
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
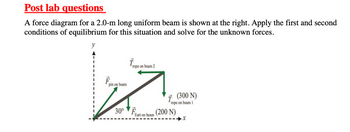
Transcribed Image Text:Post lab questions
A force diagram for a 2.0-m long uniform beam is shown at the right. Apply the first and second
conditions of equilibrium for this situation and solve for the unknown forces.
y
F.
pin on beam
rope on beam 2
T
(300 N)
rope on beam 1
30° Fart on beam (200 N)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- . The diagram below shows a rod of length 10m placed horizontally and supported from one end. Three forces, F1, F2, and F3 are acting on it separately. Calculate the torque due to a) F1 b) F2 c) F3, if it makes an angle of 30 degrees with the rod. (3mks) (2mks) (2mks) F2 = 20N| %3D F = 10N sm F = 30N 4m 6m 8marrow_forwardPlease answer the question in the picture below. Thank you so much for your help!!arrow_forwardA 2.00 m long horizontal uniform beam of mass 20.0 kg is supported by a wire as shown in the figure. The wire makes an angle of 20.0 degrees with the beam. Attached to the beam 1.40 m from the wall is a ball with a mass of 40 kg. What is the tension in the string? a)1,000 Nb) 1,090 N c) 2,100 N d) 2,250 N e) 2,680 Narrow_forward
- The uniform seesaw shown below is balanced on a fulcrum located d1 = 3.5m from the left end. The bigger boy on the left end has a mass m1 =75 kg. The smaller boy on the right end has a mass of m2 = 55 kg and is a distance d2 = 4.5 m from the fulcrum. The mass of the board is mb. Draw all forces acting on the seesaw board showing their directions and locations. Where would you draw the weight of the board? Identify and show the direction of rotations caused by the torques provided by all forces about the fulcrum. If the seesaw is in static equilibrium, write down the two conditions of static equilibrium symbolically using the forces and distances in the figure. Solve for the mass of the board. Calculate the force of fulcrum on the board.arrow_forwardA uniform beam of length L = 7.10 m and weight 4.05 × 10² N is carried by two workers, Sam and Joe, as shown in the figure below. Determine the force that each person exerts on the beam. Sam Joe F F Sam II = -1.00 m N N Z Z -2.00 m- Larrow_forwardThe wow expert Hand written solution is not allowed.arrow_forward
- A 12 000-N shark is supported by a rope attached to a 4.60-m rod that can pivot at the base. (a) Calculate the tension in the cable between the rod and the wall, assuming the cable is holding the system in the position shown in the figure. (Give you answer to three significant digits.) b) Find the horizontal force exerted on the base of the rod magnitude ------- N c) Find the vertical force exerted on the base of the rod. Ignore the weight of the rod. magnitude ------ Narrow_forwardProblem As shown below, a horizontal beam is in equilibrium. The orange circle represents the hinge and the 5 m long cable has a tension of 594 N. 3 m 5 m 4 m 2 162 N CEFFER C Bw #3 Determine the weight of the beam as well as the magnitude & direction of the force that the hinge exerts on the beam. beam weight = hinge force magnitude = hinge force direction = $ 4 21 % 5 o relative to the horizontal. LION MacBook Pro 6 & 7 *0 o th tvarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON