
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
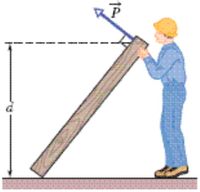
A construction worker attempts to lift a uniform beam off the floor and raise it to a vertical position. The beam is 1.88 m long and weighs 490 N. At a certain instant the worker holds the beam momentarily at rest with one end a distance d = 1.02 m above the floor, as shown in the figure, by exerting a force P→ on the beam.
(a) What is the magnitude of P→?
(b) What is the magnitude of the (net) force of the floor on the beam?
(c) What is the minimum value the coefficient of static friction between beam and floor can have in order for the beam not to slip at this instant?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two uniform planks, each of mass m = 7.45 kg and length L = 2.51 m, are connected by a hinge at the top and by a chain of negligible mass attached at their centers, as shown in the figure. The assembly will stand upright, in the shape of an A, on a frictionless surface without collapsing. If the chain has the length 0.81 m, find each of the following:a) the absolute value of the tension in the chain,b) the absolute magnitude of the force on the hinge of each plank,arrow_forwardA man holds a 198-N ball in his hand, with the forearm horizontal (see the figure). He can support the ball in this position because of the flexor muscle force M, which is applied perpendicular to the forearm. The forearm weighs 18.5 N and has a center of gravity as indicated. Find (a) the magnitude of M and the (b) magnitude and (c) direction (as a positive angle counterclockwise from horizontal) of the force applied by the upper arm bone to the forearm at the elbow joint. Upper arm bone - Flexor muscle M Elbow joint cg 0.0510 mt T0.0890 m 0.330 m-arrow_forwardA house painter is standing on a uniform, horizontal platform that isheld in equilibrium by two cables attached to supports on the roof.The painter has a mass of 75.0 kg and the mass of the platform is 20.0kg. The distance from the left end of the platform to where the painteris standing is d = 2.00 m and the total length of the platform is 5.0 m.(a) How large is the force exerted by the left hand cable? (b) Howlarge is the force exerted by the right hand cable? [Hint: You can placeyour axis in any convenient location if the object is not rotating.]arrow_forward
- A man holds a 195-N ball in his hand, with the forearm horizontal (see the figure). He can support the ball in this position because of the flexor muscle force M , which is applied perpendicular to the forearm. The forearm weighs 20.7 N and has a center of gravity as indicated. Find (a) the magnitude of M and the (b) magnitude and (c) direction (as a positive angle counterclockwise from horizontal) of the force applied by the upper arm bone to the forearm at the elbow joint. Upper arm bone- Flexor muscle M Elbow cg joint 0.0510 m+ 0.0890 m -0.330 m- (a) Number i Units (b) Number i Units (c) Number i Units >arrow_forwardA scaffold of mass 71 kg and length 4.8 mis supported in a horizontal position by a vertical cable at each end. A window washer of mass 64 Kg stands at a point 2.4 m from one end. What is the tension in (a) the nearer (relative to the person) cable and (b) the farther (relative to the person) cable? (a) Number Unitsarrow_forwardA telephone pole has been knocked over by the wind so that it makes an angle of theta= 15 degrees with the vertical. The wind has stopped blowing and the pole is to be cut down. Once the cut is across most of the thickness of the pole, the pole begins to tip over. As the pole tips, the bottom of the pole stays attached to the base by the remaining part of the pole that was not cut (but the torque from the base on the tipping pole is negligible). There is a nail (of negligible mass) on the pole located a distance x = 47 m from the cut. The length of the pole from the cut to the top is L=69m. Remember that the moment of inertia of a stick of mass m and length L about its end is (13)mL2. If theta= 67.5 degrees, what is the magnitude of the angular acceleration of the nail?arrow_forward
- #11arrow_forwardA child of weight 30 kg (m2) walks along a uniform board of weight 10 kg (m1) and length = 10 m. The board is supported by two legs (symmetry to the center) with negligible weight shown in the figure. How close (i.e. find x) could the child walk to the right end before the board flips (in m)?arrow_forwardThe 12-ft boom AB has a fixed end A. A steel cable is stretched from the free end B of the boom to a point C located on the vertical wall. If the tension in the cable is 500 lb, determine the moment about A of the force exerted by the cable at B. Solution: y A 8 ft 12 ft C i + 4.8 ft → • According to definition, moment about A of the force at B can be expressed as MA = r • The arm 7 = k; • The components of the force: B 1. Direction vector of the force F is 2. Length of the direction vector is 3. Unit vector of the force F is λ = → ft; 4. Thus the tension force on B is resolved to F = + i+ 1 + + k; k; k (lb); XF ◆arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON