
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
A child, who is L = 41 m from the bank of a river, is being carried helplessly downstream by the river's swift current of 1.0 m/s. As the child passes a lifeguard on the river's bank, the lifeguard starts swimming in a straight line until she reaches the child at a point downstream.
a.) If the lifeguard can swim at a speed of 2.0 m/s relative to the water, how long does it take her to reach the child?
Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units.
b.)How far downstream does the lifeguard intercept the child?
Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units.
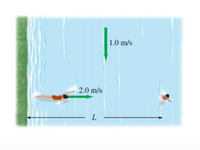
Transcribed Image Text:1.0 m/s
2.0 m/s
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1 :Introduction
The velocity of an object is defined as the ratio of its distance to the time taken ,that is , .
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- iii. A boat's speed in still water is vgw = 2.2 m/s. If the boat is to travel directly across the river whose current is vws = 1.5 m/s, a) Find the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the boat relative to the shore b) If the river is 132m wide, how long will it take to cross the river? River current N w- Earrow_forwardYou are traveling to the North-East at 50 m/s. Simultaneously you are being pushed towards the East at a speed of 10 m/s. a. If you proceed in this manner for 10 minutes, what is the displacement vector from the t=0 location? b. How far do you travel in the East direction during these 10 mins.?arrow_forwardSally is on a kayak that comes to a stop a small distance from the dock. Since it is such a small distance, Sally decides to jump to the dock. She makes the jump, but the kayak moves away from her as she jumps. Since Sally is interested to see what happens on other boats, she makes the same jump from a yacht that is much larger than the kayak. Which boat will move away from Sally more quickly? 1)It is impossible to predict which boat moves away from Sally more quickly. 2)The yacht will move away from Sally more quickly because it is larger in mass. 3)Both boats will move away at the same speed because Sally has not changed mass and momentum must be conserved. 4)The kayak will move away from Sally more quickly because the yacht is larger in mass.arrow_forward
- An archer fish spies a meal of a grasshopper sitting on a long stalk of grass at the edge of the pond in which he is swimming. The fish is to successfully spit at and strike the grasshopper, which is 0.200 m away horizontally and 0.745 m above his mouth. a. What is the minimum speed at which the archer fish must spit? answer in m/s b. What angle (in degrees) above the horizontal must he spit? answer in degreesarrow_forward*61. O A person looking out the window of a station- ary train notices that rain- drops are falling vertically down at a speed of 5.0 m/s relative to the ground. When the train moves at a constant 25 velocity, the raindrops make an angle of 25° when they move past the window, as the drawing shows. How fast is the train moving?arrow_forward▼ Part A A walker and a runner are on a straight horizontal section of a track. In the reference frame of the Earth, the walker has an initial position XEwi = +5.0 m and the runner has an initial position XEri+15.0 m. Three seconds later, the walker has a position XEwf = +11 m and the runner has a position XErf +3.0 m. What is the runner's velocity in the reference frame of the walker, vwr? ► View Available Hint(s) O Vwr= -2.0 m/s O Vwr=-6.0 m/s O VW-18.0 m/s O Vwr= -4.0 m/s Review Submitarrow_forward
- Sheena can row a boat at 3.20 mi/h in still water. She needs to cross a river that is 1.20 mi wide with a current flowing at 1.80 mi/h. Not having her calculator ready, she guesses that to go straight across, she should head upstream at an angle of 25.0° from the direction straight across the river. a.)What is her speed with respect to the starting point on the bank? b.)How long does it take her to cross the river?arrow_forwardGeese migrate along north and south directions for well over a thousand kilometers in some cases traveling speeds up to about 100 km/h. If one such bird is flying at 100km/h relative to the air but there is a 34.0 km/h wind blowing from the west to east. A.) at what angle relative to the north-south direction should this bird head so that it will be traveling directly southward relative to the ground? Express answer in degrees b.) how long will it take the bird to cover a ground distance of 500 km from north to south? ( Note: Even on cloudy nights many birds navigate using the earth's magnetic field to fix the north-south direction)arrow_forwardA river flows due south with a speed of 2.8 m/s. A man steers a motorboat across the river; his velocity relative to the water is 4.9 m/s due east. The river is 600 mm wide. a-What is the magnitude of his velocity relative to the earth? b-What is the direction of his velocity relative to the earth? c-How much time is required to cross the river? d-How far south of his starting point will he reach the opposite bank?arrow_forward
- 5a. An airplane maintains a speed of 693 km/h relative to the air it is flying through as it makes a trip to a city 724 km away to the north. (Assume north is the positive y-direction and east is the positive x-direction.) What time interval is required for the trip if the plane flies through a headwind blowing at 32.4 km/h toward the south? harrow_forwardA swimmer is capable of swimming 0.50 m/sm/s in still water. Part A At what upstream angle must the swimmer aim, if she is to arrive at a point directly across a 45 mm wide river whose current is 0.30 m/sm/s? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. Part B How long will it take her? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forwardng A woman is on a train leaving the station at 3.0 m/s, while a friend waving goodbye runs alongside the car she's in. Call the train's direction of motion the + direction. ▼ Part B Once the train has reached a speed of 10 m/s, how fast must the woman walk, and in which direction, to keep up with her friend? Express your answer with the appropriate units. VIw= Submit μÀ Value 3 @ m S O Previous Answers Request Answer Review ?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON