
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
(a) Find the conditional input demand function for inputs 1 and 2, as well as the cost function for this firm.
(b) What is the firm's marginal cost when it is producing y units of output?
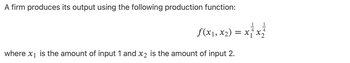
Transcribed Image Text:A firm produces its output using the following production function:
f(x₁, x₂) = x₁ x ₂
= x ²₁ x ²1/
where x₁ is the amount of input 1 and x₂ is the amount of input 2.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Assume a firm's short-run cost function is given by the following expression: C(q) = 2+q+q2 If the firm can sell each unit of their output at a price of p=9 dollars, what is the maximum profit the firm can earn in the short-run? a.) Maximum Profit = ? dollarsarrow_forwardIf the average cost function of a good is 15 AC = +20 + 11 '이 find the fixed costs and an expression for the marginal cost function. The fixed costs are (Type a whole number.) The expression for the marginal cost function is (Simplify your answer. Type an expression using Q as the variable.)arrow_forwarddefine total fixed costsarrow_forward
- Suppose a firm has the following production function Q = f(K,L) = (1/2)L(2/3)K(1/3) and a total cost function TC = wL + rK The rental cost of capital is 2 euros per hour and the labor wage is 4 euros per hour. Suppose also that in the short-run, the firm uses 8 machines in the production process. (a) Show that the firm’s short-run average cost (SRAC) is SRACK=8 = (16/Q)+ 4√? (b) Draw the SRAC curve(c) By solving the first order conditions that the global minimum of production is 4(d) Show that the firm’s long-run average cost (LRAC) is 12. Hint: Start by obtaining the firm’s long-run expansion path(e) Draw both the SRAC and the LRAC and explain why the SRAC is always equal or above the LRAC.arrow_forward14. The research department of Acme, Inc. has determined the marginal cost function for one particular item to be m(x) = 0.12e0.04x dollars per item, where x is the number of items produced. If Acme's fixed costs amount to $3,000, find the cost function, C(x), for the company.arrow_forwardSuppose a firm’s cost function is given by: C= 50 + 4q2 a) Find the equations for AFC, AVC and MC. b) If w=$4, what’s the short run production function for this firm?arrow_forward
- When a firm produces one unit, the variable cost is $3. When the firm produces two units, the variable cost is $6. What is the marginal cost associated with two units of production.arrow_forwardCraig and Javad run a paper company. Each week they need to produce 1,000 reams of paper to ship to their customers. The paper plant's longrun production function is Q = 4KL, where Q is the number of reams produced, K is the quantity of capital rented, and L is the quantity of labor hired. The weekly cost function for the paper plant is C = 20K + 4L, where C is the total weekly cost. (a) What ratio of capital to labor minimizes Craig and Javad's total costs? (b) How much capital and labor will Craig and Javad need to rent and hire in order to produce 1,000 reams of paper each week? (c) How much will hiring these inputs cost them?arrow_forwardA5arrow_forward
- K A cereal factory has weekly fixed costs of $22,000. It costs $1.26 to produce each box of cereal. A box of cereal sells for $4.06. Find the rule of the cost function c(x) that gives the total weekly cost of producing x boxes of cereal. OA. c(x)=1.26x OB. c(x)=22,000+ 1.26x OC. c(x)=22,000 +4.06x OD. c(x)=22,000+ 2.8xarrow_forwardA farm produces rice, which is sold in 50 kilogram bags. Let Q denote the number of bagsproduced per week during harvest time. Costs C are denoted in units of dollars. The totalweekly cost function for producing the product is C = 4Q + 100. The total weekly income function for this product is I = 50Q – 2Q2. What is the profit function P as a function of Q and sketch it using P values 0, 5, 10,15, 20 and 25.arrow_forward1. Suppose the total-cost function for a firm is given by C = qw 1/4 3/4 a. Use Shephard's lemma to compute the (constant output) demand functions for each input, k and 1. b. Calculate the average cost and marginal cost. c. Describe the returns to scale for the underlying production function for q.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education