
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
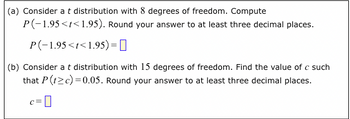
Transcribed Image Text:(a) Consider a t distribution with 8 degrees of freedom. Compute
P(-1.95<t<1.95). Round your answer to at least three decimal places.
P(-1.95<t<1.95) =
(b) Consider a t distribution with 15 degrees of freedom. Find the value of c such
that P (t≥c)=0.05. Round your answer to at least three decimal places.
C= 0
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 9 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- SAT scores are normally distributed with mean = 1000 and standard deviation = 200. 15) Take a sample of 30 students. According to the Central Limit Theorem, what is the distribution N(A,B) of the sample mean SAT scores x of the 30 students? Put the value of A in the top box and the value of B in the bottom box. (Round B to 2 decimal places) a. b. 16) Using the distribution you found in #15, if you have a sample of 30 students, find the z-score if the sample mean SAT score ("x-bar") for the 30 students is 972. 17) Find the Table A entry for the z-score you found in # 16. ( 18) Using the previous answers in this section, determine the probability that the mean SAT score of the 30 students is below 972.arrow_forwardA. P(t10>1.75), where t10 has a t distribution with 10 degrees of freedomarrow_forwardUse the central limit theorem to find the mean and standard error of the mean of the indicated sampling distribution. Then sketch a graph of the sampling distribution. The per capita consumption of red meat by people in a country in a recent year was normally distributed, with a mean of 120 pounds and a standard deviation of 39.9 pounds. Random samples of size 18 are drawn from this population and the mean of each sample is determined. H = o: = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Sketch a graph of the sampling distribution. Choose the correct graph below. OA. O B. Oc. OD. -110.6 9.4 129.4 101.2 120 138.8 -350.6 9.4 369.4 91.8 120 148.2 Click to select your answer(s). P Type here to search 11:24 AM 2/1/2021 Home Endarrow_forward
- (a) Consider a t distribution with 20 degrees of freedom. Compute P(-1.64<t<1.64). Round answer to at least 3 decimal places. P(-1.64<t<1.64)= (b) Consider a t distribution with 27 degrees of freedom. Find the value of c such that P(t is less than or equal to c)=0.05. Round answer to at least 3 decimal places. c=arrow_forwardDetermine the t-value in each of the cases. i Table of t-Distribution Areas Click the icon to view the table of areas under the t-distribution. (a) Find the t-value such that the area in the right tail is 0.05 with 12 degrees of freedom. 1.782 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) (b) Find the t-value such that the area in the right tail is 0.25 with 5 degrees of freedom. 0.727 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) -Area in (c) Find the t-value such that the area left of the t-value is 0.01 with 26 degrees of freedom. [Hint right tail - 2.479 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) (d) Find the critical t-value that corresponds to 95% confidence. Assume 10 degrees of freedom. Table VI (Round to three decimal places as needed.) t-Distribution Area in Right Tail df 0.25 0.20 0.15 0.10 0.05 0.025 0.02 0.01 0.005 0.0025 0.001 0.0005 127.321 14.089 636.619 31.599 12.924 8.610 6.869 1 1.376 1.963 3.078 6.314 12.706 4.303 3.182 2.776 2.571 15.894 31.821 63.657 9.925 5.841 4.604…arrow_forward(a) Consider a t distribution with 9 degrees of freedom. Compute P(-1.48arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardesc A T option :9: F1 Use the ALEKS calculator to solve the following problems. N (a) Consider a t distribution with 9 degrees of freedom. Compute P(-1.15arrow_forward(a) Consider a t distribution with 5 degrees of freedom. Compute P(-1.88 < t < 1.88). Round your answer to at least three decimal places. P(-1.88 < t < 1.88) = || (b) Consider a t distribution with 5 degrees of freedom. Find the value of c such that P (t≥ c) = 0.10. Round your answer to at least three decimal places. C = 0arrow_forwardHow do I solve for b?arrow_forwardUse the ALEKS calculator to solve the following problems. |(a) Consider a t distribution with 17 degrees of freedom. Compute P (-1.46arrow_forward(a) Consider a t distribution with 14 degrees of freedom. Compute P(-1.45arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman