Question
A daredevil on a motorcycle leaves the end of a ramp with a speed of 31.0 m/s as in Figure P5.23. If his speed is 29.0 m/s when he reaches the peak of the path, what is the maximum height that he reaches? Ignore friction and air resistance.
M
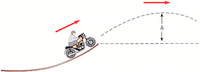
Transcribed Image Text:The image depicts a motorcycle rider performing a jump off a ramp. The ramp is angled upwards, and the motorcycle is shown ascending it. A dashed line indicates the trajectory of the motorcycle as it leaves the ramp and travels through the air.
Key features of the diagram:
1. **Motorcycle and Rider**: Positioned on an upward-sloping track, moving towards the ramp.
2. **Trajectory Path**: A dashed curve represents the path followed by the motorcycle after leaving the ramp, illustrating the parabolic motion typical of projectile movement.
3. **Velocity Arrows**: Two red arrows indicate the direction of velocity. One points upward along the ramp, while the other points horizontally, indicating the continuation of motion in the air.
4. **Height (\( h \))**: A vertical arrow labeled \( h \) points from the top of the ramp to the peak of the trajectory, marking the maximum height reached by the motorcycle after takeoff.
These elements combine to illustrate concepts of physics such as projectile motion, velocity, and height in the context of a motorcycle jump.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A 9.0-kg bunny slides from rest down a frictionless incline from a height of 5.0 m. A constant frictional force, introduced at point A, brings the bunny to rest at point B, 19 m to the right of point A. What is the Speed of the bunny before it reaches point A? What is the coefficient of kinetic friction, µk, of the surface from A to B?arrow_forwardA daredevil on a motorcycle leaves the end of a ramp with a speed of 29.0 m/s as in the figure below. If his speed is 27.3 m/s when he reaches the peak of the path, what is the maximum height that he reaches? Ignore friction and air resistance.arrow_forwardA daredevil on a motorcycle leaves the end of a ramp with a speed of 32.4 m/s as in the figure below. If his speed is 30.5 m/s when he reaches the peak of the path, what is the maximum height that he reaches? Ignore friction and air resistance.marrow_forward
- 1. A 7.50-kg box initially at rest slides down a 15.0 m long incline that makes an angle of 22.0° with the horizontal (see figure). At the bottom of the incline, the speed of the box is 3.00 m/s. a) Draw a free body diagram, detailing all of the forces acting on the box. b) Using the work done by non-conservative forces relationship, find the algebraic expression for the coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the incline. c) Calculate the coefficient of kinetic friction.arrow_forwardA child stands on a bank beside a pond, grasps the end of a 20.0 m long rope attached to a nearby tree and swings out to drop into the water. When the rope makes an angle of 15.0⁰ with the vertical, the child's speed is 5.00 m/s. a) At what point in the swing does the child's maximum speed occur? b) What is the child's maximum speed? Ignore all frictional effects. c) Assuming the child started from rest, what angle did the rope initially make with respect to the vertical?arrow_forwardA block slides across the ground and comes to rest in 12.0 m. muk = 0.200. Find the initial speed using conservation of E. Correct answer: 6.86 m/sarrow_forward
- A roller-coaster car is moving at 4.12m/s along a straight horizontal track before entering the first drop. What will the speed of the coasterbeat point B? Ignore friction and air resistance.arrow_forwardA 2.1 x 10³-kg car starts from rest at the top of a 5.1-m-long driveway that is inclined at 18° with the horizontal. If an average friction force of 4.0 x 103 N impedes the motion, find the speed of the car at the bottom of the driveway. m/s Submit Answerarrow_forwardSuppose a 85 kgkg sprinter, starting from rest, runs the first 14 mm in 3.0 ss at constant acceleration, a reasonable model. a. What is the magnitude of the horizontal ground force acting on the sprinter? b.What is the sprinter's power output at 1.0 ss, 2.0 ss, and 3.0 ss?arrow_forward
- 68. Starting from rest, Megan zooms down a frictionless slide from an initial height of 4.0 m. What is her speed at the bottom of the slide2arrow_forwardB9arrow_forwardQ. In Figure, a block slides along a path that is without friction until the block reaches the section of length L-0.85 m, which begins at height h-2.0m on a ramp of angle 0-45, In that section, the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.40. The block passes through point A with a speed of 8.0 m/s. If the block can reach point B (where the friction ends), what is its speed there, and if it cannot, what is its greatest height above A? A.8.9 m/s B. 6.9 m/s C. 4.9 m/s D. 2.9 m/s E. 1.9 m/s len buth secin.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios