
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
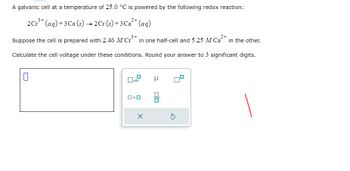
Transcribed Image Text:A galvanic cell at a temperature of 25.0 °C is powered by the following redox reaction:
2 Cr³+ (aq) + 3 Ca (s) → 2Cr (s) + 3 Ca²+ (aq)
Suppose the cell is prepared with 2.46 M Cr³+ in one half-cell and 5.25 M Ca²+ in the other.
Calculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.
0
0x10
X
μ
S
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A certain half-reaction has a standard reduction potential E=+0.21 V. An engineer proposes using this half-reaction at the anode of a galvanic cell that must provide at least 1.00 V of electrical power. The cell will operate under standard conditions. Note for advanced students: assume the engineer requires this half-reaction to happen at the anode of the cell. Is there a minimum standard reduction potential that the half-reaction used at the cathode of this cell can have? Data O yes, there is a minimum. E red = v If so, check the "yes" box and calculate the minimum. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. If there is no lower limit, check the "no" box. O no minimum Is there a maximum standard reduction potential that the half-reaction used at the cathode of this cell can have? O yes, there is naximum. Pred = Iv If so, check the "yes" box and calculate the maximum. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. If there is no upper limit, check the "no" box. no maximum By using the information…arrow_forwardWhen a lead acid car battery is recharged by the alternator, it acts essentially as an electrolytic cell in which solid lead(II) sulfate (PbSO4) is reduced to lead at the cathode and oxidized to solid lead(II) oxide (PbO) at the anode. Suppose a current of 75.0 A is fed into a car battery for 61.0 seconds. Calculate the mass of lead deposited on the cathode of the battery. Be sure your answer has a unit symbol and the correct number of significant digitsarrow_forwardWhen a lead acid car battery is recharged by the alternator, it acts essentially as an electrolytic cell in which solid lead(II) sulfate (PBSO4) is reduced to lead at the cathode and oxidized to solid lead(II) oxide (PbO) at the anode. Suppose a current of 46.0 A is fed into a car battery for 24.0 seconds. Calculate the mass of lead deposited on the cathode of the battery. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. Also, be sure your answer contains a unit symbol.arrow_forward
- Find the voltage of the cell if the right half-cell contains 0.330 M AgNO₃ (aq) and the left half-cell contains 0.115 M Cu(NO₃)₂ (aq). Express your answer to three significant figures.arrow_forwardHelp with the following question Round the answer to 3 sig figsarrow_forward|| Using the Nernst equation to calculate nonstandard cell voltage A galvanic cell at a temperature of 25.0 °C is powered by the following redox reaction: 0 2+ 2+ Cu (aq) + Zn (s) → Cu (s) + Zn²+ (aq) 2+ 2+ Suppose the cell is prepared with 1.39 M Cu in one half-cell and 2.14 M Zn in the other. Calculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. 0 x10 ロ・ロ X μarrow_forward
- A galvanic cell at a temperature of 25.0 °C is powered by the following redox reaction: 3Cu (aq) + 2A1 (s) 3Cu (s)+2A1* (aq) 2+ 3+ Suppose the cell is prepared with 2.15 M Cu“ in one half-cell and 7.31 M Al" in the other. Calculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. AL Rightsarrow_forwardthe Nernst equation to calculate nonstandard cell voltage A galvanic cell at a temperature of 25.0 °C is powered by the following redox reaction: 2+ 2+ Sn²+ (aq) + Ba(s) → Sn (s) + Ba²+ (aq) 2+ 2+ in one half-cell and 3.14 M Ba Suppose the cell is prepared with 2.84 M Sn Calculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. 0 ロ・ロ μ 00 09 Ś ? in the other.arrow_forward4. A galvanic cell consisting of a magnesium electrode and a standard hydrogen electrode is constructed. The cell generates a voltage, Ecell, of 2.099 V. The standard reduction potential for the two half-cell reactions are as follows: Mg²+ (aq) + 2e → Mg (s) 2H+ (aq) + 2e → H₂ (g) -2.38 V OV (i) Determine the standard cell potential, Eºcell. (ii) Assuming a Mg²+ (aq) concentration of 1 mol dm³ and a H₂ (g) pressure of 1 atm, calculate the theoretical pH of the cell. You may use concentrations/partial pressures in place of activities.arrow_forward
- Calculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forwardA galvanic cell at a temperature of 25.0 °C is powered by the following redox reaction: 2Cr³+ (aq) + 3 Ca(s) → 2Cr(s) + 3Ca²+ (aq) Suppose the cell is prepared with 6.35 M Cr³+ in one half-cell and 0.492 M Ca²+ in the other half. Calculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Cr³+ (aq) + 3e → Cr(s) Ca²+ (aq) + 2e →→ Ca(s) There are 6 galvanic cell. Er The standard cell potential (E°) for this galvanic cell is +2.124 red = -0.744 V Ered= -2.868 V volatage is 2.15 Under these conditions, the reaction quotient is moles of electrons transferred during to operate this V V. 0.00295 In order to increase the cell voltage for this cell ✔ [ Select ] V. and the cell It is impossible to change the voltage Not enough information Q>1 Q<1 3arrow_forwardA galvanic cell at a temperature of 25.0 °C is powered by the following redox reaction: 2+ 2103 (aq) +12H (aq)+5Co (s) → I2 (s)+6H₂O (1)+5Co²+ (aq) + Suppose the cell is prepared with 0.361 MIO3 and 7.57 M H in one half-cell and 2.53 M Co Calculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. ☐ μ ロ・ロ 2+ in the other.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY