
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A damping
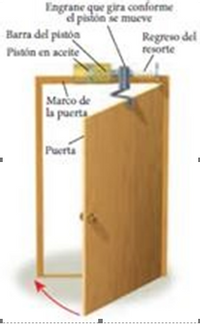
Transcribed Image Text:Engrane que gira conforme
d pision se mueve
Barra del pistón
Piaón en acecite
Regreso del
resorte
Marco de
la puerta
Pucrta
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I need the answer quicklyarrow_forwardFor the same question, the Impeller hub will be pressed onto the taper shaft with the Nut. How much FORCE should the nut create for this? Also, if the nut loosens and falls off, calculate whether the connection will be DISCONNECTED by itself. (Do not take the values from the previous question, use the values given in this question!) Engine power P=27 kW, RPM n=1684 rpm, Connection MEDIUM vibrating, Conical inclination angle α=1, Coefficient of Friction μ=0.3 , Average of the conical part diameter d=24 mm, connection width b=96 mmarrow_forwardPARTS A & B solve carefully and label each part and CIRCLE FINAL ANSWER ( Use image Below) Part A - Assuming the elements are all linear, determine a model for the mass-spring-damper system. Make sure to clearly define the direction of positive velocity. Simplify your answer such that the model is in terms of the parameters (?, ?, ??, ??), the input force (?), the spring deflection and the mass velocity as well as their time derivatives. Part B - Take the ANSWER from PART A and replace the damping constant ? with the nonlinear expression ? = ?? + ?? + ? , with ? as the velocity of the mass.arrow_forward
- Part D - Present the equations of motion for the system, including the rate of change of deflection. Make sure to simplify your equations as much as possible.arrow_forwardA four-cylinder automobile engine must be supported on three shock mounts,as shown in the picture. The engine block assembly weighs500 lbs. If the unbalanced force produced by the engine is given by200 sin 100 t lb, design three shock mounts (each stiffness k andviscous damping constant c) such that the vibration amplitudemaximum 0.1 inarrow_forwardQ3/A polyamide A-3 flat belt 6 in wide is used to transmit 15 hp under light shock conditions where Ks = 1.25, and a factor of safety equal to or greater than 1.1 is appropriate. The pulley rotational axes are parallel and in the horizontal plane. The shafts are 8 ft apart. The 6-in driving pulley rotates at 1750 rev/min in such a way that the loose side is on top. The driven pulley is 18 in in diameter. See Fig. 17-10. The factor of safety is for unquantifiable exigencies. 1750 rpm 6 in -96 in 18 in (a) Find the torque capacity that would put the drive as built at the point of slip, as well as the initial tension Fi. (b) Find the belt width b that exhibits nfs = nd = 1.1. (c) For part b find the corresponding Fla, Fc, Fi, F2, power, and nfs. (d) What have you learned?arrow_forward
- The external and internal diameter of a single plate clutch are 125 mm and 100 mm, respectively. It is used to transmit power at limited (maximum) axial pressure of 0.2 MPa. Which of the following is the axial force exerted by the springs? Assume uniform wear conditions. Choices: 790N1960N 440N 980Narrow_forwardQ1: Determine the equivalent spring constant of the system shown in Fig. 1 k₁ k3 0000 mão S k₂ 0000 ks 0000-0000 eeeeeeee K₁ Fig.1arrow_forwardmechanical principles Explain the natural frequency of vibration in a mass-spring system.arrow_forward
- Question 2 A reciprocating engine is installed on the fifth floor of a new building to provide ventilation services, which can be modelled as a rigid rectangular plate resting on four elastic columns. The total mass of the engine and floor is 1000 kg. At the rated speed of the engine, which is 750 rev/min, the engineers experienced large vibrations of the floor. It has been decided to reduce these vibrations by suspending a spring-mass system at the bottom surface of the floor as the absorber. (a) If the stiffness of the absorber is 980 kN/m, find the mass of the dynamic absorber to be attached to the floor. (b) Find the values of the absorber mass and absorber stiffness in order to have the natural frequencies of the combined system at least 25% away from the forcing frequency. Verify your answer with a calculation.arrow_forwardA helical compression spring is required to provide a minimum force of 150 lb at installation and have a working deflection of 1 in. The spring rate is 75 lb/in. The coil must fit in a 2.1-in-dia hole with 0.1 in total clearance. Use 0.25-in diameter unpeened music wire and squared/ground ends. Use a 15% clash allowance, shear modulus G = 11.5 Mpsi, and weight density γ = 0.285 lb/in3. Assume Sys = 0.6Sut. Part A Find the shear stress at the initial deflection. Express your answer in pounds per square inch to three significant figures. τiτi = Part B Find the mean stress. Express your answer in pounds per square inch to three significant figures. Part C Find the alternating stress in the coil. Express your answer in pounds per square inch to three significant figures. Part D Find the fatigue safety factor for infinite life in shear. Express your answer using three significant figures.…arrow_forwardAs illustrated in the figure below, the bedplate of an experimental diesel engine is supported on four springs to isolate the vibrations from the test frame. The effective weight of the diesel engine and bedplate is 43kg and the stiffness of each of the four springs is 250 kN/m. Using a simplified approach - by applying Newton's Second Law assuming a single degree of freedom system and ignoring damping - what rotational engine speed is best avoided? Bedplate Test engine Supporting springs Figure: Sketch of a test engine mounting arrangement Give your answer in rad/s to 1 decimal place.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY