
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
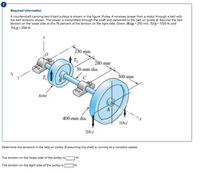
Transcribed Image Text:Required information
A countershaft carrying two V-belt pulleys is shown in the figure. Pulley A receives power from a motor through a belt with
the belt tensions shown. The power is transmitted through the shaft and delivered to the belt on pulley B. Assume the belt
tension on the loose side at Bis 15 percent of the tension on the tight side. Given: B(dB) = 210 mm, T(AJ = 1720 N, and
TA2) = 258 N.
230 mm
| T,
280 mm
30-mm dia.
300 mm
B(dB)
400-mm dia.
T(A2)
T(A:)
Determine the tensions in the belt on pulley Bassuming the shaft is running at a constant speed.
The tension on the loose side of the pulley is
N.
The tension on the tight side of the pulley is |
N.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- An axle is composed of elements laid by S355 E-module 2.1x105 N/mm2, transverse contraction factor 0.3. As shown in the picture, we have on the right side two forces of 10,000 N whichshows at an angle 15 upwards and forms a moment which is statically compensated by the force F2 on the left side. The shaft is stored in positions A and B. In the same position (for the sake of simplicity) there are two critical cross-sections that lead to stress concentrations.v) Determine b nom which is necessary to transfer the torque you have calculated when the coefficient of friction is 0.3. Comment on the result when you compare b real and b nom.vi) Determine G max.vii) Does the sleeve withstand the stresses when the permissible stress is 355 N/mm2?arrow_forwardA countershaft carrying two V-belt pulley is shown in Figure 1. Pulley A receivespower from a motor through a belt with the belt tensions shown. The power is transmittedthrough the shaft and delivered to the belt on Pulley B. Assume the belt tension on the loose sideat B is 15 percent of the tension on the tight side.(a) Determine the tensions in the belt on pulley B (assuming the shaft is running at a constantspeed).(b) Find the magnitudes of the bearing reaction forces assuming the bearings act as simplesupports.(c) Draw the shear force and bending moment diagrams for the shaft.arrow_forwardA single-piece bicycle crank is shown below under the following load: the rider pedals forward with a vertical force Fp = 500 N on the left pedal and no force on the right pedal. The chain exerts a force Fc on the chainring. The spindle is a solid cylinder with a diameter d = 16 mm. 1. Draw a free-body diagram of the entire crankset and find the reactions at the ball bearings and the force from the chain.arrow_forward
- Solve both show all steps and solutionsarrow_forwardFigure B b 30° 2b 30° Н. 4 of 4 Correct Note that the internal reactions at B are not included in the free-body diagram of the subsystem ABC. Part D-A tractor shovel The tractor shovel shown (Figure 4) carries a 535 kg load that has its center of mass at H. The shovel's dimensions are: a = 50.0 mm, b = 200 mm, c = 300 d = 100 mm, and e = 350 mm. Find the reaction force at E. Assume that the positive direction of the x and y axes is to the right and upward, respectively. Enter the Cartesian components of the reaction force at E separated by a comma. Express your answers in newtons to three significant figures. ► View Available Hint(s) ET, Ey = Submit VE ΑΣΦ ↓↑ vec ? Narrow_forwardFor two existing torques, what third force at a given distance from the pivot will balance them? Imagine a meter stick set up as in the figure. It hangs from a central bracket, and two hanging masses can hang from it from each of their brackets. At a third location, a force probe can either pull up or pull down on the stick, depending on what is needed to balance the stick. The mass of the meter stick is 120 g. sketch the situation (drawing r1, r2, r3, F1, F2, and F3) and determine the magnitude (value) and direction (+ or -) of each torque. Don't include the mass of a bracket that would hold the hanging mass in place; assume the mass listed is the entire mass hanging at that point. For each trial, use the principle of equilibrium (where the sum of torques is zero) to calculate the third, unknown force acting at x3arrow_forward
- For two existing torques, what third force at a given distance from the pivot will balance them? Imagine a meter stick set up as in the figure. It hangs from a central bracket, and two hanging masses can hang from it from each of their brackets. At a third location, a force probe can either pull up or pull down on the stick, depending on what is needed to balance the stick. The mass of the meter stick is 120 g. sketch the situation (drawing r1, r2, r3, F1, F2, and F3) and determine the magnitude (value) and direction (+ or -) of each torque. Don't include the mass of a bracket that would hold the hanging mass in place; assume the mass listed is the entire mass hanging at that point. For each trial, use the principle of equilibrium (where the sum of torques is zero) to calculate the third, unknown force acting at x3arrow_forwardFor two existing torques, what third force at a given distance from the pivot will balance them? Imagine a meter stick set up as in the figure. It hangs from a central bracket, and two hanging masses can hang from it from each of their brackets. At a third location, a force probe can either pull up or pull down on the stick, depending on what is needed to balance the stick. The mass of the meter stick is 120 g. sketch the situation (drawing r1, r2, r3, F1, F2, and F3) and determine the magnitude (value) and direction (+ or -) of each torque. Don't include the mass of a bracket that would hold the hanging mass in place; assume the mass listed is the entire mass hanging at that point. For each trial, use the principle of equilibrium (where the sum of torques is zero) to calculate the third, unknown force acting at x3arrow_forwardA crank shaft is operated as shown in the figure. A load F1 = 9.73 N is applied and the operator %3D dz applies a load P to counter. The system is in equilibrium and all of the bearings are perfectly dz aligned such that they do not produce moments on the rotating crank. The geometry is given by, w = 7.31 [m), dl = 9.69 m], d2 = 7.57 m). 6.14 (m), d5 = 3.7 (m), %3D d1 d3 = 9.87 (m), d4 %3D F2 and h1 4.4 (m), find the following: %3D F1 Part 1. Express the reaction forces exerted on the bar by the journal bearing at point B. Use the coordinate system shown in the diagram 10 5% 100% Submit [N] Part 2. Express the reaction forces exerted on the bar by the journal bearing at Point A. Use the coordinate system shown in the diagram. 5% 100% 10 Submit [N]arrow_forward
- Please solve Correctly and Explain. I would like to learnarrow_forwardplease i need her solving with using the formulas attached below of pin joint linkagearrow_forwardA countershaft carrying two V-belt pulleys is shown in the figure. Pulley A receives power from amotor through a belt with the belt tensions shown. The power is transmitted through the shaft anddelivered to the belt on pulley B. Assume the belt tension on the loose side at B is 15 percent ofthe tension on the tight side.(a) Determine the tensions in the belt on pulley B, assuming the shaft is running at a constantspeed.(b) Find the magnitudes of the bearing reaction forces, assuming the bearings act as simplesupports.(c) Draw shear-force and bending-moment diagrams for the shaft. If needed, make one set for thehorizontal plane and another set for the vertical plane.(d) At the point of maximum bending moment, determine the bending stress and the torsionalshear stress.(e) At the point of maximum bending moment, determine the principal stresses and themaximum shear stress.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY