
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
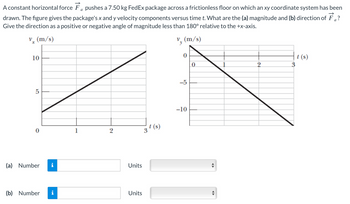
Transcribed Image Text:A constant horizontal force pushes a 7.50 kg FedEx package across a frictionless floor on which an xy coordinate system has been
drawn. The figure gives the package's x and y velocity components versus time t. What are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction of F?
Give the direction as a positive or negative angle of magnitude less than 180° relative to the +x-axis.
Vy (m/s)
v (m/s)
x
10
5
(a) Number
(b) Number
1
a
2
Units
Units
t (s)
3
0
-5
-10
IL
0
◄►
3
t(s)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In a time of 2.67 h, a bird flies a distance of 86.7 km in a direction 30.2 degrees east of north. Take north to be the positive y direction and east to be the positive x direction. Express your answers in km/h. What is the x component of the bird’s average velocity? What is the y component of the bird’s average velocity?arrow_forwardThe head injury criterion (HIC) is used to assess the likelihood of head injuries arising from various types of collisions; an HIC greater than about 1000 s is likely to result in severe injuries or even death. The criterion can be written as HIC=(aavg/g)^2.5Δt, where aavg is the average acceleration during the time Δt that the head is being accelerated, and g is the free-fall acceleration. The figure shows a simplified graph of the net force on a crash dummy's 4.5 kg head as it hits the airbag during a automobile collision. What is the HIC in this collision? Give your answer in seconds.arrow_forwardA mountain climber encounters a crevasse in an ice field. The opposite side of the crevasse is 2.75 m lower, and is separated horizontally by a distance of 4.10 m. To cross the crevasse, the climber gets a running start and jumps in the horizontal direction with a speed of 6 m/s. (a) Draw a diagram showing motion of climber. In your diagram write known and unknown, vo, h and w. (b) Find x- and y-components of initial velocity. (c) Calculate time as climber lands. (d) where does the climber land, and (e) what is climber's speed on landing?arrow_forward
- A rock of mass 51.2 kg accidentally breaks loose from the edge of a cliff and falls straight down. The magnitude of the air resistance that opposes its downward motion is 15.7 N. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the rock?arrow_forwardThe position of a dragonfly that is flying parallel to the ground is given as a function of time by 7 = [2.90 m + (0.0900 m/s²)t²] i – (0.0150 m/s³)t³ j. Part B At the time calculated in part (a), what is the magnitude of the acceleration vector of the insect? Express your answer with the appropriate units. xa μÅ Xb a = 0.062 a b X.10n m Submit Previous Answers Request Answer ?arrow_forwardProblem 8: A person is standing on top of a building. While standing at the edge of the building the person throws a water balloon downward with a speed of 24 m/s and at an angle of 36° below the horizontal. It takes 3.1 s for the water balloon to hit the person's friend. Part (a) How high is the building in meters? Numeric : A numeric value is expected and not an expression. h = Part (b) How fast is the water balloon moving when it hits the friend on the ground? Give your answer in m/s. Numeric : A numeric value is expected and not an expression. v= Part (c) What was the horizontal distance between the friend on the ground and the building in meters? Numeric : A numeric value is expected and not an expression. dx = %3!arrow_forward
- A girl throws a stone with an initial velocity of 4.44 m/s at 60.7° above the horizontal. If air resistance is negligible, after how much time tmax does the stone reach its maximum height? tmax Sarrow_forwardThe vector position of a particle varies in time according to the expression i = 7.40 î - 6.202² j where ř is in meters and t is in seconds. (a) Find an expression for the velocity of the particle as a function of time. (Use any variable or symbol stated above as necessary.) v = m/s (b) Determine the acceleration of the particle as a function of time. (Use any variable or symbol stated above as necessary.) m/s? (c) Calculate the particle's position and velocity at t = 3.00 s. m m/s toarrow_forwardv(m/s) The opposite figure shows the relationship between speed and 3 time. an object is in motion, the distance traveled by the object t(s) during (6s) in meters is equal to: 3 6arrow_forward
- A boxer's fist and glove have a mass of m = 1.04 kg. The boxer's fist can obtain a speed of v = 9.25 m/s in a time of t = 0.21 s. Write a symbolic expression for the magnitude of the average acceleration, aave, of the boxer's fist, in terms of the variables provided. Find the magnitude of the average acceleration, aave, in meters per square second. Write an expression for the magnitude of the average net force, Fb, that the boxer must apply to his fist to achieve the given velocity. (Write the expression in terms of m, v and t.) What is the numerical value of Fb, in newtons?arrow_forwardA small block travels up a frictionless incline that is at an angle of 30.0° above the horizontal. The block has speed 5.10 m/s at the bottom of the incline. Assume g = 9.80 m/s2. How far up the incline (measured parallel to the surface of the incline) does the block travel before it starts to slide back down?arrow_forwardAn object moves in the x-y plane with a constant acceleration of 2i +3j meters per second squared. The object starts at the origin with some initial velocity. After four seconds (4 seconds) the velocity of the object is 2i + 8j meters per second. Determine the object’s initial velocity. Leave answer in i-j notation. Determine the position of the object at time, t = 4 seconds. Leave answer in i-j notation. Thank you for your help.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON