
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
A force of magnitude Fx acting in the x-direction on a 1.30-kg particle varies in time as shown in the figure below. (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.)
(a) Find the impulse of the force. (Give your answer to one decimal place.)
kg · m/s =
(b) Find the final velocity of the particle if it is initially at rest.
m/s =
(c) Find the final velocity of the particle if it is initially moving along the x-axis with a velocity of −2.95 m/s.
m/s =
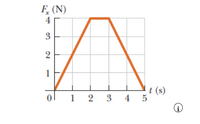
Transcribed Image Text:F, (N)
4
3
2
1
ol 1 2
t (s)
4 5
3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two objects collide head-on (see figure.below). The first object is moving with an initial speed of v1j = 7.93 m/s and the second object is moving with an initial speed of v2i = 10.00 m/s. Assuming the collision is elastic, m1 = 5.22 kg, and m2 = 6.29 kg, determine the final velocity of each object. (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer. Positive is to the right, and negative is %3D %3D %3D to the left. Due to the nature of this problem, do not use rounded intermediate values in your calculations-including answers submitted in WebAssign.) Vif = m/s %3D V2f = m/s V1 V2arrow_forwardA 12-kg hammer strikes a nail at a velocity of 7.6 m/s and comes to rest in a time interval of 8.9 ms. Part A What is the impulse given to the nail? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. FAt= Submit Part B F = Submit LOW Value ΜΑ Request Answer What is the average force acting on the nail? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. μĂ Value Request Answer Units Units P Pearson ? ? Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education Inc. All rights reserved. | Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Permissions | Contact Us |arrow_forwardWhen there is motion is both directions, state which direction is positive at the START of the problem. For the impulse-momentum and the conservation of momentum problems: Plug your GIVEN VALUES into the equation FIRST then do the algebra. Use the following equations: F t = m vf -m vi m1 vi1 + m2 vi2 = m1 vf1 + m2 vf2 m1 vi1 + m2 vi2 = (m1 + m2) vf (m1 + m2) Vi = m1 vf1 + m2 vf2 4. ) Tom is standing on a 32.2 pound sled sliding across a frozen lake at 1.50 ft/s. Tom weighs 128.8 pounds. He jumps off the sled in the opposite direction at 0.50 ft/s. a. ) what is the velocity of the sled after Tom jumps off? Show all unity conversion step by step - if any.arrow_forward
- A 41.0-kg child steps off a 3.2-ft-high diving board and executes a cannonball jump into a pool. (The child holds her body in a tight ball so that air resistance is negligible as she falls downward.) What is the impulse exerted by the water on the child? (Assume up is positive. Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.)arrow_forwardThe x-component of a force on a 15-g golf ball by a golf club versus time is plotted in the attached figure. a. Find the x-component of the impulse, in newton-seconds, during the following interval: [50 msec, 100 msec] b. Find the change in the x-component of the momentum, in kilogram meters per second, during the following interval: [50 msec, 100 msec]arrow_forwardYou drop a 15-g ball from a height of 1.5 m and it only bounces back to a height of 0.85 m. What was the total impulse on the ball when it hit the floor? (Ignore air resistance.) Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. Enter positive value if the impulse is upward and negative value if the impulse is downward. F-Δt=__________arrow_forward
- Now consider the interactions between the two objects that undergo a collision. Apply the Impulse-Momentum Theorem to explain the changes in the momentum of the individual objects and that of the entire system. Use appropriate physics terminology in your discussion. As a matter of semantics, we say that a force is exerted on an object by another object; an impulse is imparted to an object by another object; an object or system can have, gain, or lose momentum; momentum is transferred from one object or system to another object or system.arrow_forwardWhen there is motion is both directions, state which direction is positive at the START of the problem. For the impulse-momentum and the conservation of momentum problems: Plug your GIVEN VALUES into the equation FIRST then do the algebra. Use the following equations: F t = m vf -m vi m1 vi1 + m2 vi2 = m1 vf1 + m2 vf2 m1 vi1 + m2 vi2 = (m1 + m2) vf (m1 + m2) Vi = m1 vf1 + m2 vf2 3.) A 0.196 N bullet strikes a 10.00 kg block of wood, which is initally at rest. The bullet becomes lodged in the block of wood and afterwards both are traveling at 1.25 m/s. a. ) what was the velocity of the bullet before striking the block of wood?arrow_forward(Please include diagram or drawing) Two clay meteors, each with a mass m, collide in outer space and stick together. This collision occurs at a distance D from the center of the Earth. Following the collision, the combined meteors move towards the Earth. Before the collision: Meteor 1 has a velocity v1. Meteor 2 has a velocity v2. The velocities V1 and v2 are at right angles to each other. a) Calculate the fraction of kinetic energy lost during the collision of the two meteors. b) Determine the velocity of the stuck-together meteors just before they crash into the Earth assuming you know the mass and radius of earth. Air resistance can be neglected.arrow_forward
- A 0.055-kg egg falls off a table that is 1.2 m high and lands on a tile floor. Part A What is the impulse delivered to the egg by the floor? Assume that the positive direction is upward. Express your answer with the appropriate units. Part B The egg lands on its side, and at the instant of impact the part of the shell farthest from the floor is 40 mm above the floor. The collision continues until the center of mass is on the floor. Estimate the time interval over which the collision lasts, assuming that the speed of the center of mass of the egg drops to zero linearly in time. Express your answer with the appropriate units. Part C What is the average force exerted by the floor on the egg? Assume that the positive direction is upward. Express your answer with the appropriate units. Part D If the floor were carpeted, the collision time interval might be extended by as much as a factor of four as the carpet "gives" under the egg. What would the average force…arrow_forwardThe diagram shows the momentum vectors of two balls after they collide at the origin. Similar to experiment 8, only one ball was initially moving. Determine the magnitude of its initial momentum if the smallest square is 0.2 kg m/s. Format of answer: #.##. 7arrow_forwardTwo objects collide head-on (see figure below). The first object is moving with an initial speed of v1i = 7.94 m/s and the second object is moving with an initial speed of v2i = 10.00 m/s. Assuming the collision is elastic, m1 = 5.17 kg, and m2 = 6.29 kg, determine the final velocity of each object. (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer. Positive is to the right, and negative is to the left. Due to the nature of this problem, do not use rounded intermediate values in your calculations—including answers submitted in WebAssign.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON