
Materials Science And Engineering Properties
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781111988609
Author: Charles Gilmore
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Fluid of mechanics
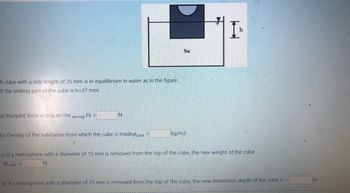
Transcribed Image Text:A cube with a side length of 35 mm is in equilibrium in water as in the figure.
If the sinking part of the cube is h=27 mm;
a) Buoyant force acting on the earring Fk =
b) Density of the substanc from which the cube is madepcube
N
new
=
Su
kg/m3
c) If a hemisphere with a diameter of 15 mm is removed from the top of the cube, the new weight of the cube
W
N
h
d) If a hemisphere with a diameter of 15 mm is removed from the top of the cube, the new immersion depth of the cube h =
m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 10 cm long rectangular bar (when subjected to a tensile load) deforms by 0.1 mm. Calculate the normal strain.arrow_forwardA 9 ft wide and infinitely long flexible strip load of 800 lb/ft2 is placed on an elastic medium as shown in Figure P8.7. Find the vertical stress increase at points A, B, and C located 3 ft below the surface.arrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you
 Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305084766Author:Saeed MoaveniPublisher:Cengage Learning
Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305084766Author:Saeed MoaveniPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Materials Science And Engineering Properties
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781111988609
Author:Charles Gilmore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305635180
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305084766
Author:Saeed Moaveni
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305970939
Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:Cengage Learning