
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
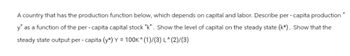
Transcribed Image Text:A country that has the production function below, which depends on capital and labor. Describe per-capita production"
y" as a function of the per- capita capital stock "k". Show the level of capital on the steady state (k*). Show that the
steady state output per- capita (y*) Y = 100K ^ (1)/(3) L^(2)/(3)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose there is an increase in the saving rate. We know that this will cause an increase in which of the following in the steady state? growth rate of output level of output growth rate of capital per worker growth rate of output per effective worker none of the abovearrow_forwardOne of the biggest challenges for stimulating economic growth in high-income countries is Group of answer choices Meeting basic human needs like food, water, and shelter Limited investment opportunities Increasing education, innovation, and technology Determining how to wisely spend large reserves of savings to promote growtharrow_forwardConsider a numerical example using the Solow Growth Model, for 2 countries. Country A: d=0.1, s=0.3, n=0.01, z=1, F(K,L)=K0.3n0.7 Country B: d=0.1, s=0.2, n=0.01, z=1.5, F(K,L)=K0.4N0.6 Which Country has a higher level of GDP per capita in steady state? O Country A O Country B Not enough informationarrow_forward
- In the steady state, _____ consumption per worker is maximized. investment per worker exceeds depreciation per worker. the growth rate of output per worker equals zero. capital per worker grows.arrow_forwardIn the Solow growth model, suppose that the per-worker production function is given by y = zk 0.4 with s = 0.15, d = 0.1, and n = 0.02. a. Suppose in country A that z= 1. Calculate the steady-state capital per worker and income per capita in country A. The steady-state capital per worker is (Round to two decimal places as needed.) The steady-state income per capita is. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) b. Suppose in country B that z = 2. Calculate the steady-state capital per worker and income per capita in country B. The steady-state capital per worker is|. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) The steady-state income per capita is (Round to two decimal places as needed.) c. As measured by GDP per capita, how much richer is country B than country A? What does this tell us about the potential differences in total factor productivity to explain differences in standards of living across countries? Country B is times richer than country A, as measured by GDP per capita. This…arrow_forwardIf a country’s GDP grows by 10% per year, why isn’t the number of years it takes to double the GDP simply 100%/10% = 10 years?arrow_forward
- Question 27 Consider countries A and B, with A having a higher population growth rate than B. According to the Solow-Swan model, output per person in A and output per person in B are the same in steady state. Answer True or False. Remember to include your explanation.arrow_forwardWhat must be the relationship between the rate of growth of technological change (g) and the population growth rate (L/L) for income per capita to continue to increase?arrow_forwardThe productivity growth rates of poorer countries tend to be _____ than those of richer countries. Higher Lower increasing slower decreasing fasterarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education