
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
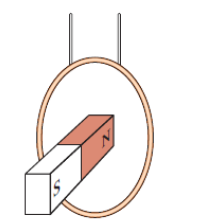
A copper loop hangs from two strings, as shown. In which direction (toward or away from the magnet) does the loop swing if the magnet
a. Is stationary?
b. Is moving toward the loop?
c. Is moving away from the loop?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A solenoid is wound on a rod 4 cm in diameter in 50 cm long. The windings carry a current of 3.5 A in the sense that is shown. The current produces a magnetic field of magnitude 4.1 mT at the center of the solenoid. The number of turns in the solenoid is closest to which? A. 4700 B. 3700 C. 470 D. 1900 E. 19arrow_forwardDetermine the direction of the induced current when the magnet is moved towards the solenoid. a) top into the page - bottom out of the page b) top out of the page - bottom into the page c) no induced current d) not enough infoarrow_forwardWhich of the following statements best describes Oersted’s Principle? a. A current-carrying conductor produces a linear magnetic field from the north to the south pole b. A current-carrying conductor creates a circular magnetic field around a wire c. A solenoid will create a magnetic field similar to that of a bar magnet d. A charge entering a magnetic field will undergo circular motion e. None of the above explain Oersted’s Principlearrow_forward
- a.) a current in the CW direction to enhance the decreasing north magnetic field. b.) a current in the CW direction to enhance the decreasing south magnetic field. c.) a current in the CW direction to oppose the increasing south magnetic field. d.) a current in the CW direction to oppose the increasing north magnetic field. e.) no current in the coil. 7.) A conducting coil is rotated at constant speed in a uniform magnetic field as shown in the figure here. The time required by the loop to make a full rotation is T. The current generated in the coil would increase Side view a.) if the angular speed of the coil increases. b.) if the area of the coil increases. c.) if the strength of the magnetic field increases. d.) All of the above are correct. e.) None of the above are correct. 8.) An RLC circuit has a resonant frequency of fo. When the circuit is driven by an AC voltag source whose frequency is 2fo, which of the following is the most accurate?arrow_forwardA negatively charged particle is moving with a constant velocity directed to the left through a region of a uniform magnetic field B directed into the page as shown in the figure, in which direction must an electric field be applied to keep the particle moving along a straight line? XB Select one: a.Upward b.Downward c.into the page d.To the leftin the plane of the page e.Out of the page 1.To the right in the plane of the pagearrow_forwardIf number of turns (N), area (A) and magnetic field (B) have same value for a square and circular loop, but current of square loop is double the current in the circular loop then maximum torque produced in the square loop will be 21 a. Double the torque in circular loop O b. Half of torque in circular loop O c. 4 times the torque in circular loop O d. Equal the torque in circular looparrow_forward
- A stationary magnet with north pole at the bottom lies at the centre of the circular coil. Determine the direction of induced current (when viewed from above) in the coil. a. no current in the coil b. a current whose direction cannot be determined from the information given c. a clockwise current in the coil d. a counterclockwise current in the coilarrow_forwardWhat is the direction of the magnetic force on a negative charge that moves as shown in the figure? B Select one: O a. In O b. there is no magnetic force O. Out O d. Left When the light is passing from rarer to a denser medium, which is the correct statement? O a. speed becomes zero O b. speed of light increases speed of light remains constant O d. speed of light decreasesarrow_forwardWhich of the following can be done to make a stronger solenoid (an electromagnet)? Select one or more: a. increase the supplied voltage b. decrease the current c. decrease the number of loops d. decrease the length of the solenoidarrow_forward
- A positively-charged point particle, q, with a speed of v = 3.0 x 105 m/s enters a uniform magnetic field, , at a 300 angle to the field as shown in the diagram below. Which of the following paths best describes the trajectory of the particle? a. A circle b. A helix c. An ellipse d. A hyperbola e. A parabolaarrow_forwardWhat will happen to the wire between the magnet poles when the switch S is close? V B switch Q Select one: a. Nothing. The wire remains in place O b Moves to the magnet's South pole O c Moves out of the screen (or page) C. d. Moves into the screen (or page) e. Moves to the magnet's North polearrow_forwardWhich of the following changes would increase the magnetic field strength at the center of the solenoid, assuming everything else remains constant? Explain why? A.Decreasing the length of the solenoid by removing turns of wire while keeping ? constant B.Decreasing ?,the current in the wire C.Decreasing ?,the number of turns of wire per millimetre D.Increasing ?,the current in the wire E.Increasing the length of the solenoid by adding turns of wire while keeping ? constantarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON