
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Make the decision for the hypothesis test.
Reject null hypothesis
Fail to reject null hypothesis
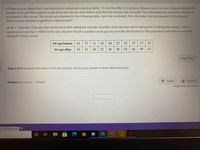
Transcribed Image Text:A fitness course claims that it can improve an individual's physical ability. To test the effect of a physical fitness course on one's physical ability, the
number of sit-ups that a person could do in one minute, both before and after the course, was recorded. Ten individuals are randomly selected to
participate in the course. The results are displayed in the following table. Can it be concluded, from the data, that participation in the physical
fitness course resulted in significant improvement?
Let d = (number of sit-ups that can be done after taking the course)-(number of sit-ups that can be done prior to taking the course) . Use a
significance level of a = 0.01 for the test. Assume that the numbers of sit-ups are normally distributed for the population both before and after
taking the fitness course.
Sit-ups before
43
37
31
42
30
25
52
35
33
41
Sit-ups after
54
51
39
52
39
30
54
46
49
43
Copy Data
Step 3 of 5: Compute the value of the test statistic. Round your answer to three decimal places.
Answer(How to Enter) 2 Points
画 Tables
国 Keypad
Keyboard Shortcuts
est/TestTakeTest#! Ing
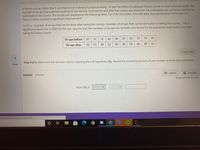
Transcribed Image Text:A fitness course claims that it can improve an individual's physical ability. To test the effect of a physical fitness course on one's physical ability, the
number of sit-ups that a person could do in one minute, both before and after the course, was recorded. Ten individuals are randomly selected to
participate in the course. The results are displayed in the following table. Can it be concluded, from the data, that participation in the physical
fitness course resulted in significant improvement?
Let d = (number of sit-ups that can be done after taking the course)-(number of sit-ups that can be done prior to taking the course). Use a
significance level of a = 0.01 for the test. Assume that the numbers of sit-ups are normally distributed for the population both before and after
taking the fitness course.
Sit-ups before
43
37
31
42
30
25
52
35
33
41
Sit-ups after
54
51
39
52
39
30
54
46
49
43
Copy Data
Step 4 of 5: Determine the decision rule for rejecting the null hypothesis Ho. Round the numerical portion of your answer to three decimal places.
Prev
国 Tables
国 Keypad
Answer 2 Points
Keyboard Shortcuts
Reject Ho if
ning.com/Portal/Test/TestTake Test#!
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Determine whether to reject H (Choose one) v the null hypothesis H. Reject Do not rejectarrow_forwardprovide an example of hypothesis testing using the t score testarrow_forwardWhen conducting a hypothesis test, we hope to avoid commiting a type 1 error, which is: 1. Not as bad as committing a type 2 error 2. rejecting a null hypothesis when it is true 3. rejecting the alternate hypothesis when it is true 4. accepting the null hypothesis when the alternate hypothesis is truearrow_forward
- If we reject the Null Hypothesis then the Test Statistic is outside the Critical Region and the Test Statistic is not significant the Test Statistic is inside the Critical Region and is the Test Statistic is significant the Test Statistic is inside the Critical Region and is the Test Statistic is not significant the Test Statistic is outside the Critical Region and is the Test Statistic is significantarrow_forwardWhen a hypothesis test is being carried out, there are four different situations that can occur depending on the truthfulness of the null hypothesis. Type I error occurs when the following situation happen The null hypothesis is false, but we mistakenly fail to reject it. The null hypothesis is true, but we mistakenly reject it. The null hypothesis is false, and we reject it. The null hypothesis is true, and we fail to reject it.arrow_forward1 - find the p-value 2 - reject or fail to reject null hypothesis?arrow_forward
- When a result is not extreme enough to reject the null hypothesis, explain why it is wrong to conclude that your result supports the null hypothesis.arrow_forward1- Type II error occurs when a false null hypothesis is not rejected Select one: True Falsearrow_forwardProvide an appropriate response. If we fail to reject the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is false, then we have made a Type B error Type I error Correct decision Type II errorarrow_forward
- In a hypothesis test, a Type II error occurs when: a false null hypothesis is rejected O a true null hypothesis is not rejected O a false null hypothesis is not rejected O a true null hypothesis is rejectedarrow_forwardIf we do not reject the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is in false, then we have made aarrow_forwardWhich statement describes a Type II Error? Fail to reject the null hypothesis H0, when H0 is actually true Reject the null hypothesis H0, when H0 is actually true Fail to reject the null hypothesis H0, when H0H0 is false Reject the null hypothesis H0, when H0 is actually falsearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman