
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
The interaction questions please (The last 3)
![**Factorial Experiment Analysis**
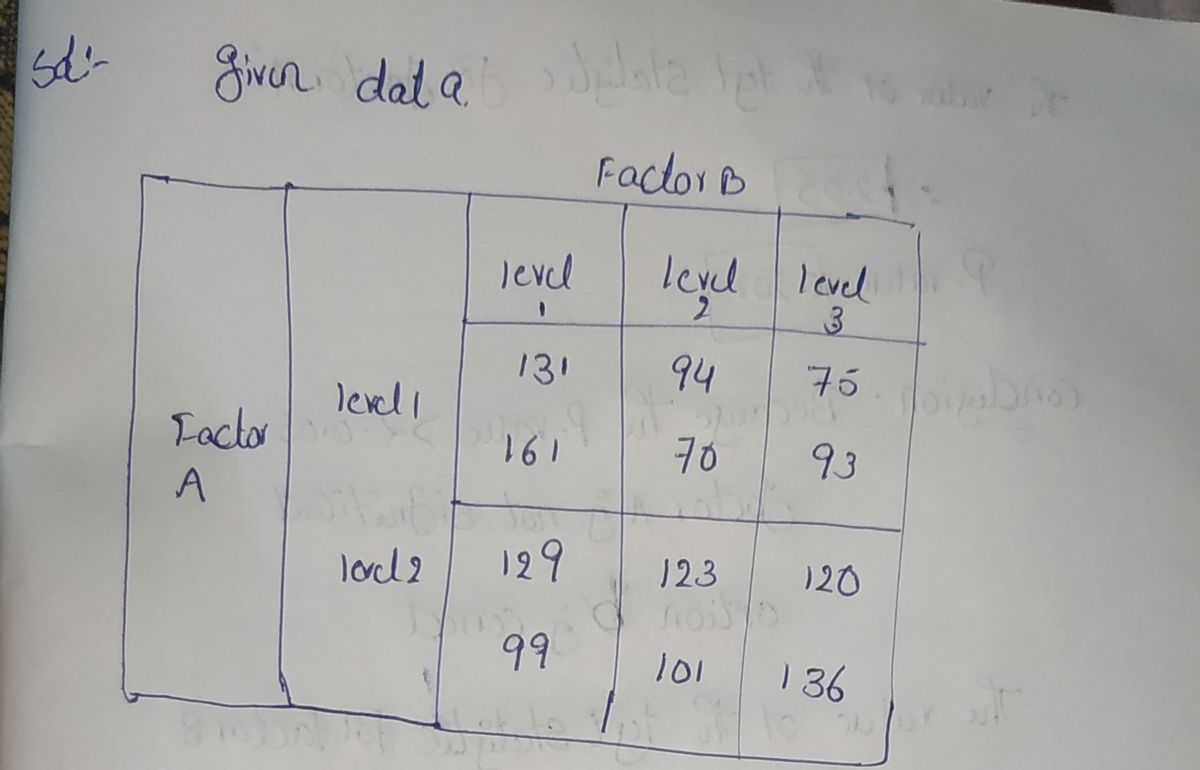
A factorial experiment involving two levels of Factor A and three levels of Factor B resulted in the following data:
| | Factor B |
|-------------|-----------------|
| | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 |
| **Factor A** | | | |
| Level 1 | 131 | 94 | 75 |
| | 161 | 70 | 93 |
| Level 2 | 129 | 123 | 120 |
| | 99 | 101 | 136 |
**Instructions:**
Conduct a test for any significant main effects and any interaction, using α = 0.05.
1. **Calculate the Test Statistic for Factor A:**
- Round your answer to two decimal places and enter it in the space provided.
- [Input box]
2. **Calculate the p-value for Factor A:**
- Round your answer to three decimal places and enter it in the space provided.
- \( p\text{-value} = \) [Input box]
3. **State Your Conclusion About Factor A:**
Choose the correct conclusion based on the calculated p-value:
- ☐ Because the \( p\text{-value} > \alpha = 0.05 \), Factor A is significant.
- ☐ Because the \( p\text{-value} > \alpha = 0.05 \), Factor A is not significant.
- ☐ Because the \( p\text{-value} \leq \alpha = 0.05 \), Factor A is not significant.
- ☐ Because the \( p\text{-value} \leq \alpha = 0.05 \), Factor A is significant.
4. **Calculate the Test Statistic for Factor B:**
- Round your answer to two decimal places and enter it in the space provided.
- [Input box]
5. **Calculate the p-value for Factor B:**
- Round your answer to three decimal places and enter it in the space provided.
- \( p\text{-value} = \) [Input box]
**Graph/Diagram Explanation:**
The table above represents the mean values obtained from a factorial experiment with two factors, A and B, each with different levels. Factor A has two levels, and Factor B has](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/8ad87420-52d2-4e34-815e-eb9bcb5c95c0/095908fa-1010-4f0e-b853-939580284db7/xvhf27g_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:**Factorial Experiment Analysis**
A factorial experiment involving two levels of Factor A and three levels of Factor B resulted in the following data:
| | Factor B |
|-------------|-----------------|
| | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 |
| **Factor A** | | | |
| Level 1 | 131 | 94 | 75 |
| | 161 | 70 | 93 |
| Level 2 | 129 | 123 | 120 |
| | 99 | 101 | 136 |
**Instructions:**
Conduct a test for any significant main effects and any interaction, using α = 0.05.
1. **Calculate the Test Statistic for Factor A:**
- Round your answer to two decimal places and enter it in the space provided.
- [Input box]
2. **Calculate the p-value for Factor A:**
- Round your answer to three decimal places and enter it in the space provided.
- \( p\text{-value} = \) [Input box]
3. **State Your Conclusion About Factor A:**
Choose the correct conclusion based on the calculated p-value:
- ☐ Because the \( p\text{-value} > \alpha = 0.05 \), Factor A is significant.
- ☐ Because the \( p\text{-value} > \alpha = 0.05 \), Factor A is not significant.
- ☐ Because the \( p\text{-value} \leq \alpha = 0.05 \), Factor A is not significant.
- ☐ Because the \( p\text{-value} \leq \alpha = 0.05 \), Factor A is significant.
4. **Calculate the Test Statistic for Factor B:**
- Round your answer to two decimal places and enter it in the space provided.
- [Input box]
5. **Calculate the p-value for Factor B:**
- Round your answer to three decimal places and enter it in the space provided.
- \( p\text{-value} = \) [Input box]
**Graph/Diagram Explanation:**
The table above represents the mean values obtained from a factorial experiment with two factors, A and B, each with different levels. Factor A has two levels, and Factor B has
![### Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) for Factors
#### Factor B Analysis
1. **Find the value of the test statistic for factor B.**
- Instruction: Round your answer to two decimal places.
2. **Find the \( p \)-value for factor B.**
- Instruction: Round your answer to three decimal places.
- \( p \)-value = [Input Field]
3. **State your conclusion about factor B.**
- Options:
- ○ Because the \( p \)-value \( \leq \alpha = 0.05\), factor B is not significant.
- ○ Because the \( p \)-value \( > \alpha = 0.05\), factor B is not significant.
- ○ Because the \( p \)-value \( > \alpha = 0.05\), factor B is significant.
- ○ Because the \( p \)-value \( \leq \alpha = 0.05\), factor B is significant.
#### Interaction Between Factors A and B
4. **Find the value of the test statistic for the interaction between factors A and B.**
- Instruction: Round your answer to two decimal places.
5. **Find the \( p \)-value for the interaction between factors A and B.**
- Instruction: Round your answer to three decimal places.
- \( p \)-value = [Input Field]
6. **State your conclusion about the interaction between factors A and B.**
- Options:
- ○ Because the \( p \)-value \( \leq \alpha = 0.05\), the interaction between factors A and B is significant.
- ○ Because the \( p \)-value \( > \alpha = 0.05\), the interaction between factors A and B is not significant.
- ○ Because the \( p \)-value \( > \alpha = 0.05\), the interaction between factors A and B is significant.
- ○ Because the \( p \)-value \( \leq \alpha = 0.05\), the interaction between factors A and B is not significant.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/8ad87420-52d2-4e34-815e-eb9bcb5c95c0/095908fa-1010-4f0e-b853-939580284db7/y9nv33i_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:### Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) for Factors
#### Factor B Analysis
1. **Find the value of the test statistic for factor B.**
- Instruction: Round your answer to two decimal places.
2. **Find the \( p \)-value for factor B.**
- Instruction: Round your answer to three decimal places.
- \( p \)-value = [Input Field]
3. **State your conclusion about factor B.**
- Options:
- ○ Because the \( p \)-value \( \leq \alpha = 0.05\), factor B is not significant.
- ○ Because the \( p \)-value \( > \alpha = 0.05\), factor B is not significant.
- ○ Because the \( p \)-value \( > \alpha = 0.05\), factor B is significant.
- ○ Because the \( p \)-value \( \leq \alpha = 0.05\), factor B is significant.
#### Interaction Between Factors A and B
4. **Find the value of the test statistic for the interaction between factors A and B.**
- Instruction: Round your answer to two decimal places.
5. **Find the \( p \)-value for the interaction between factors A and B.**
- Instruction: Round your answer to three decimal places.
- \( p \)-value = [Input Field]
6. **State your conclusion about the interaction between factors A and B.**
- Options:
- ○ Because the \( p \)-value \( \leq \alpha = 0.05\), the interaction between factors A and B is significant.
- ○ Because the \( p \)-value \( > \alpha = 0.05\), the interaction between factors A and B is not significant.
- ○ Because the \( p \)-value \( > \alpha = 0.05\), the interaction between factors A and B is significant.
- ○ Because the \( p \)-value \( \leq \alpha = 0.05\), the interaction between factors A and B is not significant.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman