
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
A detailed graph of position versus time is shown.
Part d. What is the average velocity during the time interval from 1.45 h to 4.6 in km/h?
Part e. What is the average position during the interval from 0.15 h to 4.6 h in km?
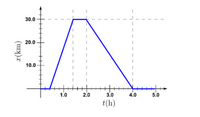
Transcribed Image Text:30.0
20.0
10.0
+
3.0
4.0
1.0
2.0
5.0
t(h)
x(km)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A woman backs her van out of her parking space with a constant acceleration of 1.8 m/s2. Assume that her initial motion is in the positive direction. Part A: How long does it take her to reach a speed of 2.1 m/s in seconds? Part B: If she then brakes to a stop in 0.65 s, what is her acceleration in meters per square second?arrow_forwardHand written solutions are strictly prohibited.arrow_forwardAsaparrow_forward
- 4. A robotic vehicle is exploring the surface of Mars. The robot, which is represented as a point, has x - and y-coordinates that vary with time: x = (3 − 2t); y = (-t² + 4t³) where x and y are in meters and t is in seconds. a. Find the average velocity of the robot between t = 0s and t = 2s. b. Find the average acceleration of the robot between t = 0s and t = 2s. c. At what time the acceleration of the robot will be zero. a. Vavg= -21 + 14ĵ m/s b. davg = 22ĵ C. m s² 2 t = = = 0.083 s 24arrow_forwardThe superhero, Sashinator, flies directly upwards for 100m in 1 second, then slows down and flies upward another 50 m for another second and grabs the supervillain, MadMaya and immediately reverses direction and flies downward for 100m in 1 second. A 250 200- 200 200 150 100 50 2. 3. 2. T 23 1. Which graph, A, B or C, shows their displacement over time? Explain your answer. m/s up m/s up D. loo 100 50 2. 5-50 -104 2. What was Sashinator's average speed during this story? Show your calculations. 3. Which graph, D, E or F shows their speed over time? Explain your answer 4. Which graph, D, E, or F shows their velocity over time? Explain your answer 5. How is the graph of distance related to the graph of speed? 6. How is the graph of displacement related to the graph of velocity?arrow_forwardAn object moves in one dimension, and its velocity versus time is shown in the graph. Express your answers in m/s2. A. What is the average acceleration between the times 0 s and 20 s? B. What is the average acceleration between the times 20 s and 50 s? C. What is the average acceleration between the times 50 s and 70 s? D. What is the average acceleration between the times 0 s and 100 s?arrow_forward
- A cheetah uses a non-constant acceleration to go from 10 m/s to 25 m/s after 5 seconds. Choose all the following statements that are correct. Than The average acceleration is 3 m/s2. We have enough information to find the distance traveled during this 5 seconds. You can't determine the average acceleration because acceleration is not constant. We have enough information to find the average velocity.arrow_forward10. An object with an initial velocity of 1 m/s to the right is initially at x = 2 m. The objecť's acceleration is a = 2t³. a) Find an expression for the velocity of the object as a function of time, i.e. v(t). b) Find the position of the object as a function of time, i.e. x(t). c) What is the objecť's average velocity and average acceleration between t =1 and t=2 seconds?arrow_forwardA safety measure when driving cars is to leave a separation of "3 s" with respect to the next car. This rule has made it possible to avoid many accidents. a. If a car travels at 60 km / h, what distance (in meters) will it travel in 3 seconds? Assuming there is an accident 20 m from where you are, what acceleration must you have to bring the car to a complete stop before reaching the accident?b. Repeat part a considering a speed of 90 km / hc. Repeat part a considering a speed of 120 km / hd. Repeat part a considering a speed of 150 km / harrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON