
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
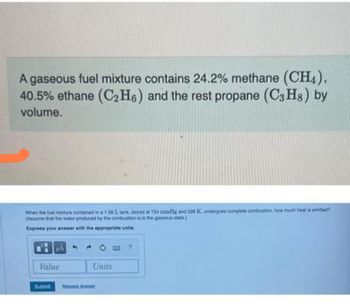
Transcribed Image Text:A gaseous fuel mixture contains 24.2% methane (CH4),
40.5% ethane (C₂H6) and the rest propane (C3H8) by
volume.
When the fuel mixture contained in a 1.56 L tank, stored at 754 mmHg and 298 K, undergoes complete combustion, how much heat is emitted?
(Assume that the water produced by the combustion is in the gaseous state.)
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
μÅ
Value
Submit
Units
Request Answer
?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Measurements show that the energy of a mixture of gaseous reactants decreases by 178. kJ during certain chemical reaction, which is carried out at a constant pressure. Furthermore, by carefully monitoring the volume change it is determined that -163. kJ of work is done on the mixture during the reaction. Calculate the change in enthalpy of the gas mixture during the reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic? kJ exothermic endothermic x10 Xarrow_forwardExplain the difference between heat capacity and specific heat of a substance. Heat capacity refers to the heat required to raise the temperature of a substance by 1 °C; specific heat refers to the heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 °C. Thus, heat capacity is an intensive property, and specific heat is an extensive one. Specific heat refers to the heat required to raise the temperature of a substance by 1 °C; heat capacity refers to the heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 °C. Thus, heat capacity is an intensive property, and specific heat is an extensive one. Heat capacity refers to the heat required to raise the temperature of a substance by 1 °C; specific heat refers to the heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 °C. Thus, heat capacity is an extensive property, and specific heat is an intensive one.arrow_forwardAn electrical heater is used to add 19.75 kJ of heat to a constant-volume calorimeter. The temperature of the calorimeter increases by 4.76°C. When 2.00 g of methanol (CH3OH) is burned in the same calorimeter, the temperature increases by 10.92°C. Calculate the molar heat of combustion for methanol (in kJ).arrow_forward
- Please don't provide handwritten solution ....arrow_forwardA 22.1g piece of aluminum (which has a molar capacity of 24.03 J/oC.mol) is heated to 82.4oC and dropped into a calorimeter containing water (specific heat capacity of water is 4.18J/goC) initially at 22.3oC. The final temperature of the water is 25.8oC. Ignoring significant figures, calculate the mass of the water in the calorimeter.arrow_forwardWhen 1.836 grams of sucrose (Molar mass 342.3 g/mol) is burned in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the calorimeter increases from 22.41°C to 26.63°C. If the heat capacity of the calorimeter is 4.900 kJ/°C, what is the heat of combustion of sucrose?arrow_forward
- calculate the heat (in J) of the reaction if 50.0 mL of HCl is added to 50.0 mL of NaOH in a coffee-cup calorimeter. The initial temperature for both solutions is 23.2oC. At the end of the reaction after the data is graphed, the final temperature is determined to be 38.5oC.arrow_forwardAt constant volume, the heat of combustion of a particular compound, compound A, is −3046.0 kJ/mol.−3046.0 kJ/mol. When 1.753 g1.753 g of compound A (molar mass =112.07 g/mol)=112.07 g/mol) is burned in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the calorimeter (including its contents) rose by 6.475 ∘C.6.475 ∘C. What is the heat capacity (calorimeter constant) of the calorimeter? Suppose a 3.771 g3.771 g sample of a second compound, compound B, is combusted in the same calorimeter, and the temperature rises from 25.65 ∘C25.65 ∘C to 29.76 ∘C.29.76 ∘C. What is the heat of combustion per gram of compound B?arrow_forwardWhen a 4.31 g sample of liquid octane (C8H18) is burned in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the calorimeter rises by 27.3 °C. The heat capacity of the calorimeter, measured in a separate experiment, is 6.2 kJ/•C. The calorimeter also contains 3.00 kg of water, specific heat capacity of 4.18 J/g°C. Determine the heat of combustion of octane in units of kJ/mol octane. Enter your answer numerically and in terms of kJ/mol.arrow_forward
- The sugar arabinose, C5 H10 O5, is burned completely in oxygen in a calorimeter. C5 H10 O5 (8) + 502(g) → 5CO2(g) + 5H2 O(1) Burning a 0.541 g sample caused the temperature to rise from 20.00°C to 20.54°C. The heat capacity of the calorimeter and its contents is 15.2 kJ/°C. Calculate AH for the combustion reaction per mole of arabinose. ΔΗ+ kJ/molarrow_forwardSolid calcium chloride dissolves in water according to the equation below.CaCl2 (s) ➝ Ca+2 (aq) + 2 Cl – (aq) ΔHº = –81.3 kJ/mol8.00 grams of solid CaCl2 dissolves in 45.0 grams of water initially at a temperature of 20.00 ºC in a perfect calorimeter. Calculate the final temperature of the solution in the calorimeter.[You may assume that no heat escapes the calorimeter and that all solutions have the same specific heat capacity as pure water (4.184 J/g·ºC)]Tfinal = Answer ºCarrow_forwardWhen a solid dissolves in water, heat may be evolved or absorbed. The heat of dissolution (dissolving) can be determined using a coffee cup calorimeter. In the laboratory a general chemistry student finds that when 0.79 g of KOH(s) are dissolved in 104.10 g of water, the temperature of the solution increases from 24.69 to 26.63 °C. The heat capacity of the calorimeter (sometimes referred to as the calorimeter constant) was determined in a separate experiment to be 1.58 J/°C. Based on the student's observation, calculate the enthalpy of dissolution of KOH(s) in kJ/mol. Assume the specific heat of the solution is equal to the specific heat of water. kJ/mol AH dissolution = BrookaCom Cengage Leaming Thermometer Cardboard or Styrofoam lid Nested Styrofoam cups Reaction occurs in solution.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY