
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
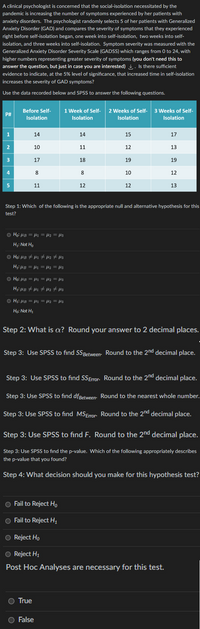
Transcribed Image Text:A clinical psychologist is concerned that the social-isolation necessitated by the
pandemic is increasing the number of symptoms experienced by her patients with
anxiety disorders. The psychologist randomly selects 5 of her patients with Generalized
Anxiety Disorder (GAD) and compares the severity of symptoms that they experienced
right before self-isolation began, one week into self-isolation, two weeks into self-
isolation, and three weeks into self-isolation. Symptom severity was measured with the
Generalized Anxiety Disorder Severity Scale (GADSS) which ranges from 0 to 24, with
higher numbers representing greater severity of symptoms (you don't need this to
answer the question, but just in case you are interested). Is there sufficient
evidence to indicate, at the 5% level of significance, that increased time in self-isolation
increases the severity of GAD symptoms?
Use the data recorded below and SPSS to answer the following questions.
1 Week of Self- 2 Weeks of Self- 3 Weeks of Self-
P#
Before Self-
Isolation
Isolation
Isolation
Isolation
1
14
14
15
17
10
11
12
13
17
18
19
19
8
8
10
12
5
11
12
12
13
Step 1: Which of the following is the appropriate null and alternative hypothesis for this
test?
○ Ho: μB = μ1 = fl2 = fl3
H₁: Not Ho
○ Ho: µB ‡µ₁ ‡µ₂ ‡ µ3
H₁: µB = µ₁ = fl2 = fl3
○ Ho: μB = μl1 = fl2 = fl3
H₂: µB ‡µ₂ ‡µlz #flz
○ H₁: μB = μl1 = flz = flz
Ho: Not H₁
Step 2: What is cx? Round your answer to 2 decimal places.
Step 3: Use SPSS to find SSBetween. Round to the 2nd decimal place.
Step 3: Use SPSS to find SS Error. Round to the 2nd decimal place.
Step 3: Use SPSS to find df Between
Round to the nearest whole number.
Round to the 2nd decimal place.
Step 3: Use SPSS to find MS Error
Step 3: Use SPSS to find F. Round to the 2nd decimal place.
Step 3: Use SPSS to find the p-value. Which of the following appropriately describes
the p-value that you found?
Step 4: What decision should you make for this hypothesis test?
O Fail to Reject Ho
O Fail to Reject H₂
O Reject Ho
O Reject H₁
Post Hoc Analyses are necessary for this test.
True
False
AWNH
2
3
4
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A research study examining differences in the effectiveness of three treatment conditions in combatting anxiety has three levels. True Falsearrow_forwardStewart Fleishman specializes in the psychiatric aspects of symptom management in cancer patients. Pain, depression, and fatigue can appear as single symptoms, in conjunction with one other symptom, or all together in patients with cancer. You are interested in testing a new kind of cognitive-behavioral therapy for the treatment of the simultaneous clustering of pain and fatigue in cancer patients. The following scores represent the decrease in symptom intensity (on a 10-point scale) following the new cognitive-behavioral therapy. Scores Patient Pain (X) Fatigue (Y) A 3 1.25 B 4 0 C 5 6.5 D 6 2.5 E 7 10 Create a scatter plot of these scores on the grid. For each of the five (X, Y) pairs, drag the orange points (square symbol) in the upper-right corner of the diagram to the appropriate location on the grid. Scores02468101086420FATIGUEPAIN Calculate the means and complete the following table by calculating the deviations from the…arrow_forwardAn epidemiologist found five cases of “big toe cancer” in the Yukon Territory. Because there were only a few cases, the epidemiologist decided to conduct a matched case-control study to determine whether shoe size larger than 9 is a risk factor for big toe cancer. Cases were individually matched to one control for daily activity, history of athlete’s foot, and history of ingrown toenails. The following data were gathered: Shoe size > 9 Pair Case Control 1 Yes No 2 No No 3 No Yes 4 Yes Yes 5 No Yes Compute the proper measure of association. Interpret your results. If you were to investigate a rare cancer in Lynchburg, where might you look for data? What would be necessary legally and ethically to be able to utilize this data set(s)? Submit your thread by 11:59 p.m. (ET) on Thursday of Module/Week 3, and submit your replies by 11:59 p.m. (ET) on Sunday of the same module/week. 1arrow_forward
- An important issue is whether there are racial differences in hypertension among children. We define hypertension as being above the 95th percentile for either systolic blood pressure (SBP) or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) among children of the same age, height, and sex. Since some of the children were observed at multiple visits, a GEE model was run of hypertension on ethnic group. There were three ethnic groups considered: Caucasian, African American, and Hispanic. The results among boys are given in Table 13.54. TABLE 13.54 Relationship between hypertension and ethnic group among 27,009 boys in the Pediatric Task Force Data Variable Regression Coefficient SE Intercept -2.07 0.026 African American 0.049 0.041 Hispanic 0.328 0.059 What is the estimated OR for hypertension comparing Hispanic boys vs. Caucasian boys? (Call this OR1.) What is a 95% CI for this estimate?arrow_forwardA scientist is studying the effect of a new type of exercise program on cardiovascular health. The scientist randomly assigns individuals to either the exercise program or a control group. The scientist wants to determine if the exercise program has a statistically significant effect on cardiovascular health. The scientist monitors cardiovascular health by measuring the blood pressure of each individual.arrow_forwardA researcher is testing the effect of one independent variable using three treatment conditions. She compares three group means where there are different people in each group. It is best for her to use which type of statistical analysis?arrow_forward
- 1) Soda consumption is very common in the U.S. For the purposes of this question, assume that 30% of the population consumes the equivalent of 3 or more 12 oz. sodas per week (this is the prevalence of the exposure). A large multi-center cohort study was conducted to evaluate the association between soda consumption and risk of diabetes. At baseline, participants were asked about their typical soda consumption, and individuals who reported consuming 3 or more sodas per week were considered exposed. Participants were followed for 10 years, and the following results were obtained: Incident Cases of Diabetes 356 236 Person-Years Contributed 3+ sodas a week 375234 <3 sodas a week 399763 a) Name the appropriate measure of association corresponding to the excess rate of diabetes attributable to soda consumption among subjects who consume 3+ sodas per week. Calculate this measure (shown as a rate, using the correct units), and provide a brief interpretation of your answer b) Calculate the…arrow_forwardResearchers have observed that high school students who watched educational television programs as young children tend to have higher grades than their peers who did not watch educational television. Is this an observational study or a controlled experiment? Explain why.arrow_forwardThe leader of two postpartum women’s support groups is interested in the depression levels of the women in her groups. She administers the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) screening test to the members of her groups. The CES-D is a 20-question self-test that measures depressive feelings and behaviors during the previous week. The mean depression level from the screening test for the 10 women in the first group is μ₁ = 16; the mean depression level for the 14 women in the second group is μ₂ = 10. Without calculating the weighted mean for the combined group, you know that the weighted mean is:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman