
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
A crate is pulled up using frictionless pulleys, as shown in the diagram, at an angle of 45 degrees. The masses are: for the small pulley, m1 = 2.5kg, for the travelling pulley, M2 = 3.0kg, and for the crate, MC = 13.0kg. What is the minimum tension (in Newtons) with which the operator must pull, in order to slowly raise the crate?
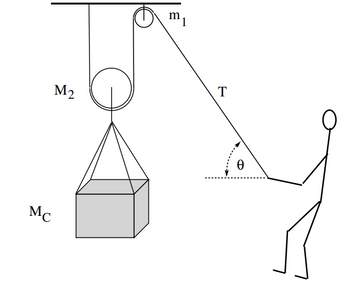
Transcribed Image Text:Mc
M₂
m
T
Ꮎ
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- make answer sleararrow_forwardA dockworker applies a constant horizontal force of 75.0 N to a block of ice on a smooth horizontal floor. The frictional force is negligible. The block starts from rest and moves 12.0 m in 4.8 s. What is the mass (in kg) of the block of ice? (Round your answer to one digit after decimal point)arrow_forwardmy question is in the image. I dont quite get how to go about solving this. I have been getting 196.2 N which is wrong. How should I be going about this?arrow_forward
- Two blocks are connected by a lightweight string passing over a pulley, as shown in the figure below. The block with mass m, = 17.5 kg on the incline plane accelerates up the plane with negligible friction. The block's acceleration is a = 1.80 m/s2, and the tension in the segment of string attached to this block is T,. The hanging block has a mass of m, = 23.5 kg, and the tension in the string attached to it is T,. The radius of the pulley is r = 0.330 m and its moment of inertia is I. The incline plane makes an angle of 0 = 37.0° with the horizontal. T T (a) What is the tension force T,? (Give your answer, in N, to at least three significant figures.) (b) What is the tension force T,? (Give your answer, in N, to at least three significant figures.) N (c) Find a symbolic expression for the moment of inertia of the pulley in terms of the tensions T, and T,, the pulley radius r, and the acceleration a. (Do not substitute numerical values; use variables only.) I = (d) What is the…arrow_forwardAn object of mass m has these three forces acting on it . F1, F2, and F3 are shown in the figure. Assume the x-direction is to the right, and the y-direction is straight upwards. Let F1 = 7 N, F2 = 9 N, and F3 = 2 N. What is the direction of the net force, expressed as the angle θ, in degrees, that the net force vector makes with respect to the +x-axis? Enter an angle between −180∘ and +180∘.arrow_forwardThree blocks are connected by ropes, as depicted in Figure 1. The coefficientof kinetic friction between m1 and m2 is 0.300, and the horizontal surface and pulleys are frictionless. What is the acceleration of the blocks?arrow_forward
- A block is placed on a frictionless 30 degree incline.the mass of the block is m=30kg.b.find the normal force?arrow_forwardThe following information pertains to questions 1, 2, and 3. A workman pulls a sled across an asphalt road using a rope at angle 0 above the horizontal direction. The workman pulls with 1,000[N] of force. The coefficients of friction of the sled with the road are u=1.00 and µ=0.70. The sled has mass m. The sled is initially at rest. T710Q0[N]. 1) Which expression gives the magnitude of fmax for the situation illustrated above? A) mg B) mg – 1000cos(0) C) - mg + 1000cos(0) D) mg-1000sin(0) E) mg+ 1000sin(0) F) None of the abovearrow_forwardTwo forces F, = -8.40i + 4.30j and F, = 7.50i + 5.30j are acting on an object with a mass of m = 7.80 kg. The forces are measured in newtons, i and j are the unit vectors. What is the magnitude of the object's acceleration? Submit Answer Tries 0/10arrow_forward
- The systems shown below are in equilibrium with m = 6.60 kg and ? = 25.0°. If the spring scales are calibrated in newtons, what do they read? Ignore the masses of the pulleys and strings and assume the pulleys and the incline are frictionless. Four figures each show different orientations of a spring scale connected to various objects. Figure (a): Two objects of mass m are attached to opposite ends of a horizontal spring scale, one on the left end and the other on the right end. The spring scale is positioned at the center of a horizontal tabletop and between two diagonal pulleys which extend outward from the left and right edges of the table. Separate strings are attached to each end of the spring scale and pass over the nearest pulley before suspending an object of mass m beside the table. Figure (b): A diagonal pulley extends outward from the leftmost edge of a horizontal surface. An object of mass m is suspended from a string which passes over the pulley and anchored at the left…arrow_forwardShown to the right is a block of mass m resting on a frictionless ramp inclined at an angle to the horizontal. The block is held by a spring that is stretched a distance d after the block is attached to it. E k= e wwwwww ▷ A Write an equation for the force constant of the spring in terms of the variables from the problem statement (m, 0, and d). Use g for the gravitational constant.arrow_forwardThree blocks are stacked on the floor. From the bottom of the stack to the top, their masses are m1, m2, and m3, respectively, as shown on the diagram. When referring to the various forces, the subscripts i=1,2,3 of the blocks will be used, and f will be used to indicate the floor. Weights, if required, will be denoted with the corresponding subscript of the block as Fg,i for i=1,2,3. The normal force exerted by object a on object b, if required, will be denoted as Fn,a→b for i=1,2,3,f but a≠b. The force of kinetic friction exerted by object a on object b, if required, will be denoted as Fk,a→b for i=1,2,3,f, but a≠b. The force of static friction exerted by object a on object b, if required, will be denoted as Fs,a→b for i=1,2,3,f, but a≠b. The floor mentioned in the problem statement is the floor of an elevator. When the elevator accelerates, all of the blocks have a common acceleration in the vertical direction. Form an expression for the net force on the top-most…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON