after the…arrow_forwardIf the resistors and batteries in Figures Q23.4 and Q23.5 are all the same, which of the two circuits dissipates more total power? Explain.arrow_forwardUse your data to come up with a mathematical expression which can be used to calculate the potential difference across a resistor in terms of the emf of the battery and the internal resistance of the battery r. (Note: your expression should work for any battery with any internal resistance, not just the specific battery used in this experiment). Show that the expression you came up with works with the data you collected. Data: emf (V) 0 3.33 6.67 10 13.33 16.67 20 23.33 26.67 30 Current (A) 0 0.33 A 0.67 A 1.00 A 1.33 A 1.67 A 2.00 A 2.33 A 2.67 A 3.00 A I graphed it and it gave me a mathmatical expression of y= 0.1x - 0.0005arrow_forward
- A 2.2 kl and a 4.0 k2 resistor are connected in parallel; this combination is connected in series with a 1.3 k2 resistor. If each resistor is rated at 0.2 W (maximum without overheating), what is the maximum voltage that can be applied across the whole network? Express your answer using two significant figures. Vmax =arrow_forwardConsider three resistors with unequal resistances connected in parallel to a battery. Which of the following statements are true? a) The algebraic sum of the currents flowing through each of the three resistors is equal to the current supplied by the battery. b) The voltage across each of the resistors is the same and is equal in magnitude to the voltage of the battery. c) The current flowing through each of the resitors is the same and is equal to the current supplied by the battery. d) The equivalent resistance of the combination of resistors is greater than the resistance of ny one of the three resistors. e) The equivalent resistance of the combination of resistors is less than the resistance of any one of the three resistors. f) The algebraic sum of the voltages across the three resistors is equal to the voltage supplied by the battery.arrow_forwardA circuit consisting of three ideal batteries with voltages 8, E1 E2, and 83, and three ideal resistors with resistances R1, R2, R3 and R3, is shown in the figure. Calculate the current Ip through point P. Let the sign of the current correspond to its direction, with "up" being positive. 81 = 23.5 V, E2 = 10.5 V, E3 = 30.0 V %3D %3D %3D R1 R2 R = 1.20 k2, R2 = 14.0 kN, R3 = 6.25 k2 14.0 kΩ, R E3 %3D Ip = %3D S TOOLS x10arrow_forward
- A battery of voltage VB = 10.0 V is connected to two resistors, R1 = 5 Q and R2 = 15 Q, which are wired in series with each other and the battery. What are the voltages V1 and V2 across those resistors?arrow_forwardThe two figure panels show two ways to connect a real (non-ideal) voltmeter and a real ammeter in a circuit to calculate the resistance R. The internal resistance of the voltmeter is Rv and the internal resistance of the ammeter is Ra. The current flows from left to right in both panels, and the potential difference Vac between points a and c in both panels is the same. In panel (a) the voltmeter reads Vac = 12.1 V and the ammeter reads I1 = 0.098 A. In panel (b) the voltmeter reads Vab = 12.0 V and the ammeter reads I2 = 0.100 A. I need help with Part E.arrow_forwardA student connects two resistors with unknown resistance values in series, and notes that the equivalent resistance R = 775 2. She then connects the same two resistors in parallel, and measures the equivalent resistance to be Rp = 155 Q. What are the resistances (in 2) of each resistor? smaller resistance Ω larger resistance Qarrow_forward
- Regarding the circuit in the left-hand part of the diagram: a) What is the current passing through each of the resistors? b) What is the current supplied by the battery? c) What is the potential difference across the 12 Ω resistor? d) How much power is turned to heat in the 4 Ω resistor? e) If we replace the circuit on the left by the one in the right-hand part of the diagram, with the same battery and only one resistor, what resistance Req should we choose to obtain the same total current?arrow_forwardwww R2 R, www R3 V A 5-year old has nothing better to do than to connect three resistors to a voltage source as shown. The resistors are R1=49 2, R2=62 2, and R3=D16 2, respectively, and the voltage source has 1.5 Volts. What is the total resistance? Submit Answer Tries 0/2 What is the current through the voltage source?arrow_forwardA student connects two resistors with unknown resistance values in series, and notes that the equivalent resistance R = 790 0. She then connects the same two resistors in parallel, and measures the equivalent resistance to be Rp = 160 02. What are the resistances (in) of each resistor? smaller resistance larger resistance Q Qarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON