
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
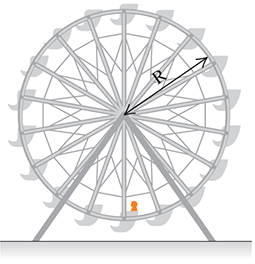
A Ferris wheel with radius R = 15.0 m is turning about a horizontal axis through its center in the figure. The linear speed of a passenger on the rim is constant and equal to 7.40 m/s.
a. What is the magnitude of the passenger's acceleration as she passes through the lowest point in her circular motion?
b. What is the direction of the passenger's acceleration as she passes through the lowest point in her circular motion?
c.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You are traveling to the North-East at 50 m/s. Simultaneously you are being pushed towards the East at a speed of 10 m/s. a. If you proceed in this manner for 10 minutes, what is the displacement vector from the t=0 location? b. How far do you travel in the East direction during these 10 mins.?arrow_forwardA car travels at a constant speed around a circular track whose radius is 3.82 km. The car goes once around the track in 246 s. What is the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration of the car? Number i Unitsarrow_forwardI understand to find the centripetal acceleration = v^2/r, but how do you figure that out when nothing is listed?arrow_forward
- Q 5 pleasearrow_forwardE. The centripetal acceleration of a particle moving in a circle is given by the formula a = s²/r where r is the radius and s is the speed of the particle. a) Consider a as a function of s and r. Compute the differential of a. b) Suppose that the particle is moving with speed 50cm/sec and the radius is 10cm. Use the differential to estimate the change in centripetal acceleration if the radius is changed to 9.80cm and the speed is changed to 51cm/sec. (Answ: 15) c) Suppose that the speed can be measured to within +3% and the radius can be measured to within +2%. Use the differential to approximate the maximum percent error in a. (Hint: The percent error in a quantity is the error in the quantity (da) divided by the quantity (a).) (Ans: 8%)arrow_forwardAn object is moving counterclockwise around a circular track at a constant speed of 3 m/s. The track is centered at the origin and has a radius of 1 m. What is the object's acceleration vector when it is at point P shown? y. P -(3플)i ○금3 + (3프) i a = +(9) i m Oa = 0 -(9플)iarrow_forward
- You re out in space, on a rotating wheel-shaped space station of radius 679 m. You feel planted firmly on the floor , due to artificial gravity. The gravity you experience is Earth-normal, that is, g = 9.81 m/s^2. How fast is the space station rotating in order to produce this much artificial gravity? Express your answer in revolutions per minute (rpm). 0.120 rpm 81.6 rpm 0.459 rpm 1.148 rpmarrow_forwardIn the movie Kill Bill the character Gogo Yubari fights with a meteor hammer, which is a bladed metal sphere on the end of a chain. Let’s assume Gogo is spinning the meteor hammer in a vertical spin, as shown below, with a radius of motion as 1 m. She spins the weapon at 18 m/s. Gogo then lets out more chain, increasing the radius to 1.62 m. What is the new velocity of her weapon?arrow_forwardQ 3 pleasearrow_forward
- V01arrow_forwardAt takeoff, a commercial jet has a speed of 68 m/s. Its tires have a diameter of 0.88 m. a. At how many rev/min are the tires rotating? b. What is the centripetal acceleration at the edge of the tire in m/s2 c. With what force must a deterimned 1.15 * 10-15 kg bacetrium cling to the rim in N? d. Take the ratio of this force to the bacterium's weightarrow_forwardA small object of mass 0.500 kg is attached by a 0 0.650 m-long cord to a pin set into the surface of a frictionless tabletop. The object moves in a circle on the horizontal surface with a speed of 6.91 m/s.1. What is the magnitude of the radial acceleration of the object?2. What is the tension of the cord?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON