
Concept explainers
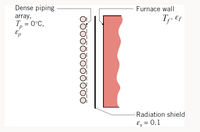
A furnace is located next to a dense array of cryogenic fluid piping. The ice-covered piping approximates a plane surface with an average temperature of Tp = 0°C and a total, hemispherical emissivity of εp = 0.56. That is, the piping can be replaced by a flat surface with the given properties. The furnace wall has a temperature of Tf = 247°C and a total, hemispherical emissivity of εf = 0.86. To minimize the heat loading on the regirgeration equipment and piping, a reflective aluminum radiation shield with a total, hemispherical emissivity of εs = 0.13 on each of its sides is installed between the pipiing and the furnace wall as shown. Assume that all surfaces are diffuse and gray and treat the problem as one-dimensional (surfaces form infinite parallel plates). What is the heat load on on the refrigeration unit? That is, what is the net radiative power at the surface which approximates the dense array of ice-cold piping, qrad,p in Watts?
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

- A one-dimensional plane wall is exposed to convective and radiative conditions at x = 0. The ambient and surrounding temperatures are T, = 20°C and Tsur = 40°C, respectively. The convection heat transfer coefficient is h = 20 W/m2-K, and the absorptivity of the exposed surface is a = 0.78. Determine the convective and radiative heat fluxes to the wall at x = 0, both in W/m2, if the wall surface temperature is T, = 29°C. Assume the exposed wall surface is gray, and the surroundings are large. qlony i W/m2 g" i W/m? dradarrow_forwardIt's a complete question. Need help asap.arrow_forwardAll information are given. Please need Correct answer!!!!arrow_forward
- A dryer is shaped like a long semicylindrical duct of diameter 1.5 m. The base of the dryer is occupied with water soaked materials to be dried, and maintained at a temperature of 370 K and emissivity of 0.5. The dome of the dryer is maintained at 1000 K with emissivity of 0.8. Determine the drying rate per unit length experienced by the wet materials.arrow_forwardTwo very large parallel plates are kept at uniform temperatures T1=800 K and T2=500 K, and have emissivities ε1=0.2 y ε2=0.7, respectively, as shown in the figure. Determine the net rate of radiation heat transfer between the two surfaces per unit surface area of the plates.arrow_forwardConsider two coaxial parallel circular disks of equal diameter D = 1 m spaced apart by 1 m, and two aligned parallel square plates (1 m * 1 m) are also spaced apart by 1 m. Determine the view factors F12 between the circular disks and the square plates. Which of the two geometries has the higher view factor value?arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





