
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
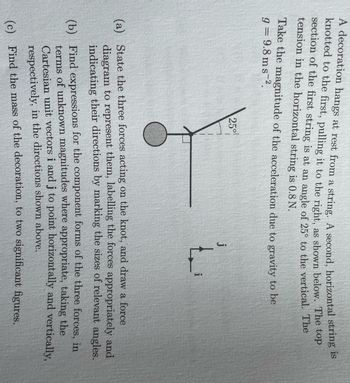
Transcribed Image Text:A decoration hangs at rest from a string. A second, horizontal string is
knotted to the first, pulling it to the right, as shown below. The top
section of the first string is at an angle of 25° to the vertical. The
tension in the horizontal string is 0.8 N.
Take the magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity to be
9 = 9.8 ms 2.
250!
j
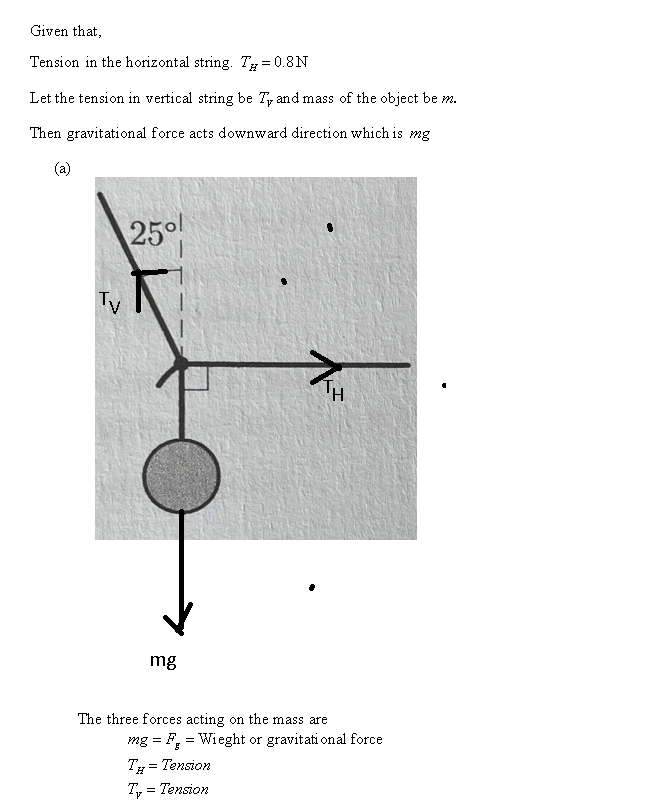
(a) State the three forces acting on the knot, and draw a force
diagram to represent them, labelling the forces appropriately and
indicating their directions by marking the sizes of relevant angles.
(b) Find expressions for the component forms of the three forces, in
terms of unknown magnitudes where appropriate, taking the
Cartesian unit vectors i and j to point horizontally and vertically,
respectively, in the directions shown above.
(c) Find the mass of the decoration, to two significant figures.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A wracking ball is suspended below two cables each at an angle with the horizontal. The left cable has tension T1 and angle 38 degrees with the horizontal. The right cable has tension T2 and angle 23 degrees with the horizontal. The Wracking ball has mass 200 kg. Find the magnitude of tension T2. T2arrow_forwardA rope is attached to a box. The box is placed on an inclined plane. The box has a mass of 70 kg. The box is moving downward while I am holding the rope. I am holding it with a force F equal to 150 N. Ignore friction. The angle 0 = 30° Draw a free body diagram. Determine the acceleration of the box.arrow_forwardIn (Figure 1), the man has a mass of 90 kg and the crate has a mass of 160 kg. The coefficient of static friction between his shoes and the ground is μ = 0.4 and between the crate and the ground is μ = 0.3. Figure t Part A Determine if the man is able to move the crate using the rope-and-pulley system shown. The man can move the crate. The man cannot move the crate. Submit ✓ Correct Part B F, Fmax = Previous Answers Prove your answer to part A by calculating the static frictional force F between the man's shoes and the ground required to move the crate and the maximum static frictional force Fmax which can be developed. Express your answers in newtons to three significant figures separated by a com_ma. 15| ΑΣΦ41 Submit Provide Feedback Request Answer vec Review N Next >arrow_forward
- Solve part a and barrow_forwardA block of mass m = 3.50 kg is pushed d = 3.00 m along a rough horizontal table by a constant applied force of magnitude F = 10.0 N directed at an angle 60 = 30.0° below the horizontal as shown in the figure below. Draw a free-body diagram that will enable you to solve the problem. Please include the horizontal and vertical components of applied force.arrow_forwardBlock B has mass 6.00 kg and sits at rest on a horizontal, frictionless surface. Block A has mass 3.50 kg and sits at rest on top of block B. The coefficient of static friction between the two blocks is 0.400. A horizontal force Vector P is then applied to block A. a) What is the largest value Vector P can have and the blocks move together with equal accelerations?arrow_forward
- A m = 1.55 kg object hangs in equilibrium at the end of a rope (taken as massless) while a wind pushes the object with a Fw = 13.1 N horizontal force. Find the magnitude of the tension in the rope and the rope's angle from the vertical. The acceleration due to gravity is g 9.81 m/s². tension: N * TOOLS x10 angle: Windarrow_forwardA decoration hangs at rest on a string. A second, horizontal string is knotted to the first, pulling it to the right. The top section of the first string is at an angle of 25° to the vertical. The tension in the horizontal string is 0.8N and acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 ms-2. A. State the 3 forces acting on the knot and draw a force diagram to represent them. B. Find expressions for the component forms of the 3 forces, using the Cartesian unit vectors i and j. C. Find the mass of the decoration, to 2 s.f.arrow_forwardA book resting on a table does not move. According to Newton's First Law, the net force on the book must be zero since the book is not moving. The force that explains why books do not fall through tables is called the normal force FN. It is a perpendicular contact force exerted by a surface. In the drawing at the right, a book is sitting on the table. The book is not moving, so the net force on it must be zero. FN Fg Q11 How does the table "know" how much normal force to exert as the weight of the object placed on top of it changes? Q12 If we had a very powerful microscope, what would we expect to see happening at the surface of the table, underneath the ball?arrow_forward
- In the diagram, all masses and angle are given. The pulleys and the string are ideal. The tension of the top string is T₁ and the tension of the bottom string is T₂. Frictional forces are negligible. m₁ T₁ a1 = a₂ cos a1 = a1 = Part1: What is the correct relationship between the magnitudes of the accelerations of blocks 1 and 2? a1 = a2 sin e a2 sin 0 a2 cos m₂ None of the Above e 1₂ m3 Part2:What is the correct FBD for block m₂? Calculatorarrow_forwarda 70kg man successfully pushes a 200kg refrigerator up a 20 angle inclinded slope. he applies a force of 3kN, parallel to the surface of the incline, pushing northwest (north meaning up in this context). friction between the refrigerator and the surface of the incline is 300 Newtons. the normal force acting on the refrigerator is 1.842 kN. choose +x axis to point eastward +y axis to point upward. calculate the weight of the refrigeratorarrow_forwardProblems 1. Three forces act on particle A located at the origin of an x-y coordinate system. Force B acts at 140° from the positive x-axis, and force C acts at 15° from the positive x-axis. The weight acts down with a magnitude of W = 100 kN. Use the equations of equilibrium to determine the magnitudes of B and C such that particle A is in equilibrium. For problems 2-5, consider the following scenario. Equilibrium of a particle: EF=0 XFx=0 and ΣFy=0. Dimensions are: h = 2.5 ft, d₁ = 4.75 ft, and d₂ = 3 ft. Give numeric answers to three significant figures. The load W = 50 lb. d₁ dz A h α W Barrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON