
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
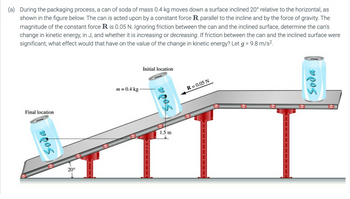
Transcribed Image Text:(a) During the packaging process, a can of soda of mass 0.4 kg moves down a surface inclined 20° relative to the horizontal, as
shown in the figure below. The can is acted upon by a constant force R. parallel to the incline and by the force of gravity. The
magnitude of the constant force R is 0.05 N. Ignoring friction between the can and the inclined surface, determine the can's
change in kinetic energy, in J, and whether it is increasing or decreasing. If friction between the can and the inclined surface were
significant, what effect would that have on the value of the change in kinetic energy? Let g = 9.8 m/s²
Final location
Soda
20°
m=0.4 kg-
1.5 m
↓
Initial location
Soda
R = 0.05 N
Soda
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A 100 kg crate slides down a ramp, starting from rest. The ramp is inclined at an angle of 21.9 degrees with respect to the horizontal and has a height of 1.37 m. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the ramp is us = 0.30. What is the work done on the crate (in Joules) by the normal force?arrow_forwardQ.6.B. Four g of air is contained in the cylinder. The air is heated until the piston raises 30 mm. The spring just touches the piston initially. Calculate (a) the temperature when the piston leaves the stops and (b) the work done by the air on the piston. 400 kN/m Frictionjess piston 300 kg Air 150 mm 200 mm ITarrow_forwardA 0.5 lbm apple is thrown from the edge of a tall building with an initial speed of 20 m/s. What is the change in kinetic energy of the apple in lbf-ft if it strikes the ground at 9840 ft/min? complete solution.arrow_forward
- B/ Water in a rigid, insulating tank is set in rotation and left. Water comes to rest after some time due to viscous forces. Considering the tank and water to constitute the system answer yes or no. (i) Is any work done during the process of water coming to rest? (ii) Is there a flow of heat? (iii) Is there any change in internal energy (U)? (iv) Is there any change in total energy (E)?arrow_forwardDetermine the work of the force when it displaces 2 m in each of the situation below: k = 10 N/m 2 m/s - 2 m Spring is originally compressed 3 m. 30 (a) (b)arrow_forwardNow suppose, instead of being lifted straight up, the (100 Kg) rock is elevated to 10 meters by rolling it up a ramp. If the rock is released and allowed to roll down the ramp, what will its kinetic energy be at the bottom of the ramp?arrow_forward
- To get up on the roof, a person (mass 66.7 kg) places an aluminum ladder (mass 9.30 kg) against the house on a concrete pad with the base of the ladder 2.27 m from the house. The ladder rests on a plastic rain gutter, which we can assume to be frictionless. The gutter is 6.96 m from the bottom of the ladder. The center of mass of the ladder is 2.32 m from the bottom. The person is standing 3.32 m from the bottom of the ladder. What are the magnitudes of the forces on the ladder at the top and bottom? At bottom of ladder: normal force = 775 friction force = 106 o N Magnitude of force on bottom of ladder = 782 x N At top of ladder, normal force = 106 X Narrow_forwardAn automobile with a linear momentum of 3.0 x 104 kg.m/s is brought to a stop in 5.0 s. What is the magnitude of the average braking force?arrow_forwardA body of mass 10 kg is initially stationary on a 45 degree inclined plane , coefficient of friction is 0.5. The body slides down the plate and attains a velocity of 20 m/s. Find out distance travel by the body along the plane.arrow_forward
- Consider the mass-on-a-spring system as shown in the figure below. The spring has a spring constant of 1.86e+3 N/m, and the block has a mass of 1.39 kg. There is a constant force of kinetic friction between the mass and the floor of 4.71 N. Starting with the spring compressed by 0.117 m from its equilibrium position, how far will the block travel once it leaves the spring? (Assume that block leaves the spring at the spring's equilibrium position, marked x=0 in the figure. Give your answer as the distance from the equilibrium position to the final position of the block.) Hint: How much work must friction do in order to bring the mass to a stop? How much distance is required for friction to do this work? Enter answer here www.m X = 0 Please enter a numerical answer below. Accepted formats are numbers or "e" based scientific notation e.g. 0.23, -2, 1e6, 5.23e-8 Image size: S M L Max marrow_forwardI need help pleasearrow_forwardA 1 Kg mass starts with an initial velocity of 100m/s at the top of an inclined plane. By how much does it compress the spring at the bottom before coming to rest? (Assume there is NO friction). HINT: Use conservation of energy. 100m/s m=IKg 一 K=12, 00 N/m 100marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY