
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
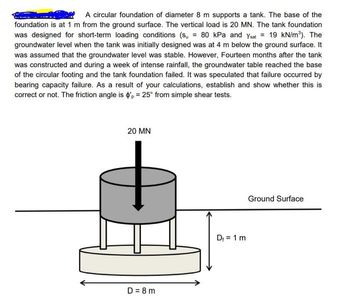
Transcribed Image Text:A circular foundation of diameter 8 m supports a tank. The base of the
foundation is at 1 m from the ground surface. The vertical load is 20 MN. The tank foundation
was designed for short-term loading conditions (su = 80 kPa and Ysat = 19 kN/m³). The
groundwater level when the tank was initially designed was at 4 m below the ground surface. It
was assumed that the groundwater level was stable. However, Fourteen months after the tank
was constructed and during a week of intense rainfall, the groundwater table reached the base
of the circular footing and the tank foundation failed. It was speculated that failure occurred by
bearing capacity failure. As a result of your calculations, establish and show whether this is
correct or not. The friction angle is $'p = 25° from simple shear tests.
20 MN
D=8m
D₁ = 1 m
Ground Surface
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A building is founded on a rectangular mat of dimensions 20 m x 10 m as shown in the plan view in figure below. A surcharge of 300 kPa is applied within the area ABCD whereas a surcharge of 100 kPa is applied within the area CDEF. Calculate the increase in vertical total stress in kPa at the depth of 5 m below Point Farrow_forwardKINDLY GET THE RIGHT ANSWER Given that B =1 m, L = 3 m, and Q = 110 kN, the soil characteristics given in the figure are Cs = 1/5 Cc, Ꝺ’c= 40 kN/m2. Field monitoring indicated that the foundation settlement was 19 mm during the first 12 months. Estimate the coefficient of consolidation for the pressure range. Estimate the settlement in 24 months.arrow_forwardIn a soil with a well developed Bt horizon (argillic horizon), the Bt horizon compared to the A1 horizon (of same soil profile) will typically have: lower bulk density more macropore space O more total pore space less macropore space and less total pore space O more total pore space and more micropore spacearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning