
Concept explainers
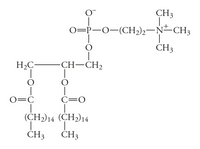
The molecule that condensed with a phosphate group to form the head group of the lipid shown in the first image (picture 6) is choline, an essential component of many cellular molecules.
(a) Draw the structure of choline and explain why it needs a transport protein in order to enter cells.
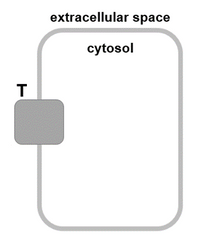
(b) Cells must transport choline from outside the cell (where it is relatively rare) to the inside of the cell (where it is relatively abundant). The diagram below represents a cell with a choline transporter (labeled T). Draw a solid arrow through the transporter to show the direction in which choline travels (into or out of the cell).
(c) Is T an active or passive transport protein for choline?
(d) For every choline molecule that moves through T, a sodium ion moves through the same transport protein at the same time. The sodium ion moves down its gradient. Add a dashed arrow to the diagram in part (b) to show the direction of movement of sodium.
(e) Is T an active or passive transport protein for sodium?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

- If crystals of deoxy Hb are exposed to air, they break. What does this imply about the 4o structure of deoxy Hb and oxy Hb and predict which subunits junctions are most affected in the change from deoxyHb to oxyHb?arrow_forwardc) Jean-François is studying a specific protein in a research laboratory. In previous experiments, he observed that this protein seems to function as a receptor protein on the surface of cells that recognizes a specific hormone involved in cell-cell communication. Jean-François prepares his final experiment, but makes a mistake in calculating how much HCl to add to one of his solutions to get the correct pH. He performs the experiment, and much to his surprise, he observes that his protein no longer seems to be recognizing the hormone anymore as he had observed in previous experiments. Propose a hypothesis that briefly explains (2-3 sentences) why the results of Jean-François’ experiment have changed. oportmost likely h beens dy the celyd must irst ir o nm cof the st omce MAnoncalest wanti patient Hewe umourcells Becnuse of falla anan intoindidual.cells. protein d) True or false: A mutation could cause the same change in Jean-François' experimental results as the change in pH described…arrow_forwardMutations of Lysine to Alanine residues near the membrane water interface disrupts binding to the lipids. Which portion of the lipid does the protein bind to, the head group or the acyl chain, given the mutation?arrow_forward
- Of the following cell membrane lipids, which one prefers to reside in the inner leaflet (or inner half) of the membrane bilayer, AND has an overall neutral charge at physiological pH (7.4)? a) PE (phosphatidylethanolamine) is inner-leaflet with an overall neutral charge at pH 7.4 b) SM (sphinogomyelin) is inner-leaflet with an overall neutral charge at pH 7.4 c) PS (phosephatidylserine) is inner-leaflet with an overall neutral charge at pH 7.4 d) PC (phosphatidylcholine) is inner-leaflet with an overall neutral charge at pH 7.4arrow_forwardNew anti-cancer agents are being developed that target fatty acid synthase (FASN) due to a requirement for lipid synthesis to promote tumor cell replication. Describe why an enzyme inhibitor targeted to the following sites would or would not work to inhibit lipid synthesis. Explain your answer. If you’re not sure whether it will work, make an argument for and against it working. ACP site on FASN The dimer interface between monomers of FASN Targeting FASN to mitochondrial matrixarrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





