
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
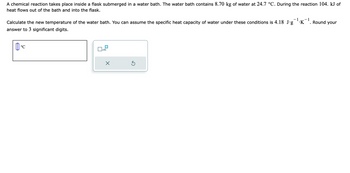
Transcribed Image Text:A chemical reaction takes place inside a flask submerged in a water bath. The water bath contains 8.70 kg of water at 24.7 °C. During the reaction 104. kJ of
heat flows out of the bath and into the flask.
1 -1
Calculate the new temperature of the water bath. You can assume the specific heat capacity of water under these conditions is 4.18 Jg ¹.K
answer to 3 significant digits.
11°C
x10
X
S
Round your
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A piece of titanium metal with a mass of 20.8 g is heated boiling water to 99.5°C and then dropped into a coffee cup calorimeter containing 75.0 g of water at 21.7°C. When thermal equilibrium is reached, the final temperature is 24.3°C. Calculate the specific heat capacity of titanium,arrow_forwardA chemical reaction takes place inside a flask submerged in a water bath. The water bath contains 3.00 kg of water at 34.6 °C. During the reaction 67.2 kJ of heat flows out of the bath and into the flask. Calculate the new temperature of the water bath. You can assume the specific heat capacity of water under these conditions is 4.18 J.g answer to 3 significant digits. °C X ¹.K 1 Round yourarrow_forwardO Thermochemistry = Using specific heat capacity to find temperature change 1/3 Bishop A chemical reaction takes place inside a flask submerged in a water bath. The water bath contains 8.70 kg of water at 33.2 °C. During the reaction 106. kJ of heat flows out of the flask and into the bath. Calculate the new temperature of the water bath. You can assume the specific heat capacity of water under these conditions is 4.18 J-g K. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. -1 C CParrow_forward
- A chemist carefully measures the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of a 1.36 kg sample of a pure substance from 25.3 °C to 30.9 °C. The experiment shows that 36. kJ of heat are needed. What can the chemist report for the specific heat capacity of the substance? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. J.g 1 – 1 .K x10 × Śarrow_forwardA chemical reaction takes place inside a flask submerged in a water bath. The water bath contains 8.70 kg of water at 20.5 °C. During the reaction 52.6 kJ of heat flows out of the flask and into the bath. Calculate the new temperature of the water bath. You can assume the specific heat capacity of water under these conditions is 4.18 J-g¹K¹. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 0°C ☐ x10 Xarrow_forwardA chemical reaction takes place inside a flask submerged in a water bath. The water bath contains 9.50 kg of water at 39.0 °C. During the reaction 146. kJ of heat flows out of the flask and into the bath. Calculate the new temperature of the water bath. You can assume the specific heat capacity of water under these conditions is 4.18 J∙g¯¹.K¯¹. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. °C 0 x10 Xarrow_forward
- Calculate the energy required to heat 593.0 g of cyclohexane from 11.1 °C to 35.6 °C. Assume the specific heat capacity of cyclohexane under these conditions -1 -1 is 1.85 J.g .K Round your answer to 3 significant digits. 0 0.0 X H 00 Sarrow_forward- 1 A 39.0 g sample of glass, which has a specific heat capacity of 0.670 J-g.°C¯', is dropped into an insulated container containing 200.0 g of water at 65.0 °C and a constant pressure of 1 atm. The initial temperature of the glass is 1.1 °C. Assuming no heat is absorbed from or by the container, or the surroundings, calculate the equilibrium temperature of the water. Be sure your answer has 3 significant digits. x10 ?arrow_forwardThe specific heat of a certain type of metal is 0.128 J/(g.°C). What is the final temperature if 305 J of heat is added to 63.2 g of this metal, initially at 20.0 °C? °C Tfinal ||arrow_forward
- A chemical reaction takes place inside a flask submerged in a water bath. The water bath contains 6.30 kg of water at 29.8 °C. During the reaction 131. kJ of heat flows out of the flask and into the bath. Calculate the new temperature of the water bath. You can assume the specific heat capacity of water under these conditions is 4.18 J.g answer to 3 significant digits. °C 0 x10 X ¹K¹. Round yourarrow_forwardA chemical reaction takes place inside a flask submerged in a water bath. The water bath contains 3.40 kg of water at 35.0 °C. During the reaction 146. kJ of heat flows out of the flask and into the bath. Calculate the new temperature of the water bath. You can assume the specific heat capacity of water under these conditions is 4.18 J-g answer has the correct number of significant digits. °C X K Be sure yourarrow_forwardAn insulated container is used to hold 42.7 g of water at 20.5 Celsius. A sample of copper weighing 9.60 g is placed in a dry test tube and heated for 30 minutes in a boiling water bath at 100.0 Celsius. The heated test tube is carefully removed from the water bath with laboratory tongs and inclined so that the copper slides into the water in the insulated container. Given that the specific heat of solid copper is 0.385 J/(g.Celsius), calculate the maximum temperature of the water in the insulated container after the copper metal is added.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY