
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
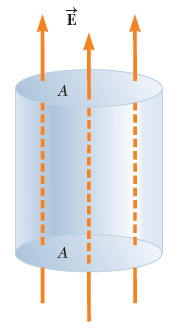
A figure shows a closed cylinder with a cross-sectional area A = 3.60 m2.
The upper and lower circular surfaces of a vertically-oriented cylinder are labeled A. Electric field vector Epoints vertically upward, going up through the lower surface, up through the cylinder, and finally pointing up through the upper surface.The constant electric field has magnitude 2.85 ✕ 103 N/C and is directed vertically upward, perpendicular to the cylinder's top and bottom surfaces so that no field lines pass through the curved surface. Calculate the electric flux (in (N · m2)/C) through the cylinder's top and bottom surfaces.
(a)top surface
__________
| N · m2 |
| C |
(b)bottom surface
_______ NM^2/C
(c)Determine the amount of charge (in C) inside the cylinder.
_______C
Transcribed Image Text:A
A
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A proton is fired horizontally into a 1.0 × 105 N/C vertical electric field. It rises 1.0 cm vertically after having traveled 5.0 cm horizontally. What was the proton's initial speed?arrow_forwardAll or nonearrow_forwardA disk of radius 3.3 cm has a surface charge density of 5.1 µC/m2 on its upper face. What is the magnitude of the electric field produced by the disk at a point on its central axis at distance z = 13 cm from the disk?arrow_forward
- A square metal plate of edge length 9.6 cm and negligible thickness has a total charge of 5.9 × 10-6 C. (a) Estimate the magnitude E of the electric field just off the center of the plate (at, say, a distance of 0.66 mm from the center) by assuming that the charge is spread uniformly over the two faces of the plate. (b) Estimate E at a distance of 23 m (large relative to the plate size) by assuming that the plate is a charged particle. (a) Number i Units (b) Number i Unitsarrow_forwardIn the figure a nonconducting rod of length L = 8.26 cm has charge -q = -4.55 fC uniformly distributed along its length. (a) What is the linear charge density of the rod? What are the (b) magnitude and (c) direction (positive angle relative to the positive direction of the x axis) of the electric field produced at point P, at distance a = 14.1 cm from the rod? What is the electric field magnitude produced at distance a = 77 m by (d) the rod and (e) a particle of charge -q = -4.55 fC that replaces the rod?arrow_forwardIn a CRT, after the electrons pass through the anode, they are moving in the z-direction at a speed of 8.40 x 10° m/s. They then pass between a pair of vertical parallel plates (A) and then between a pair of horizontal parallel plates (B). All four of these plates are squares 2.50 cm on a side. The plates of each pair are separated by 1.50 cm.The electric field between plates (A) is zero. As the beam exits the space between plates (B), it has been deflected 2.00 mm downward (Ay = -2.00 mm). In what direction is the beam moving now? Enter a positive value if the angle is below the horizontal and enter a negative value if the angle is above the horizontal. (A) Plates for horizontal deflection Electron gun (B) Plates for vertical deflection Heated filament - (source of electrons) Cathode (-) Anode (+) + Uniform E field seen from side + Electron beam Cathode - Conductive coating - Fluorescent screenarrow_forward
- What is the horizontal component of the electric field at location L?arrow_forwardA 96 cm diameter loop is rotated in a uniform electric field until the position of maximum electric flux is found. The flux in this position is measured to be 3.1 x 10° N m/C. What is the electric field strength? Answer in units of N/C.arrow_forwardA square metal plate of edge length 9.4 cm and negligible thickness has a total charge of 5.6 × 10-6 C. (a) Estimate the magnitude E of the electric field just off the center of the plate (at, say, a distance of 0.44 mm from the center) by assuming that the charge is spread uniformly over the two faces of the plate. (b) Estimate E at a distance of 39 m (large relative to the plate size) by assuming that the plate is a charged particle.arrow_forward
- A uniform electric field of magnitude E = 38 N/C points along the x-axis. A circular loop of radius R = 26 cm is centered at the origin with the normal to the loop pointing θ = 45 degrees above the x-axis. Calculate the electric flux in units of N⋅m2/C that passes through the loop.arrow_forwardFor each contour map in the figure estimate the e electric fields at points 1 and 2. Don't forget that E is a vector quantity. (а) 0 V 10 V 20 V 30 V 40 V 0 m 1 m 2 m 3 m 4 m (b) 0 V 10 V 20 V 30 V 40 V 0 m 1 m 2 m 3 m 4 marrow_forwardA positive particle traveling upwards with initial speed vo = 10°m/s enters a region of uniform electric field pointing rightward. Part A 10 cm and horizontal distance d 4.5cm from the particle's initial location. The particle has What electric field magnitude is needed to direct the particle through the small hole that is located a vertical distance h 10 14kg and charge q 10 °C. Gravity is negligible. Answer to 3 significant figures. mass m N/Carrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON